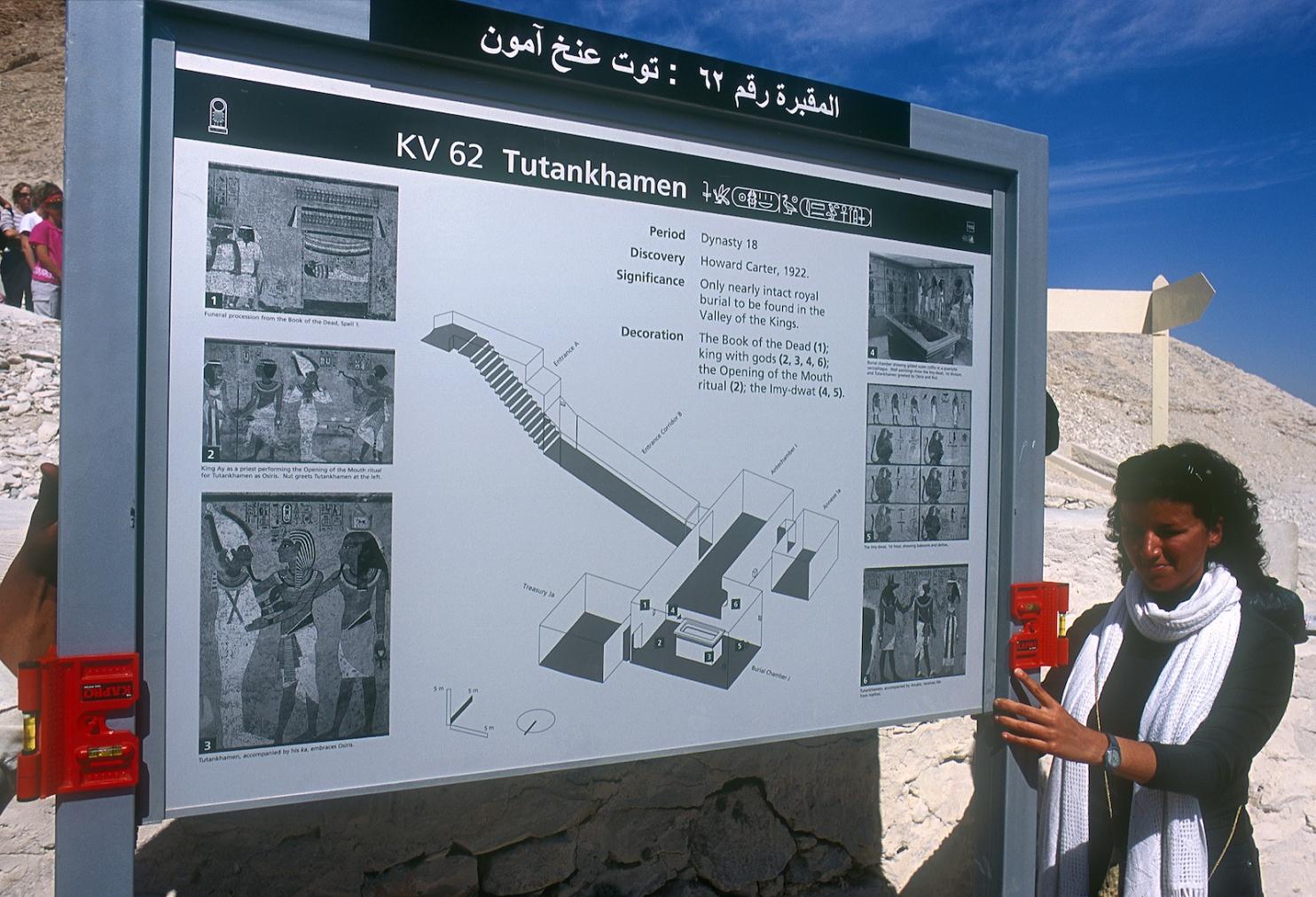
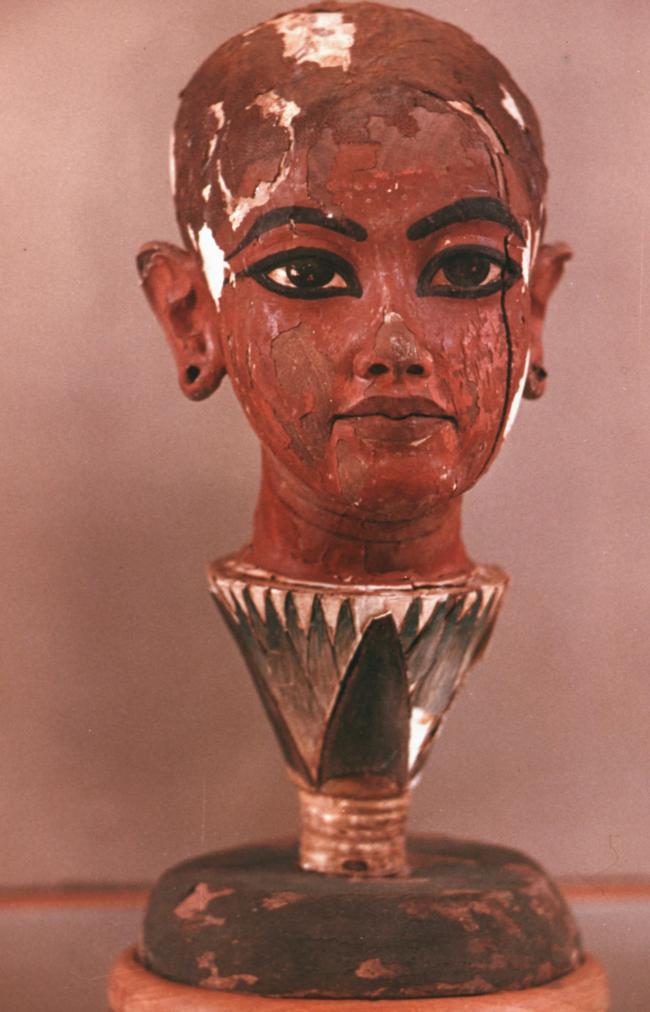
KV 62
Tutankhamen
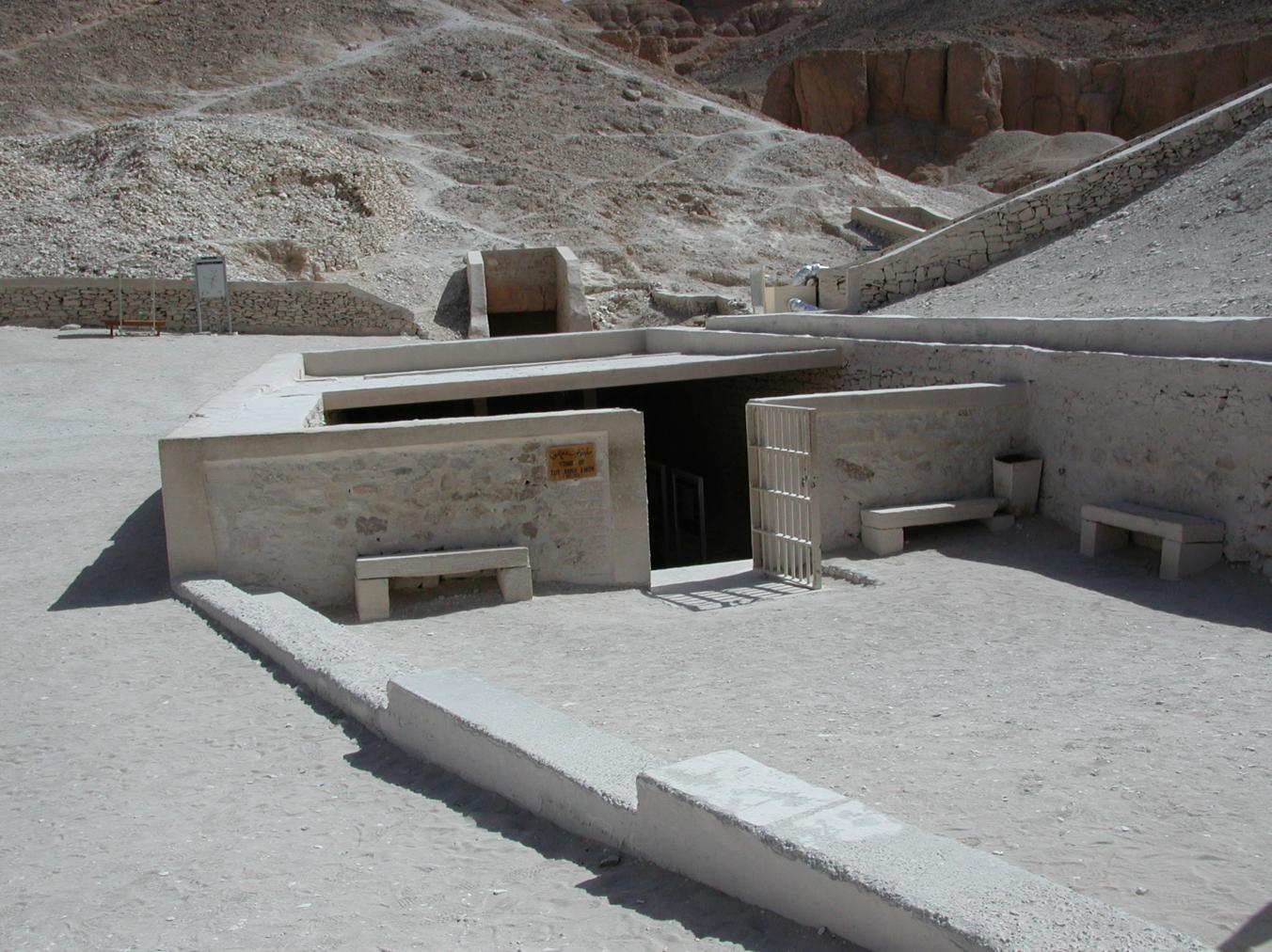
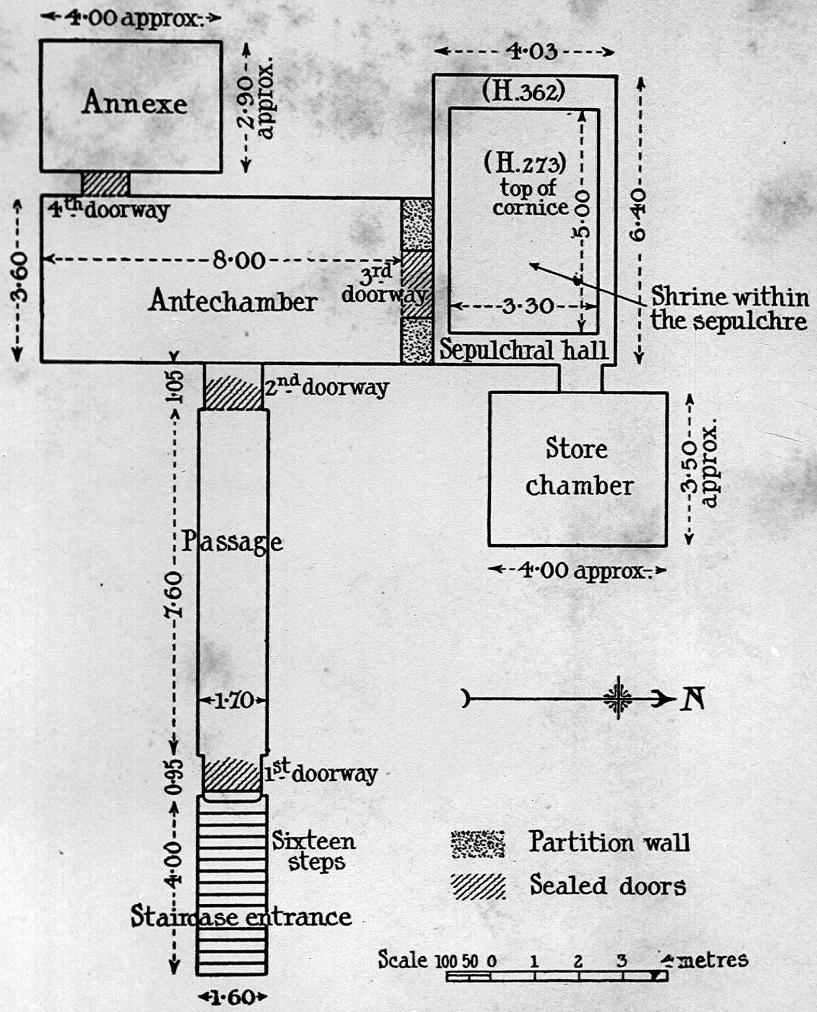
Entryway A
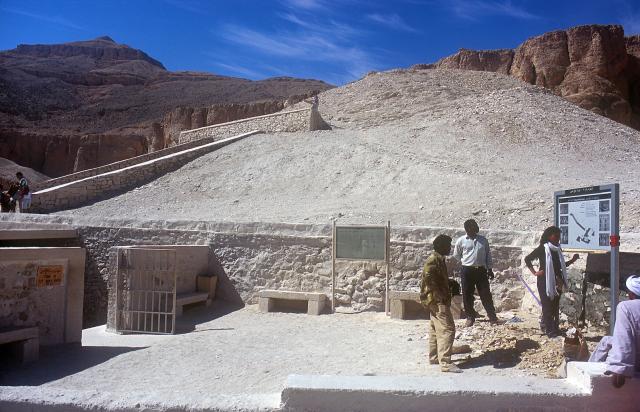
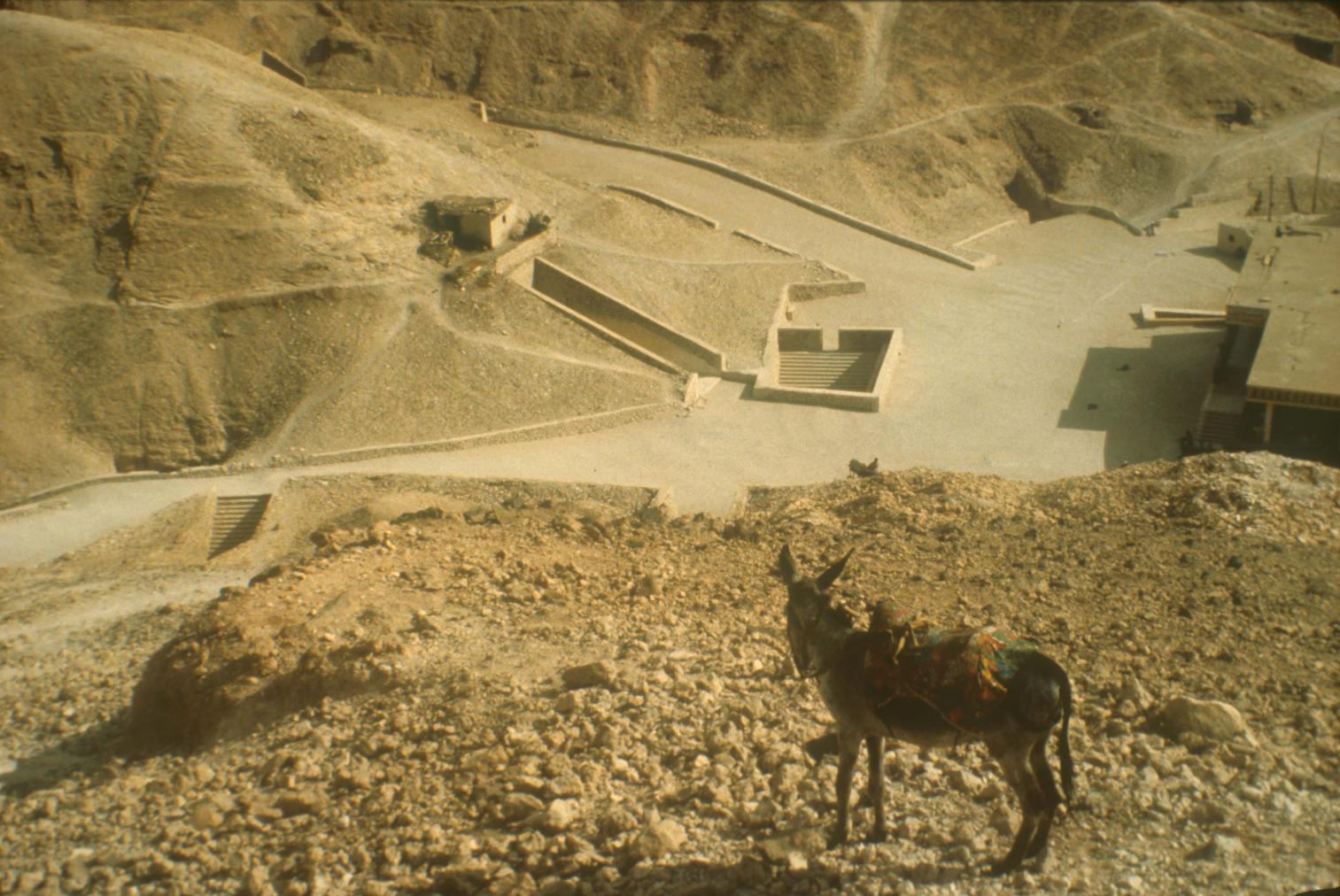
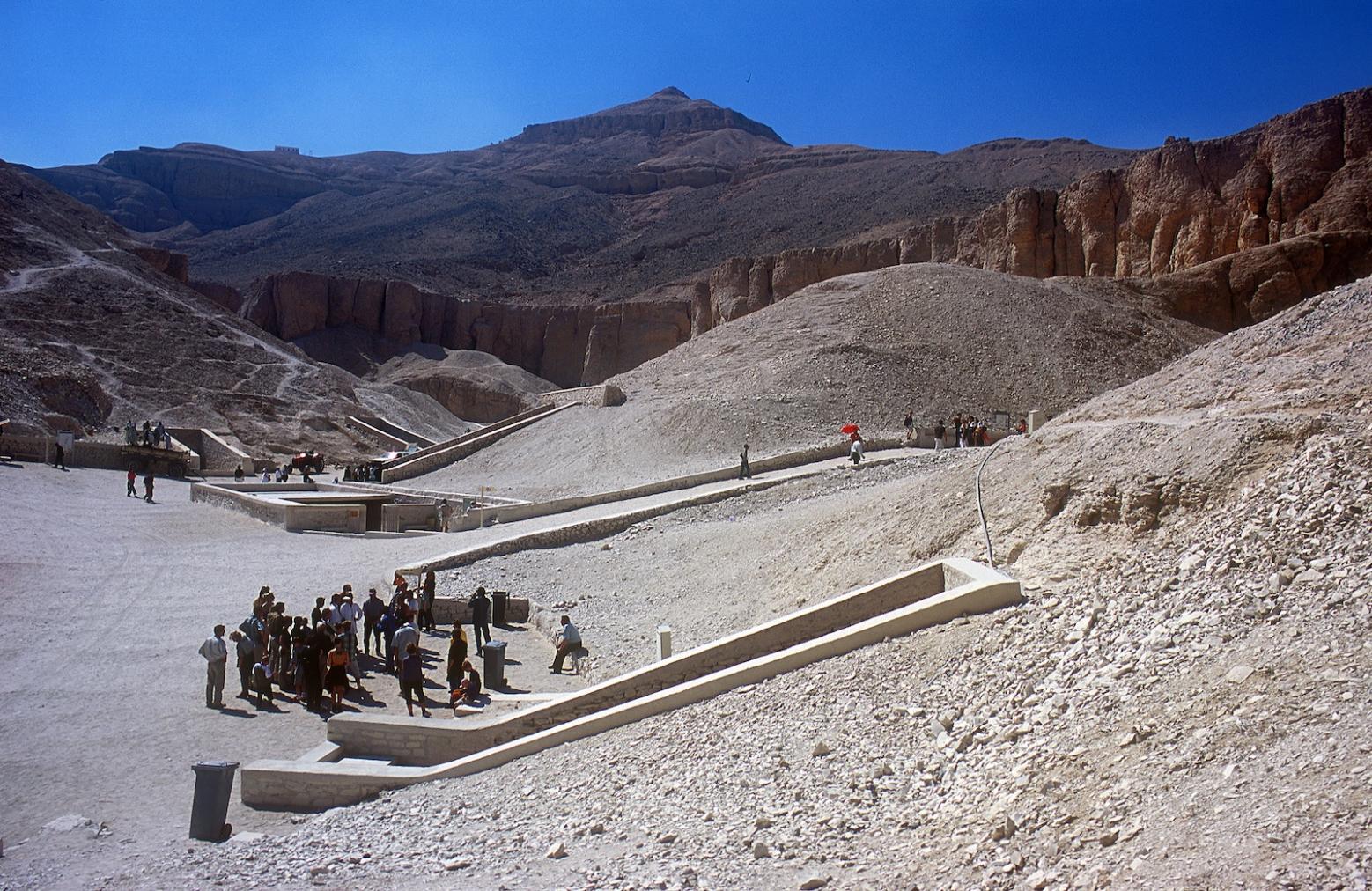
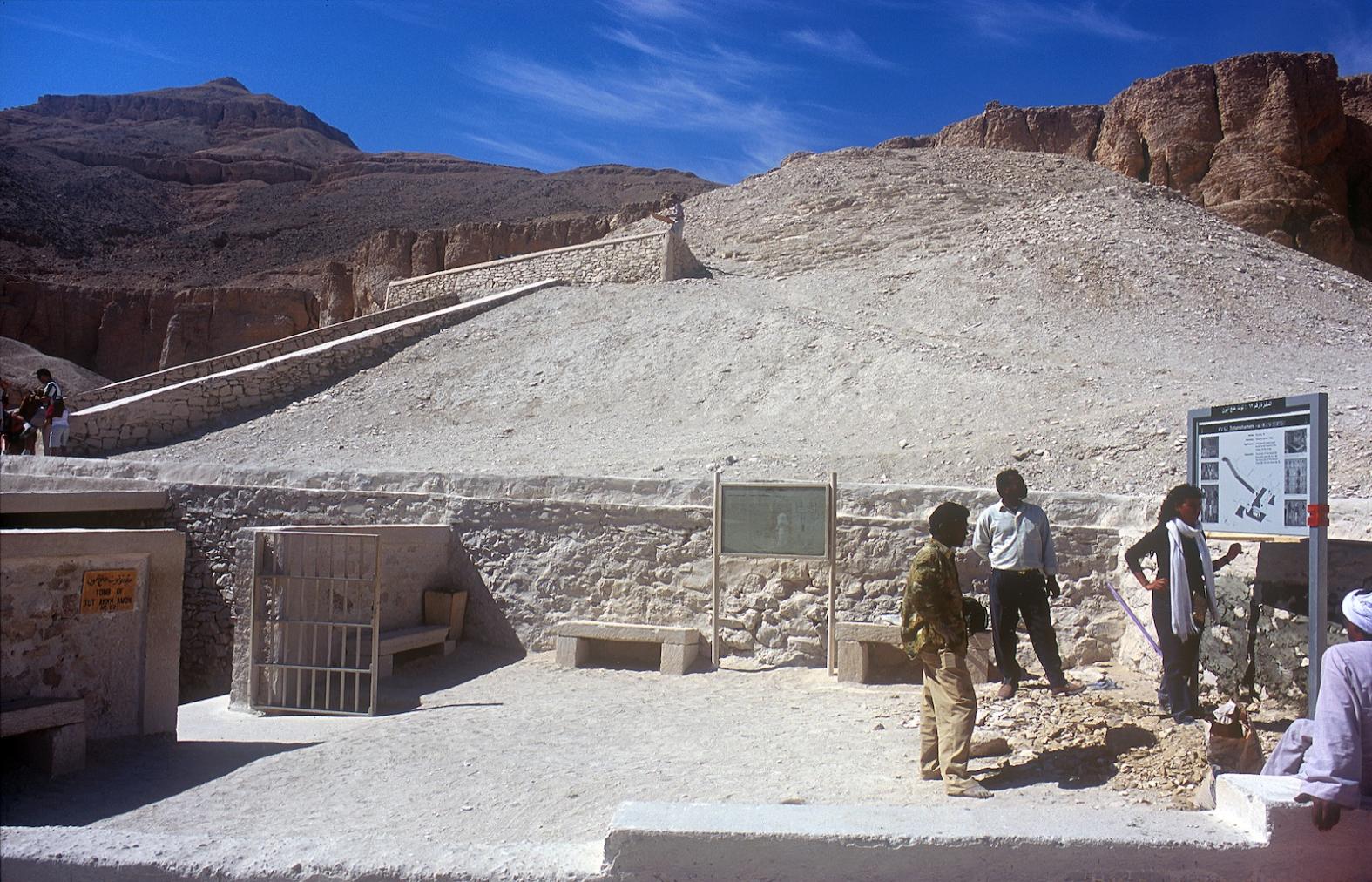
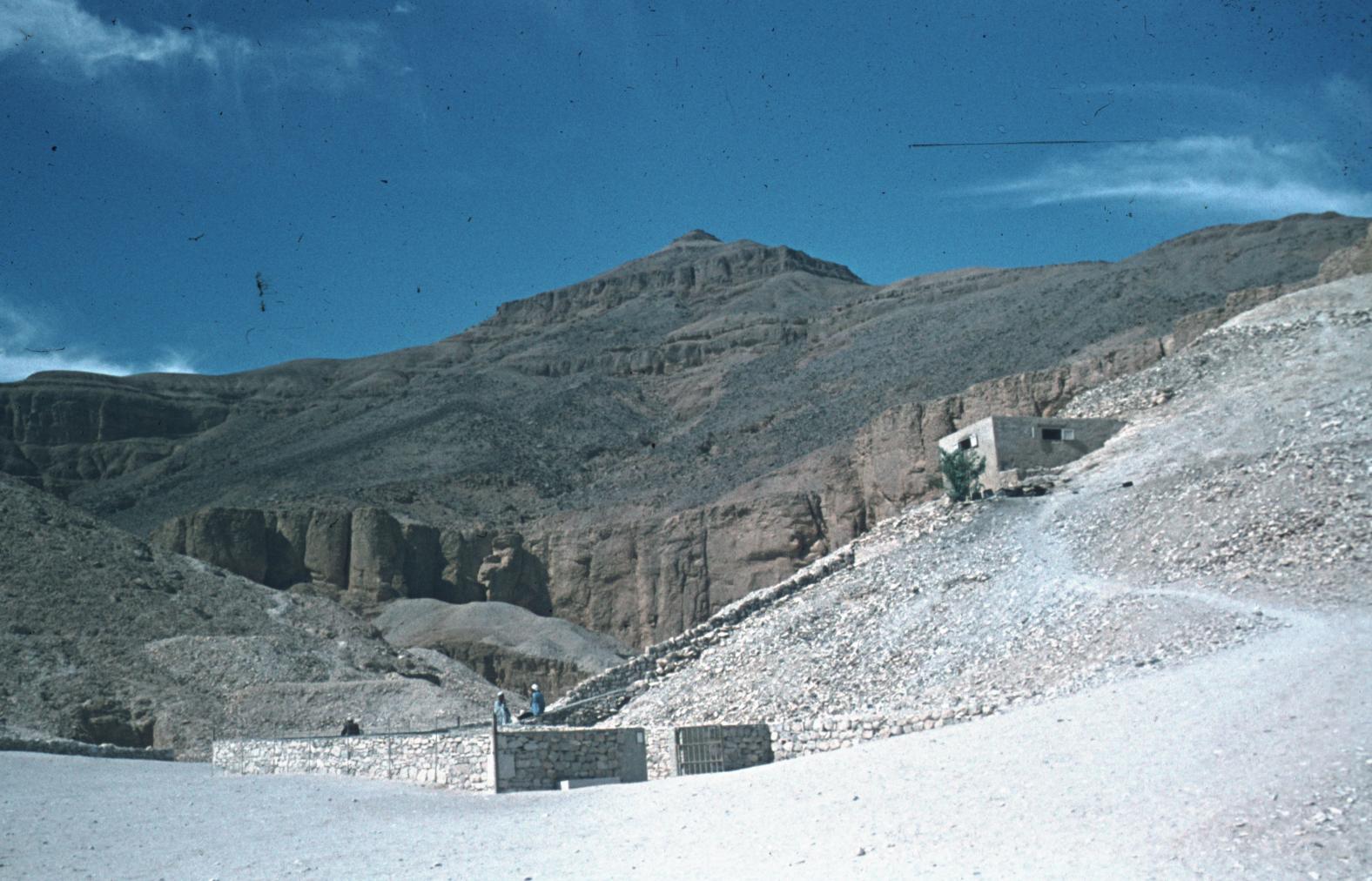
See entire tombSixteen steps descend through the bedrock toward gate B. The westernmost end of the stairway is roofed in by the rock of the valley floor. The last six steps of the entrance were cut back in ancient times, together with the lintel and jambs of gate B, in order to allow passage of larger pieces of funerary furniture. These features were all subsequently reconstructed in stone and plaster. Recently, a shelter was built over the entrance.
Gate B
See entire tombThe lintel and jambs of the doorway were cut away in antiquity to allow for the passage of large pieces of funerary furniture. The lintel was subsequently replaced with a heavy, limewashed beam. Carter removed the original blocking when he discovered the tomb, and again had to widen the gate when he removed the shrine panels.
Porter and Moss designation:
Corridor B
See entire tombThe corridor originally contained material left over from the funeral feast, as well as material associated with the embalming of the king, according to Reeves. After the first robbery, the bulk of this material was removed to KV 54 and the corridor was filled with limestone chips and rubble to impede access to the tomb chambers. This was unsuccessful, as shown by the tunnel made by the second group of robbers through the upper left of the blocking debris. This tunnel was filled with rubble before the third sealing of the tomb.
Porter and Moss designation:
Gate I
See entire tombThe jambs in gate I, like those in gate B, were cut back in antiquity. Carter removed the original blocking of the gate when he discovered the tomb.
Porter and Moss designation:
Chamber I
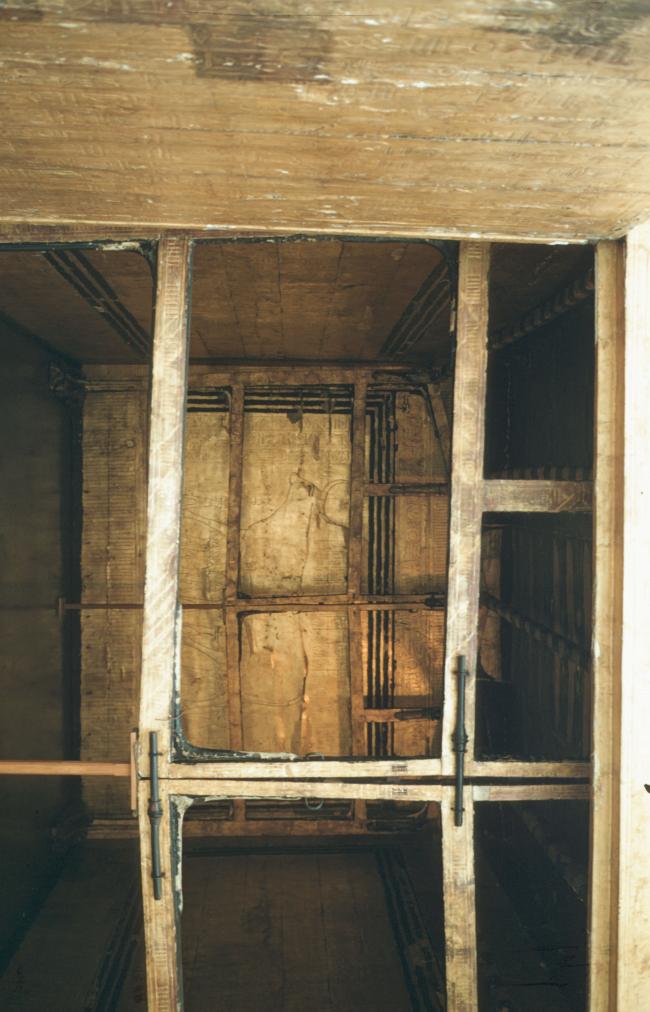
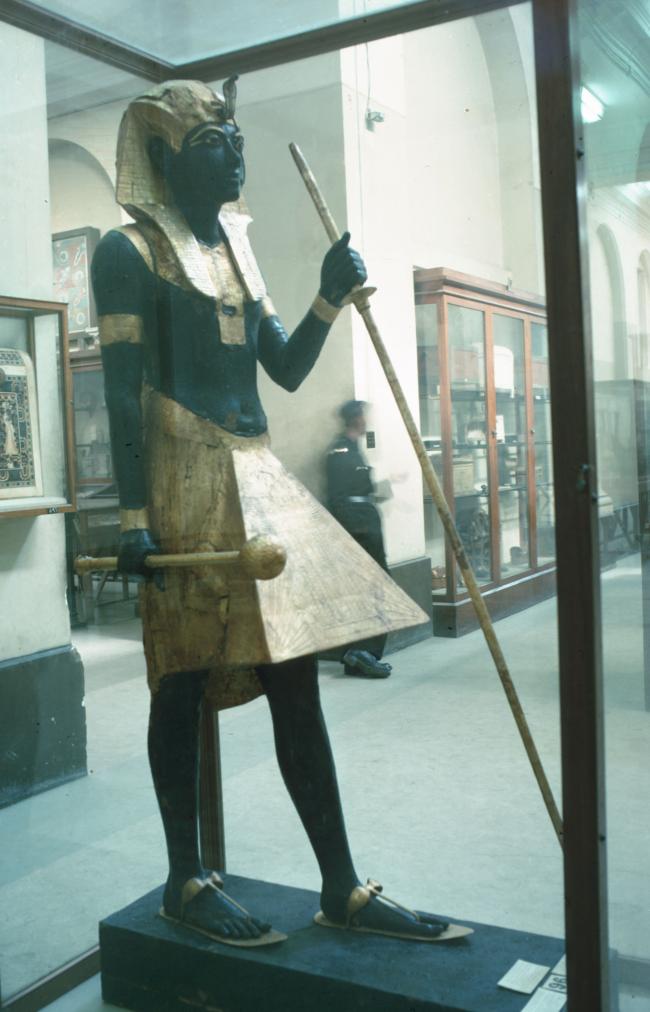
See entire tombThis chamber (called the Antechamber by Carter) is long and rectangular, similar to the pillared section of the burial chambers in other tomb, but without pillars. The walls are rough and undecorated, as are all other chamber walls except burial chamber J. This chamber held over six hundred objects. Near the left (south) end of the rear (west) wall a low doorway leads to side chamber Ia. At the right (north) end of the rear (west) wall are remains of the abandoned cutting of a gate. Chisel marks on the ceiling of burial chamber J indicate that chamber I originally extended about two meters farther to the right (north). Near the floor in the center of the west wall of chamber I is a small recess.
Porter and Moss designation:


Gate Ia
See entire tombAlthough this is a low gate, black paint lines above the opening indicate that it was intended to be higher. Carter removed the original blocking when clearing the tomb.
Porter and Moss designation:
Side chamber Ia
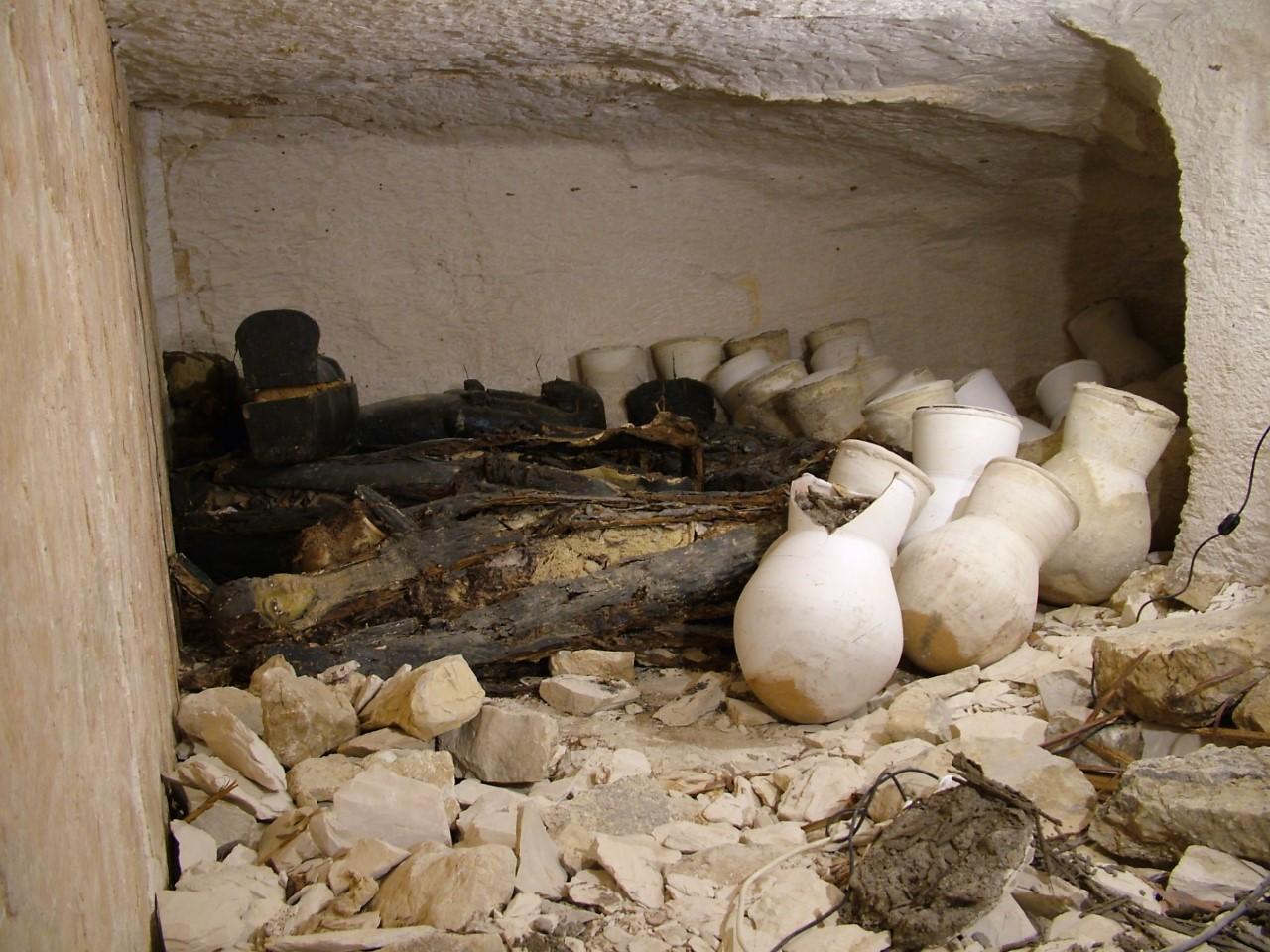
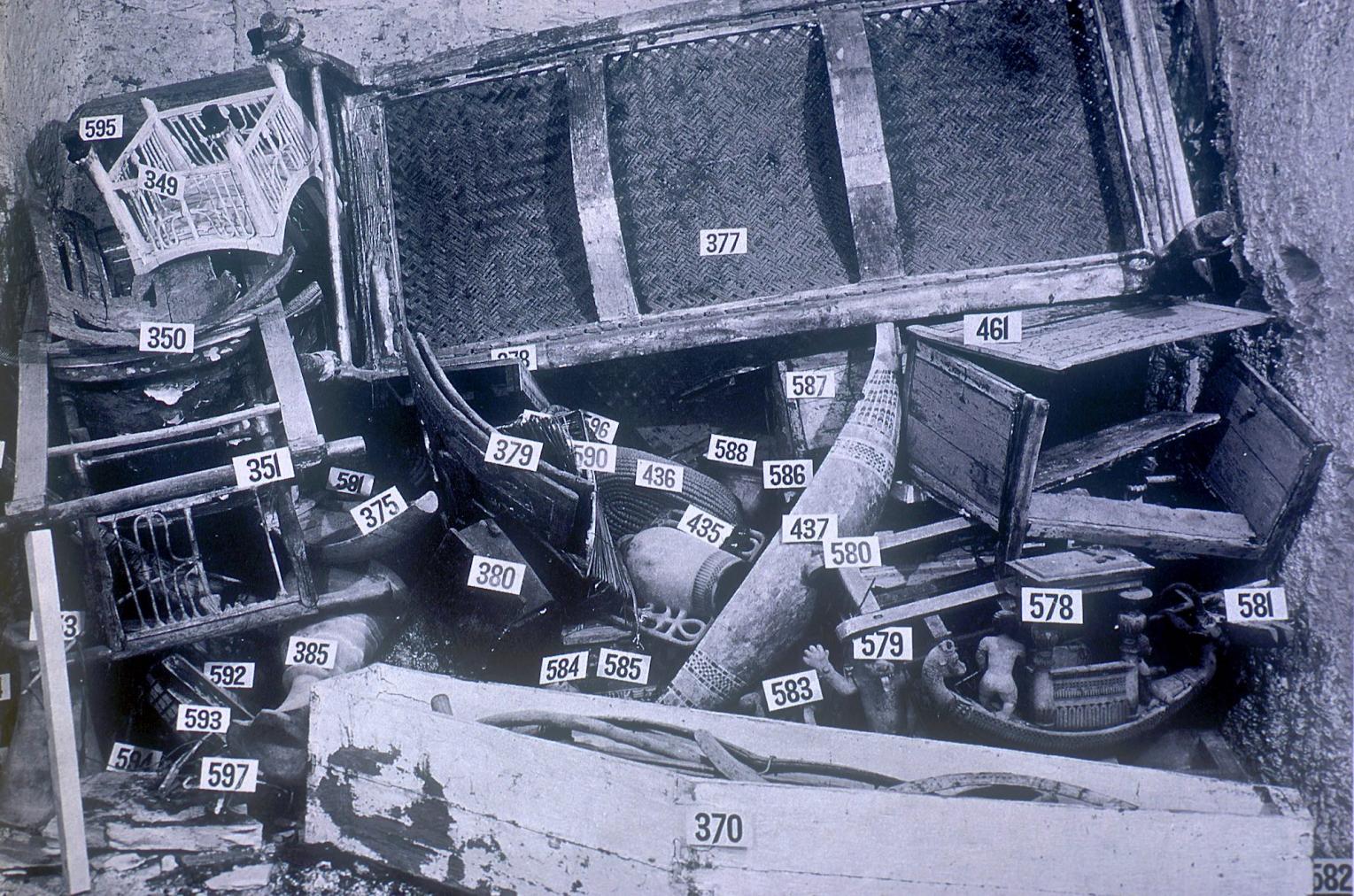
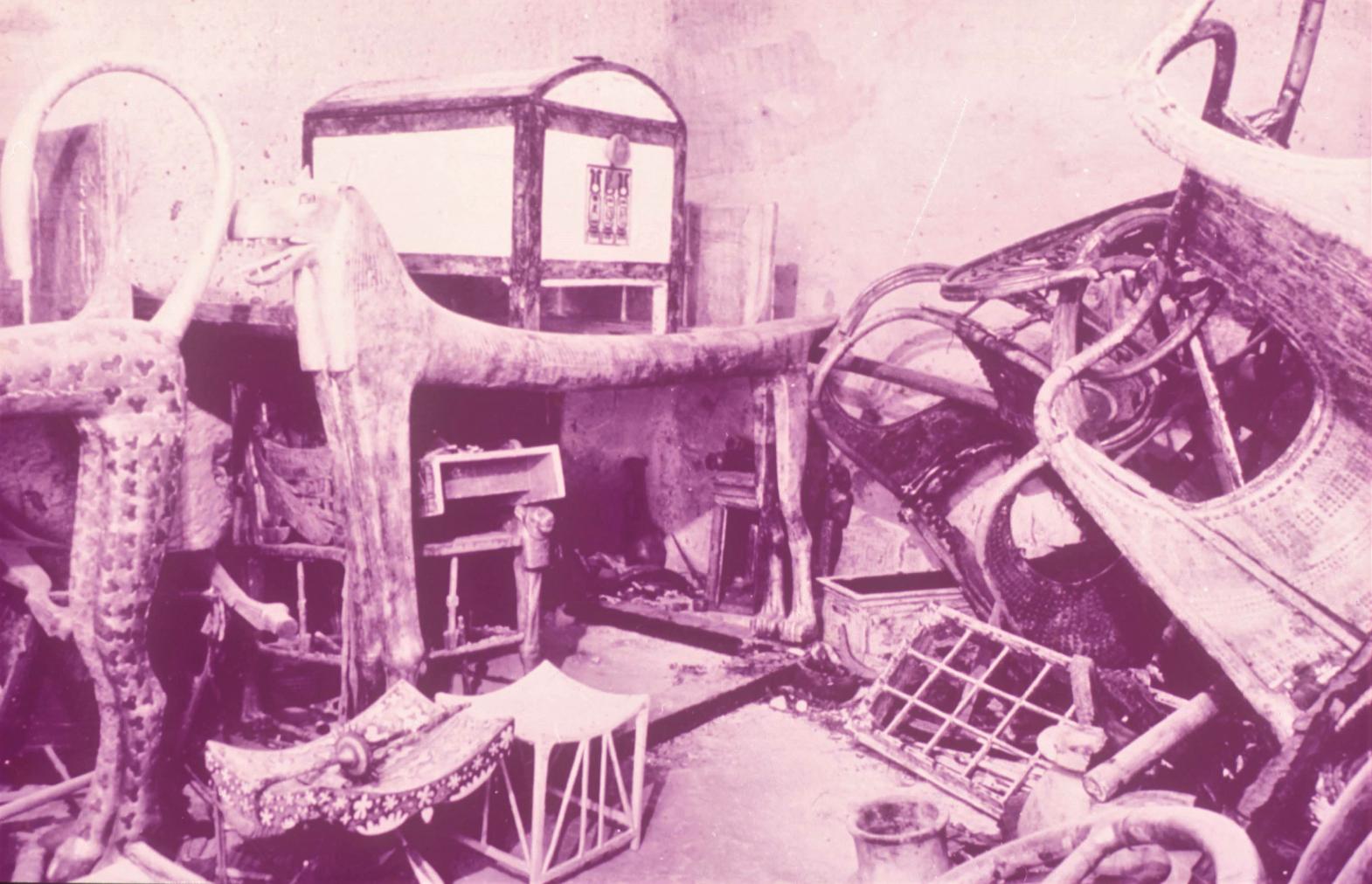
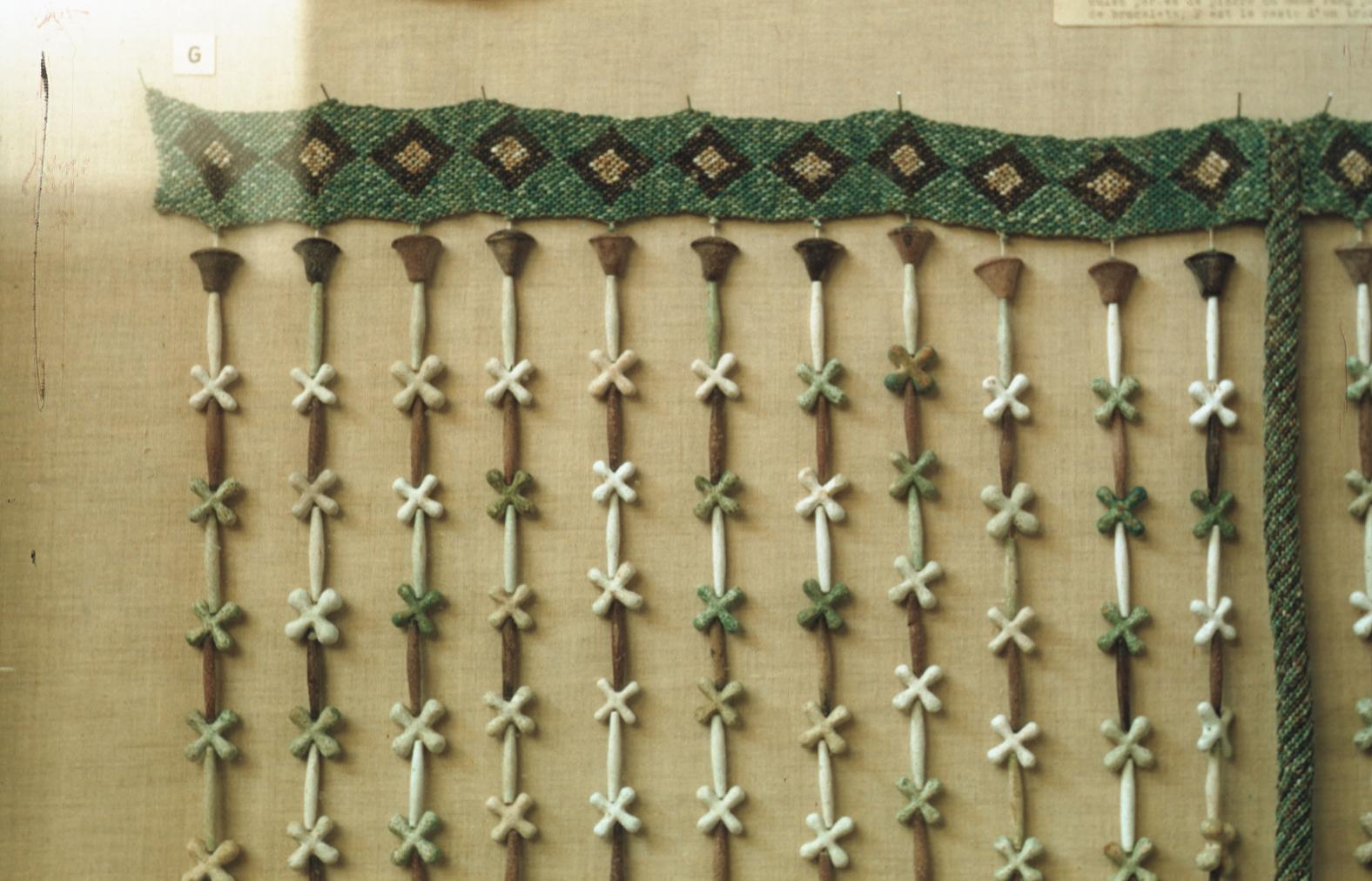
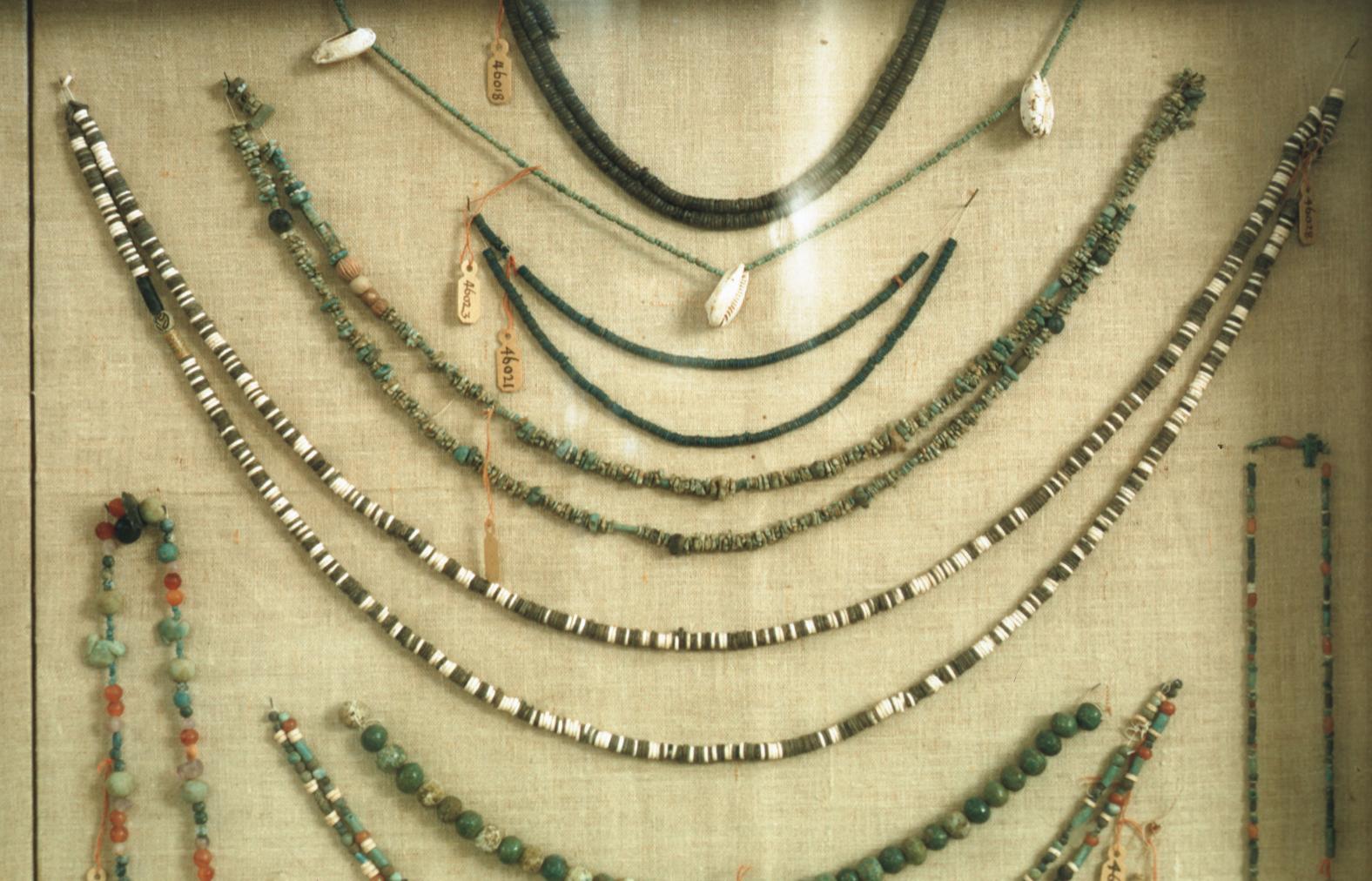
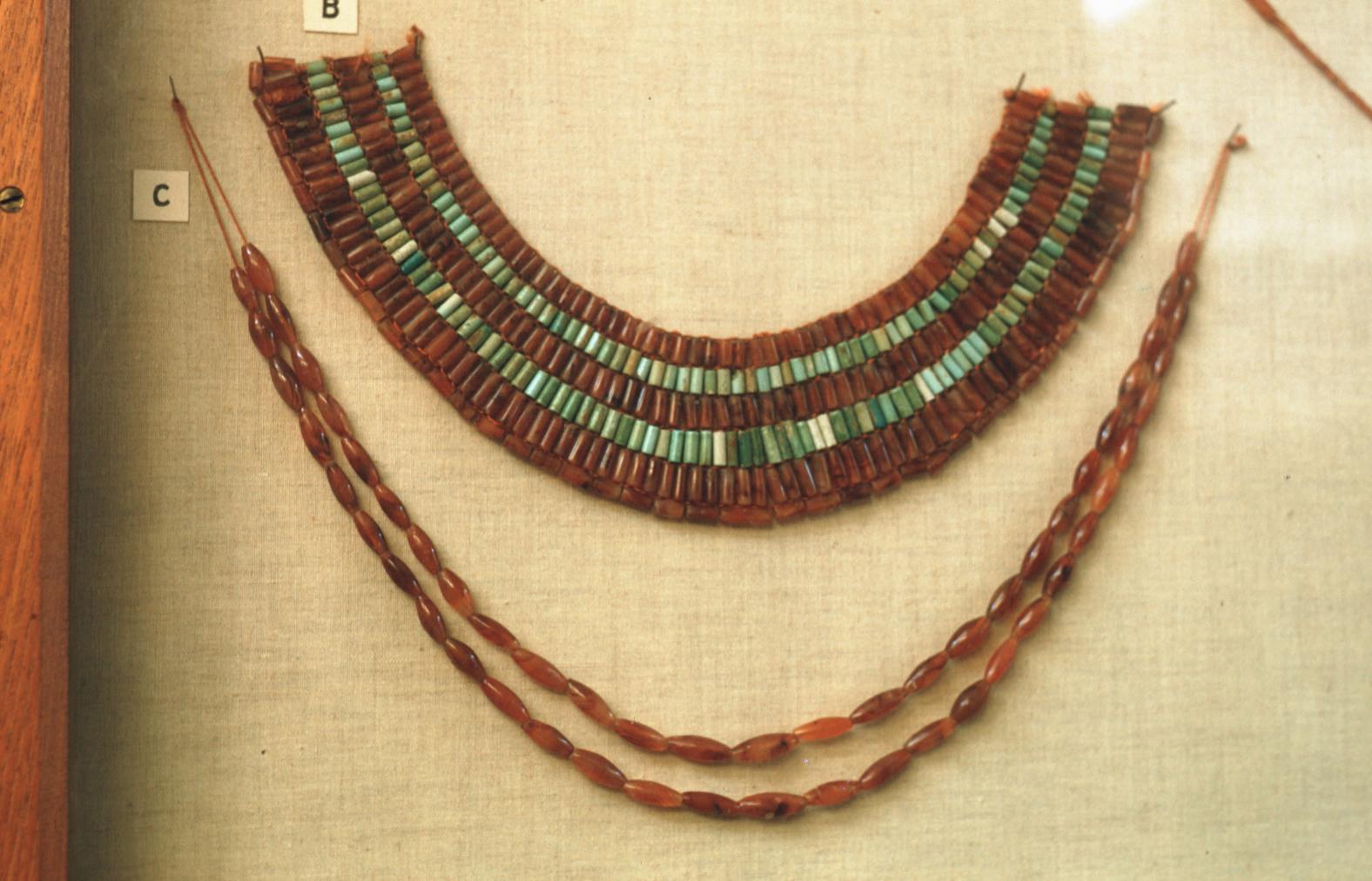
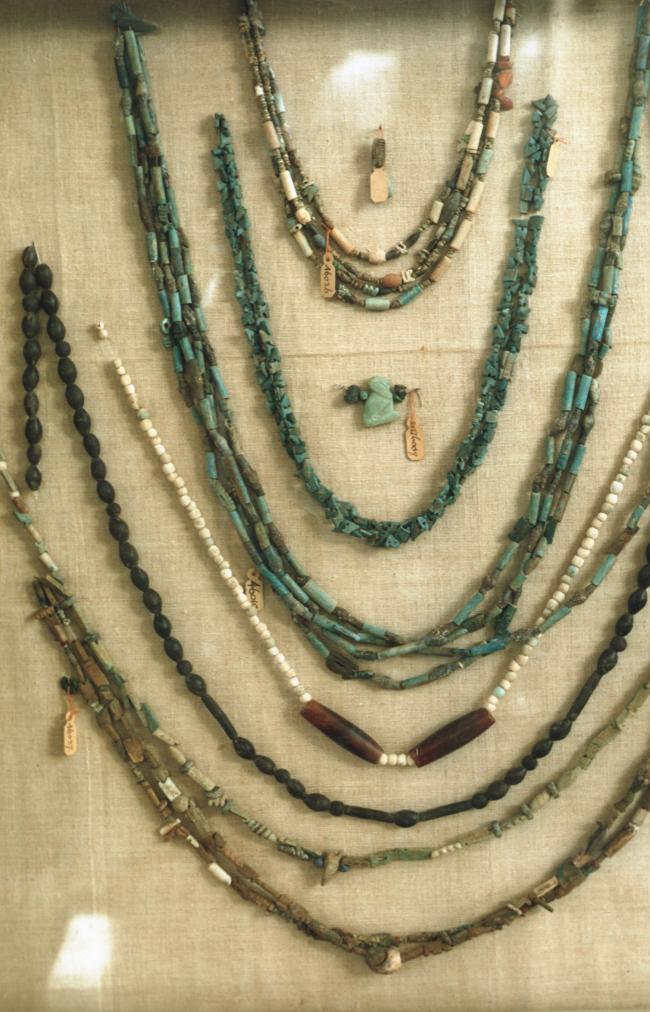
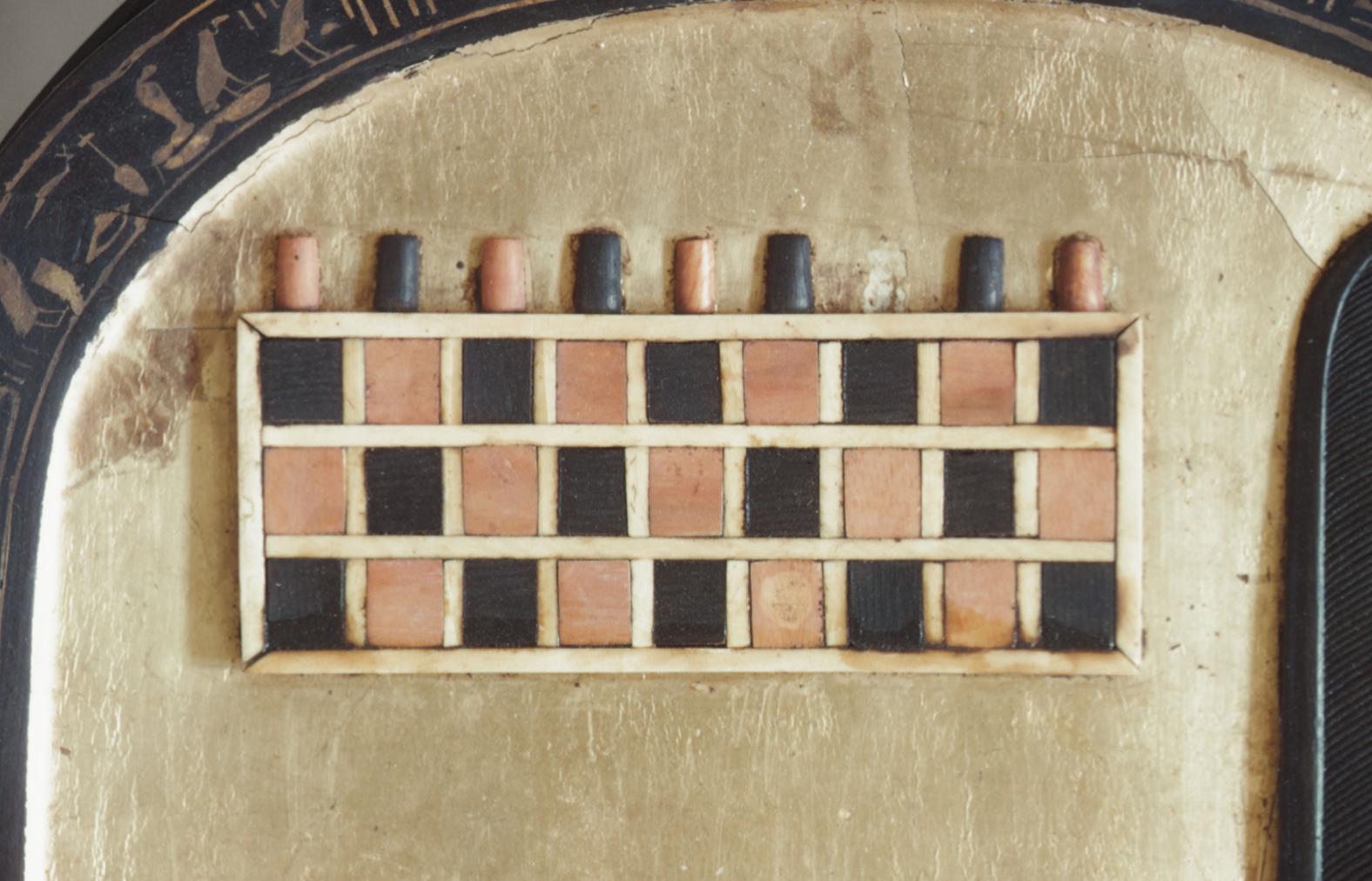
See entire tombThis rectangular side chamber (called the Annexe by Carter), is the equivalent to the side chambers used for storage located off chamber F in traditional tombs. Carter noted that masons' control marks in red were visible upon the walls. The floor of this chamber is 0.9 m lower than the floor of chamber I. The chamber contained a disordered array of furniture, baskets, wine jars, calcite vessels, model boats, and shabtis.
Porter and Moss designation:
Gate Ib
See entire tombAt the right (north) end of the rear (west) wall of chamber I is an abandoned cutting for a gate to a second side chamber intended here before the construction of the burial chamber J. Black lines from the top and left side of the cutting indicate the planned dimensions of the gate.
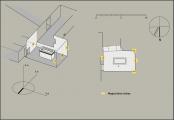
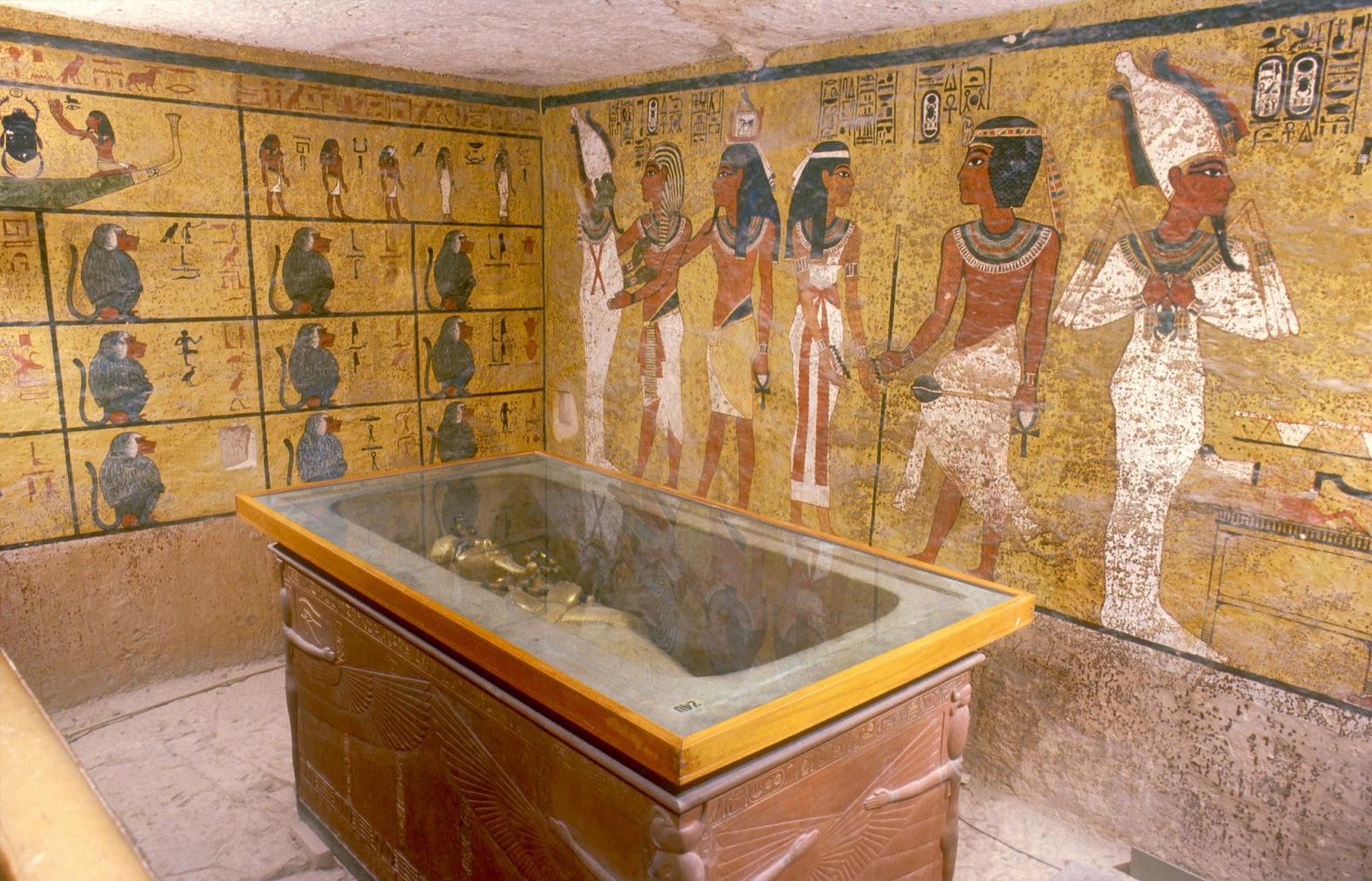
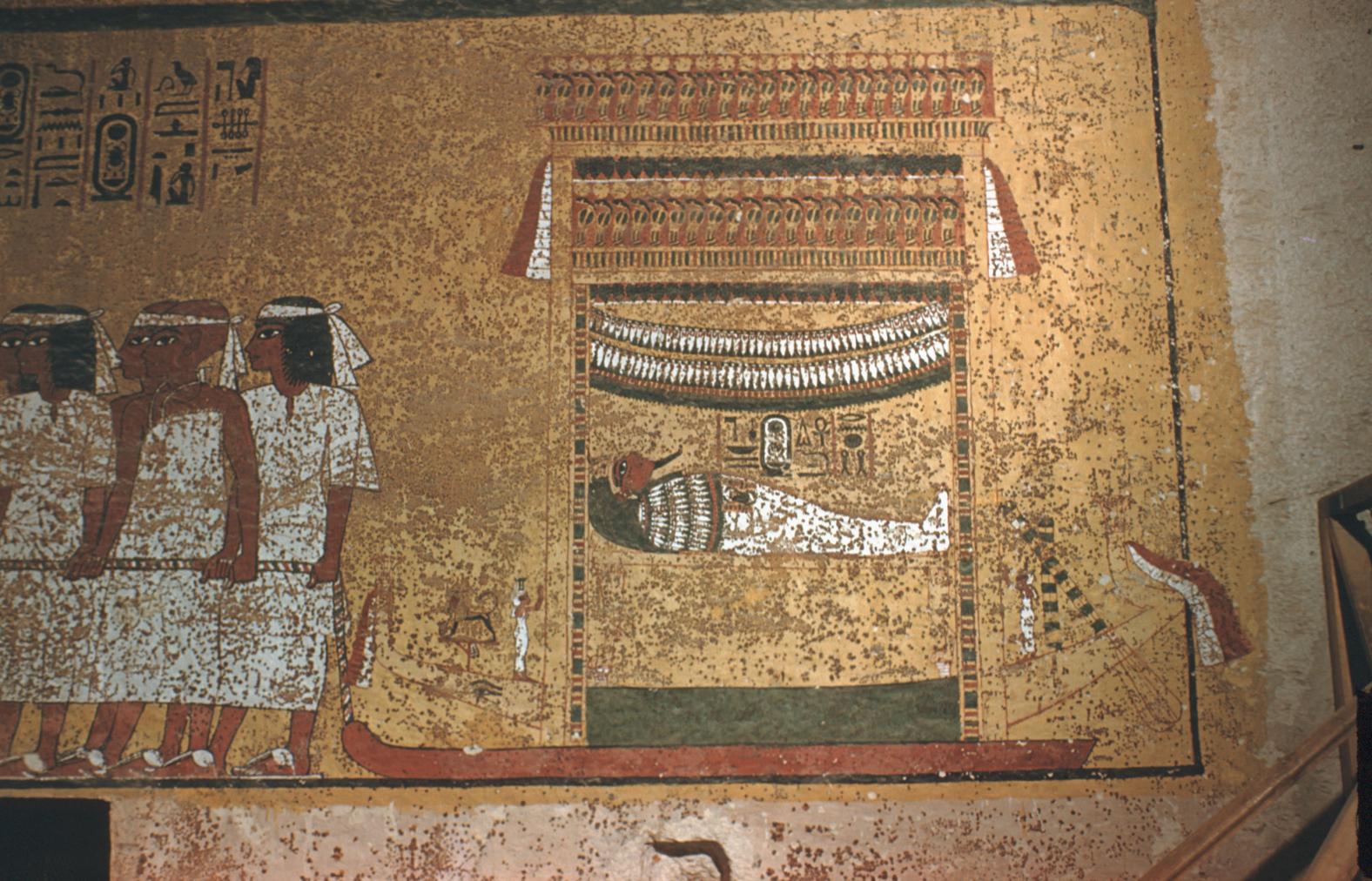
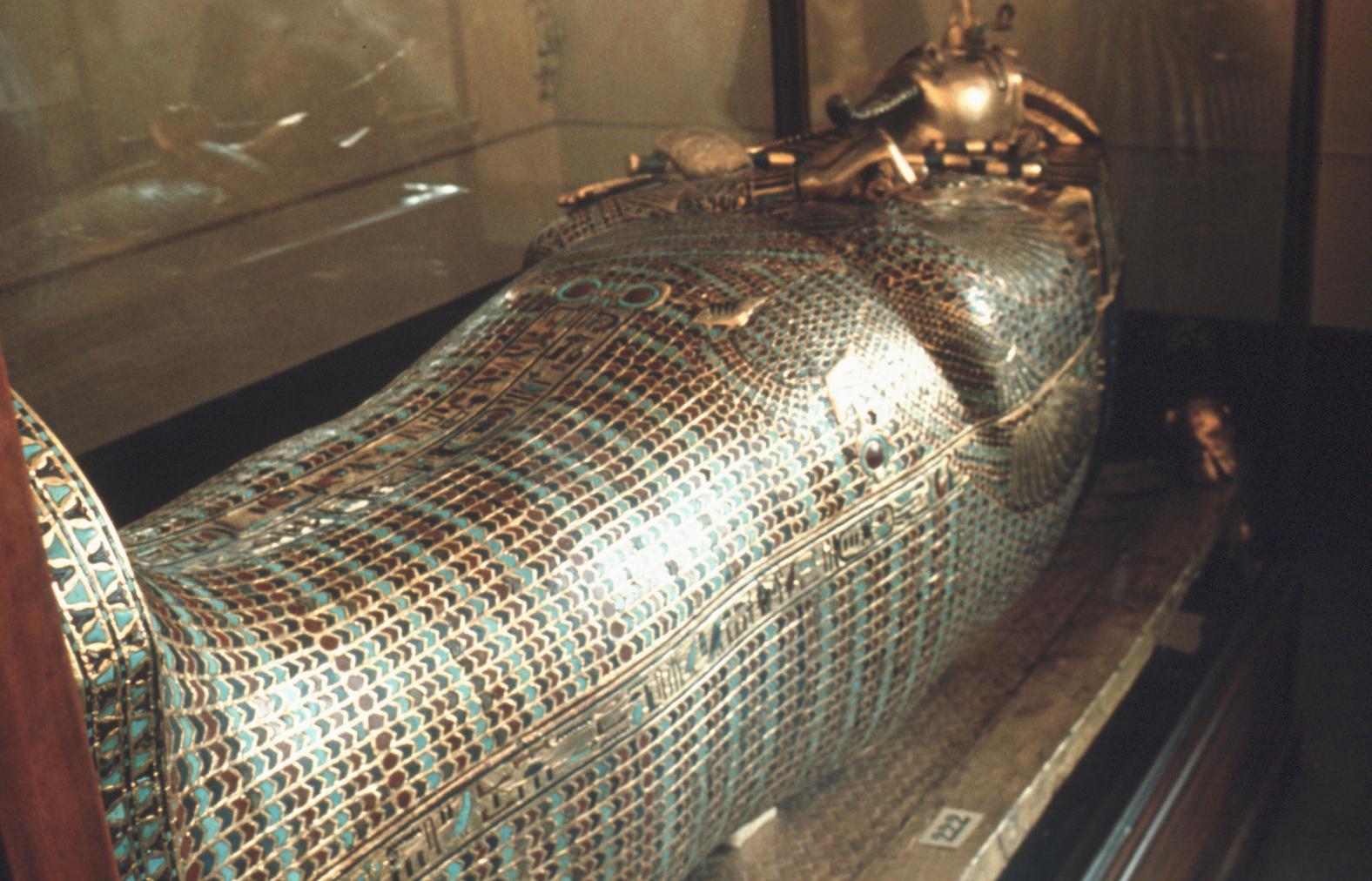
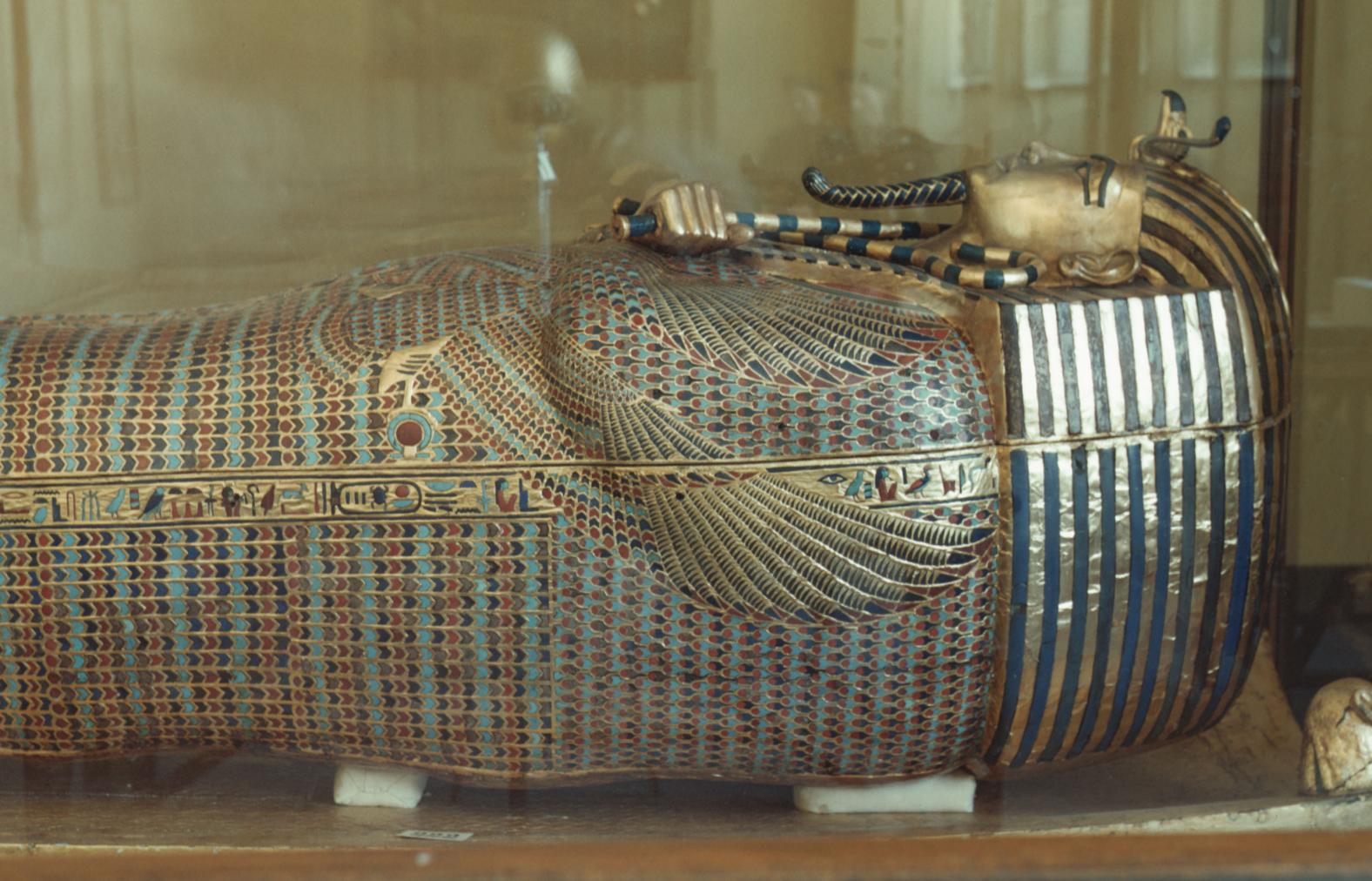
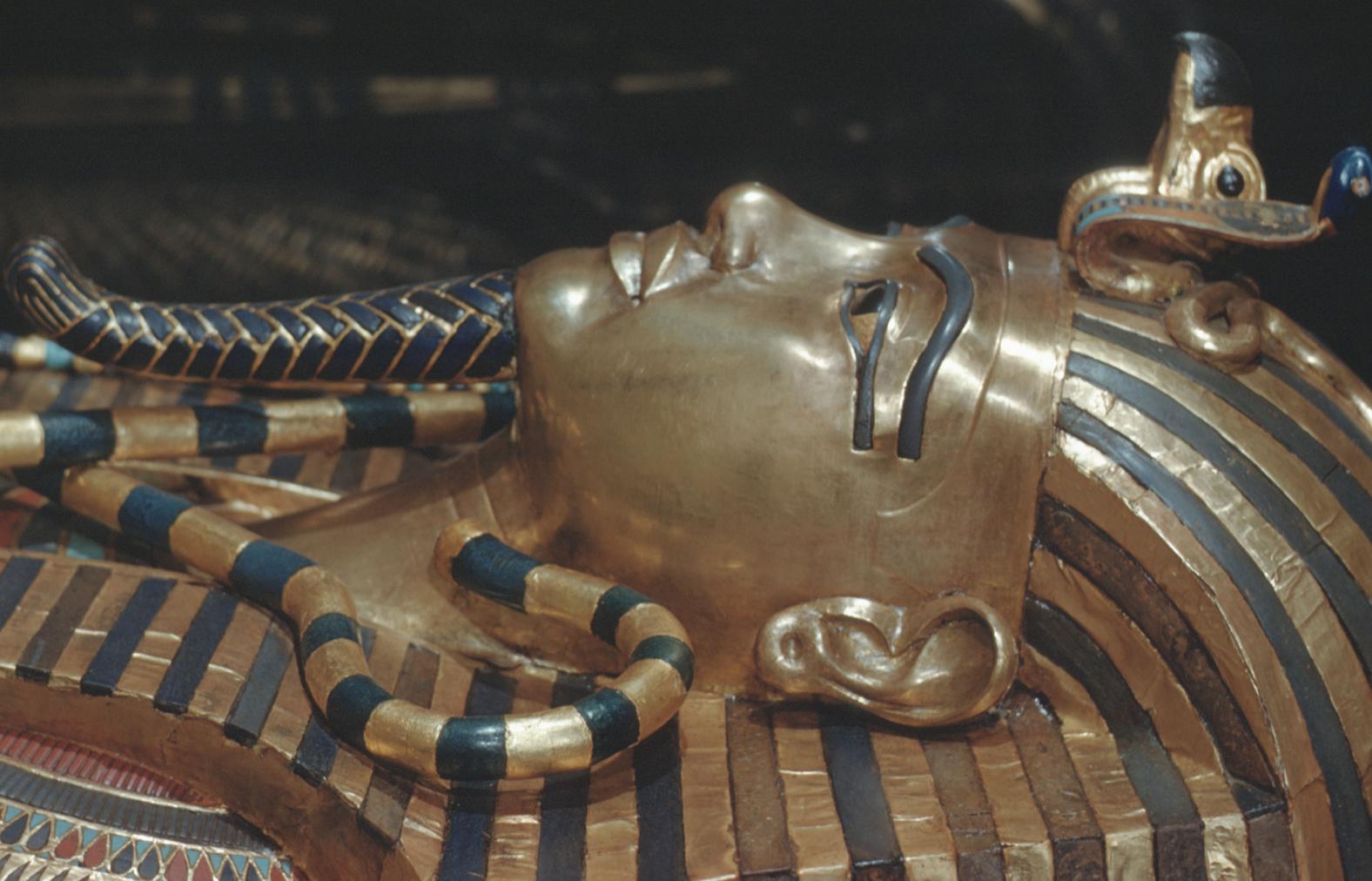
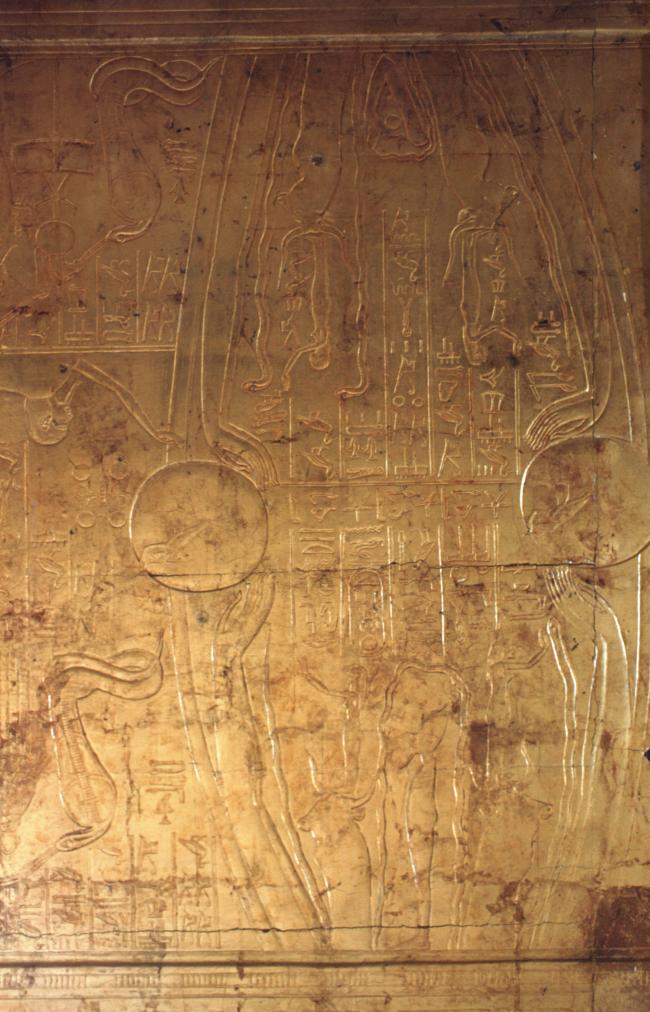
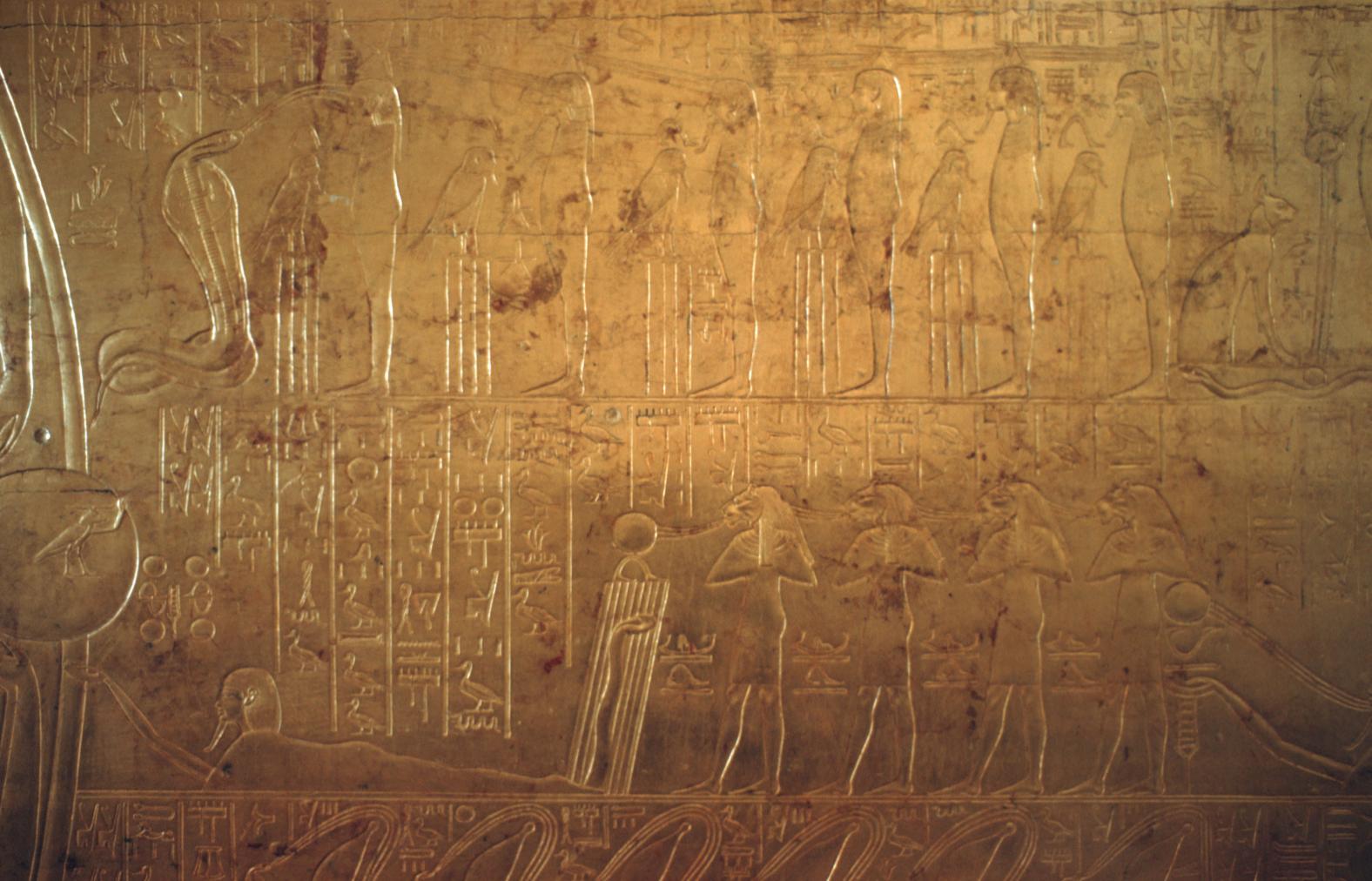
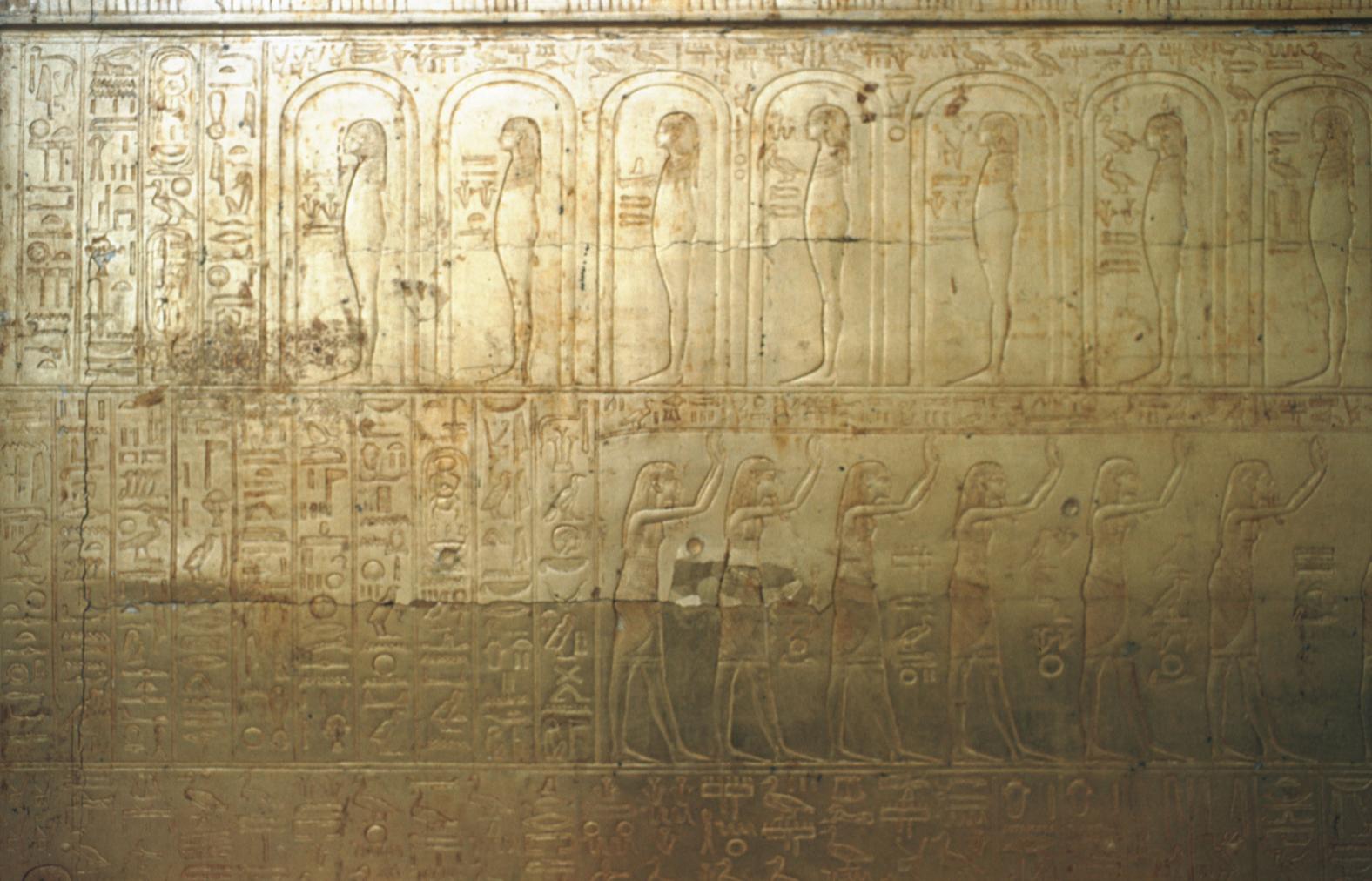
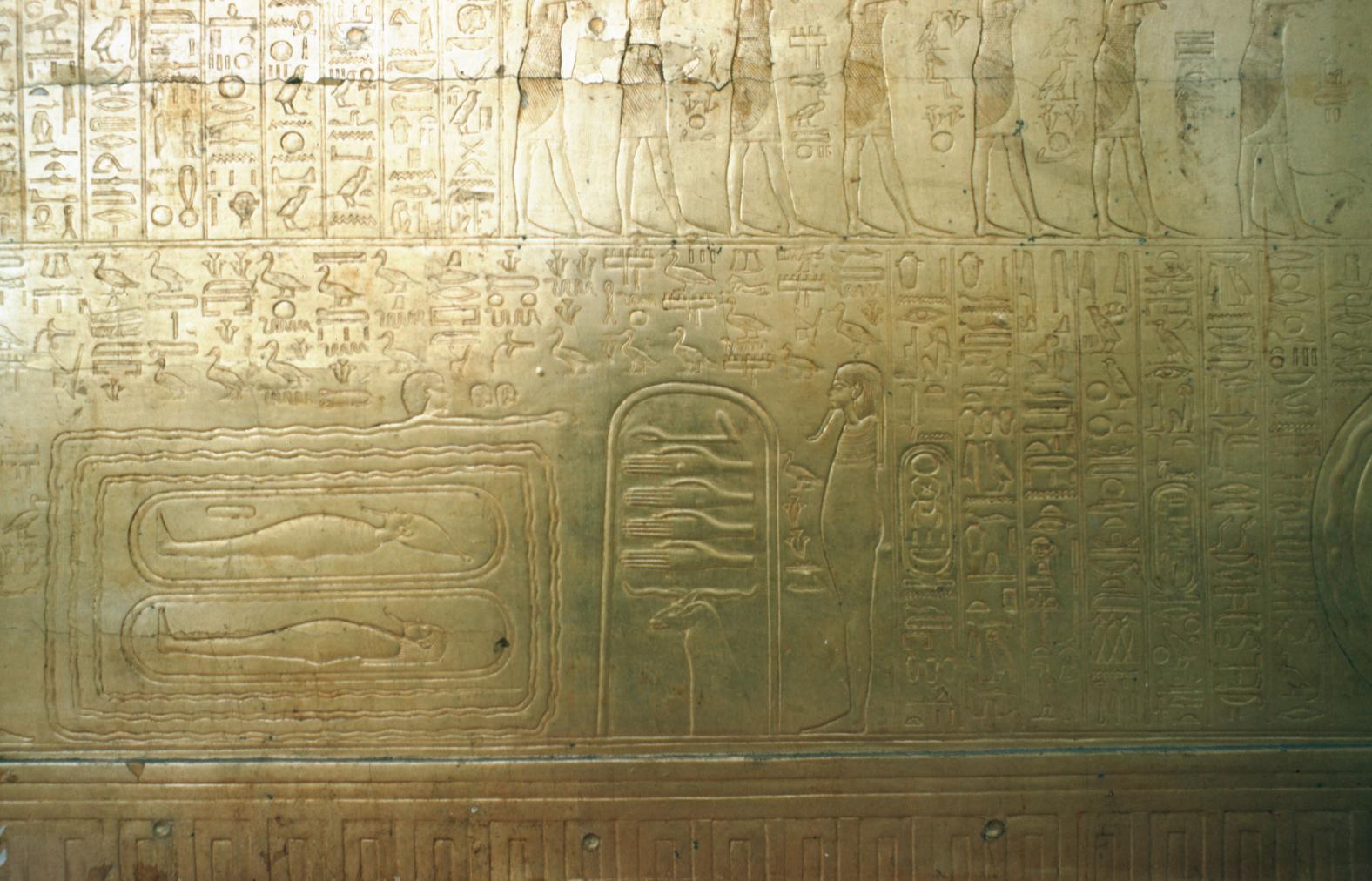
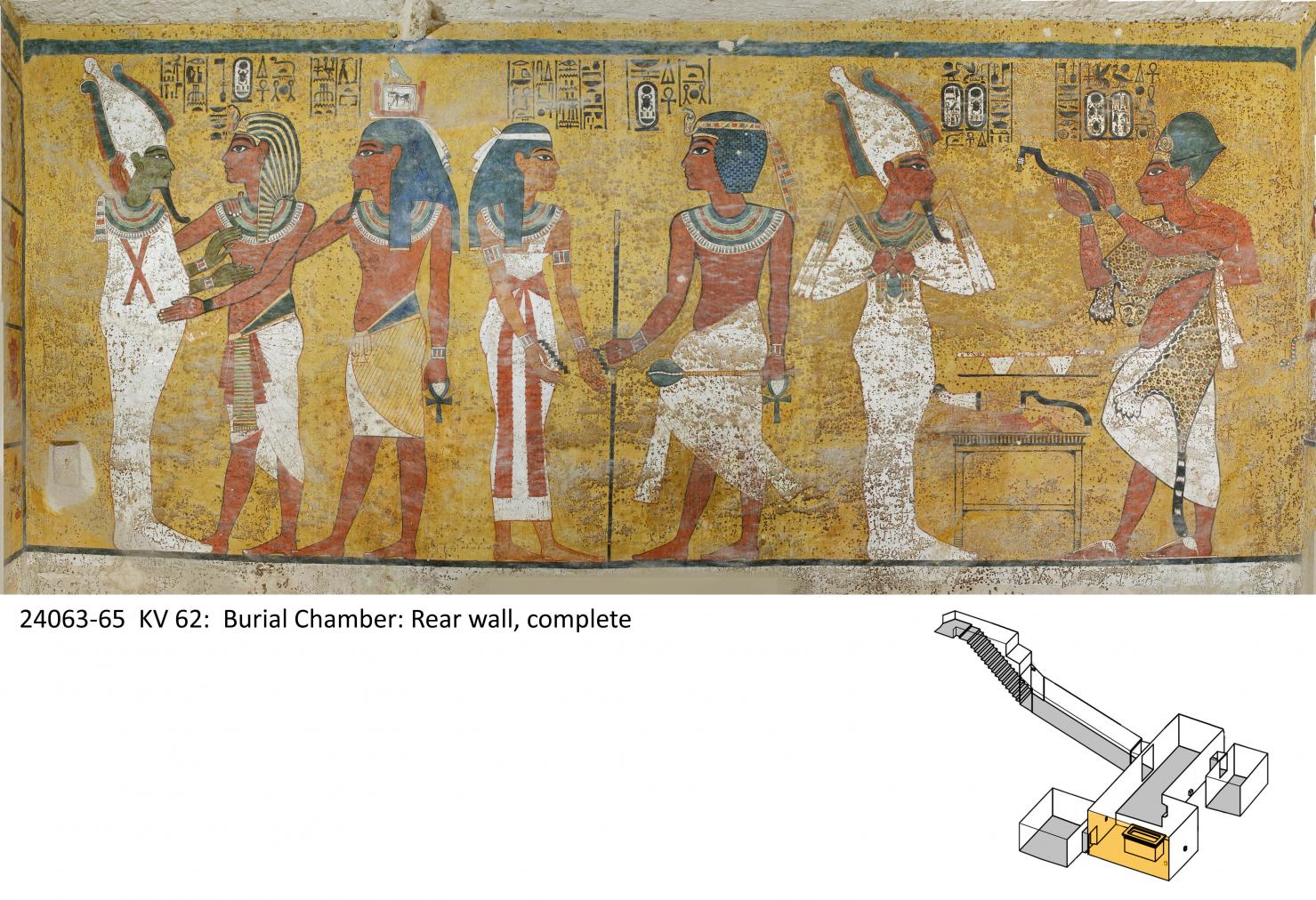
Burial chamber J
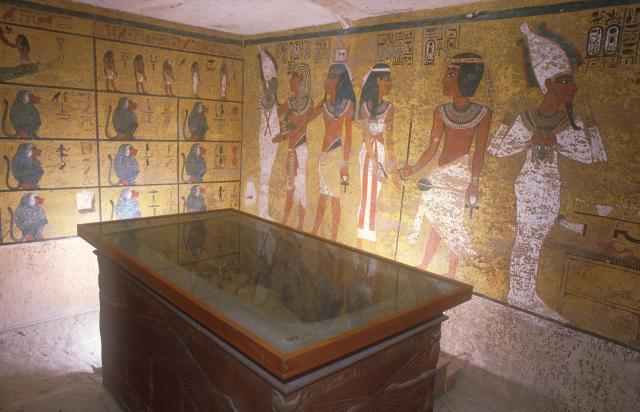
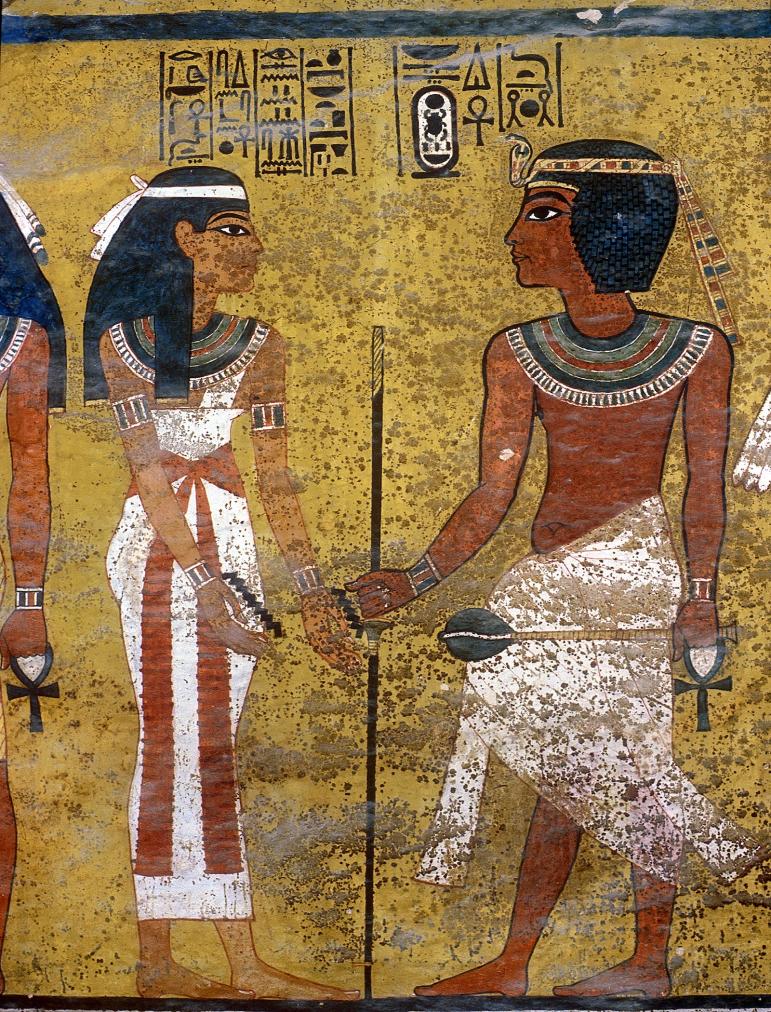
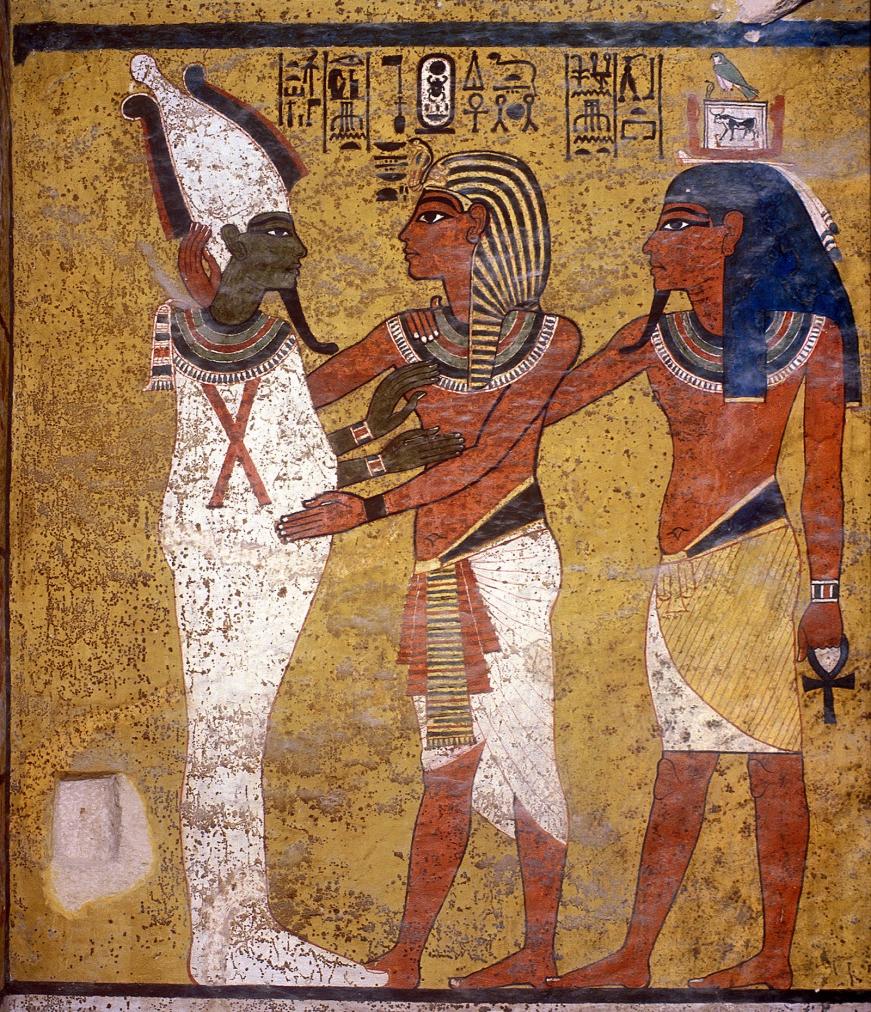
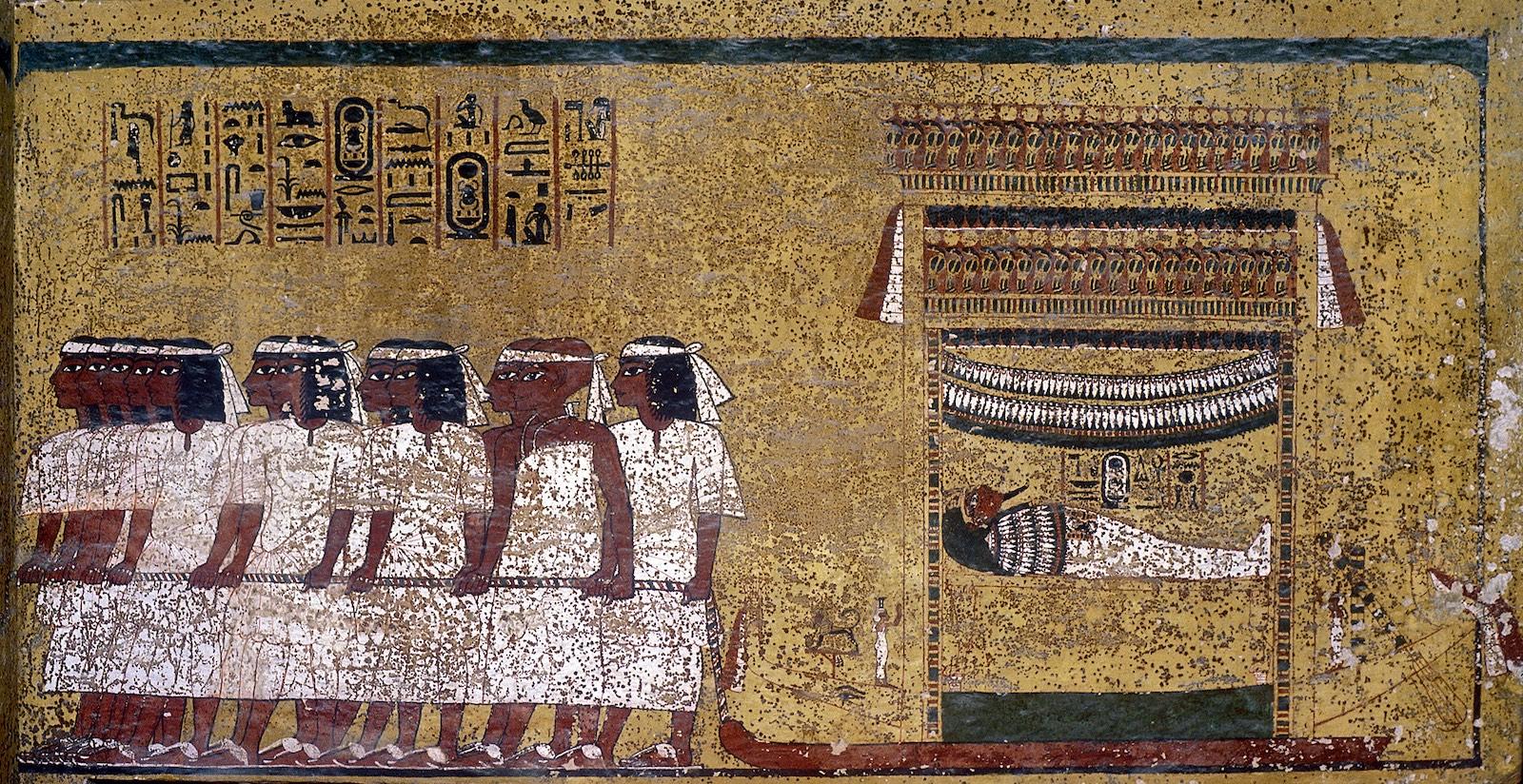
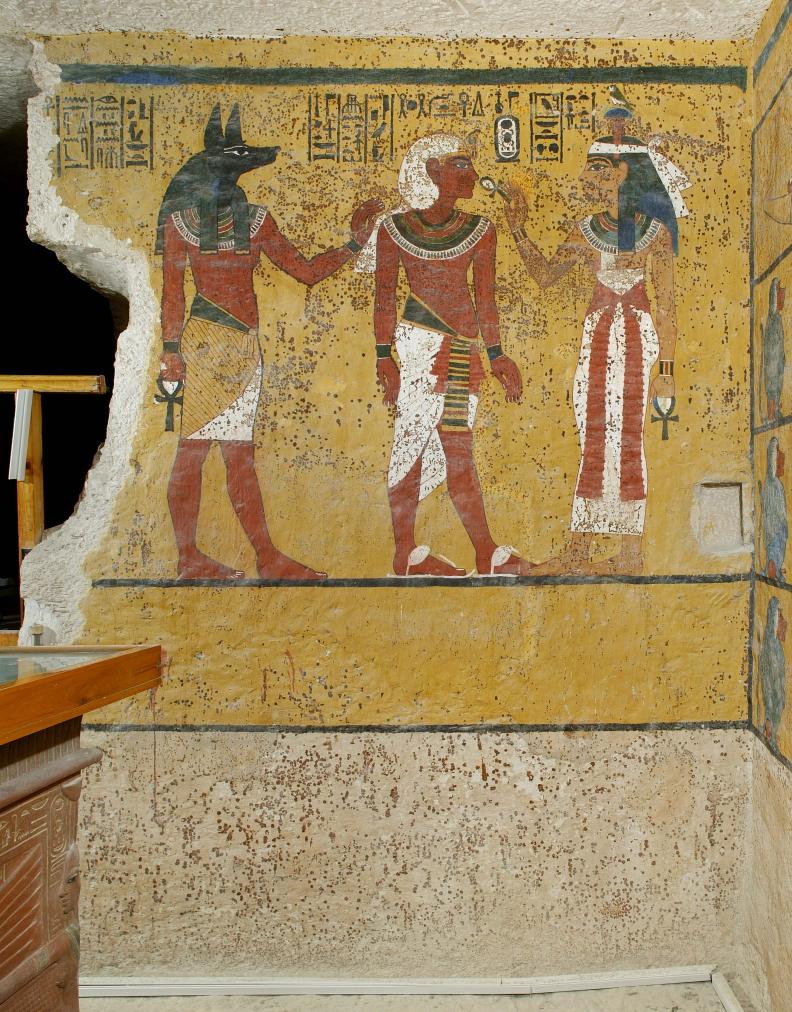
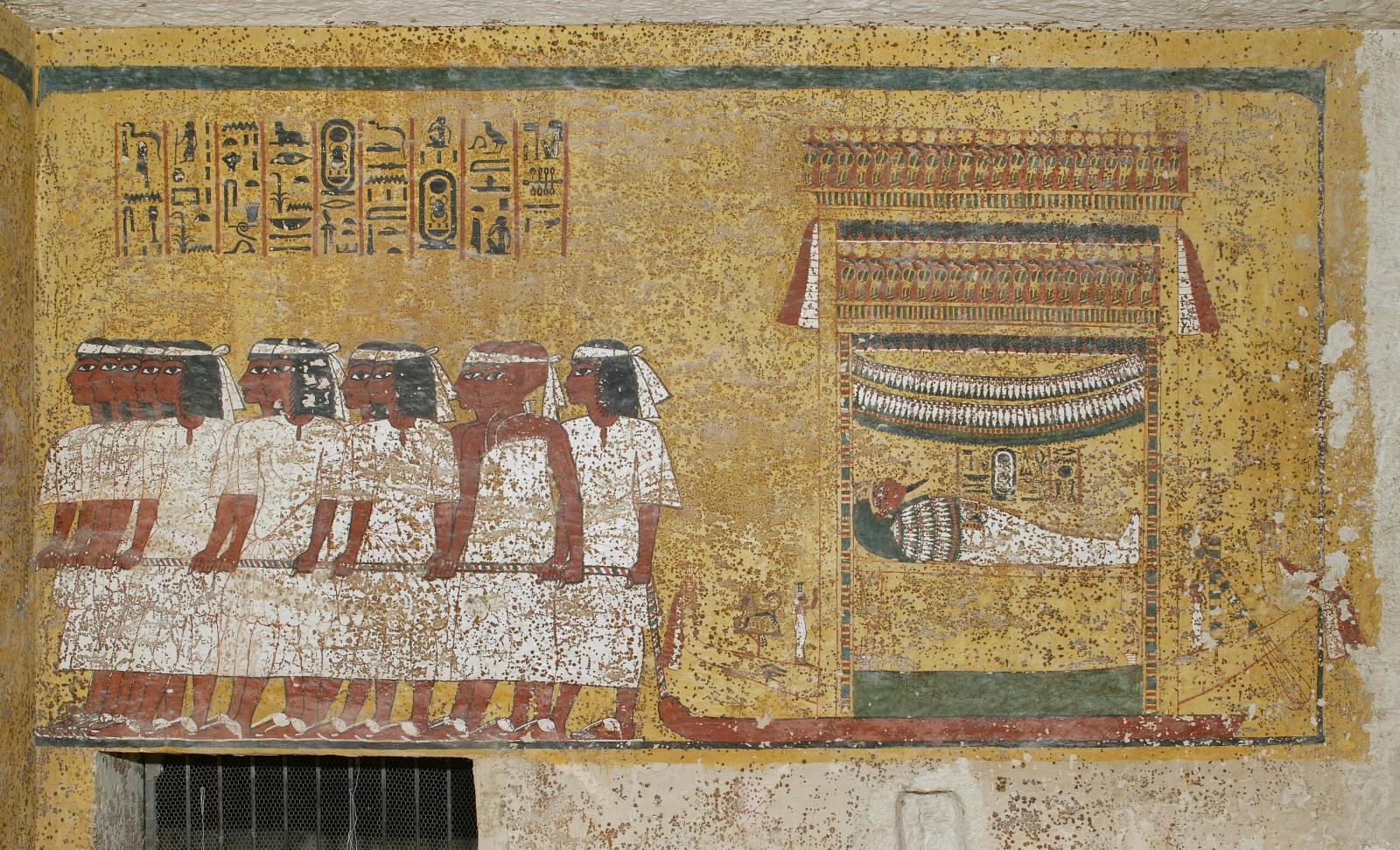
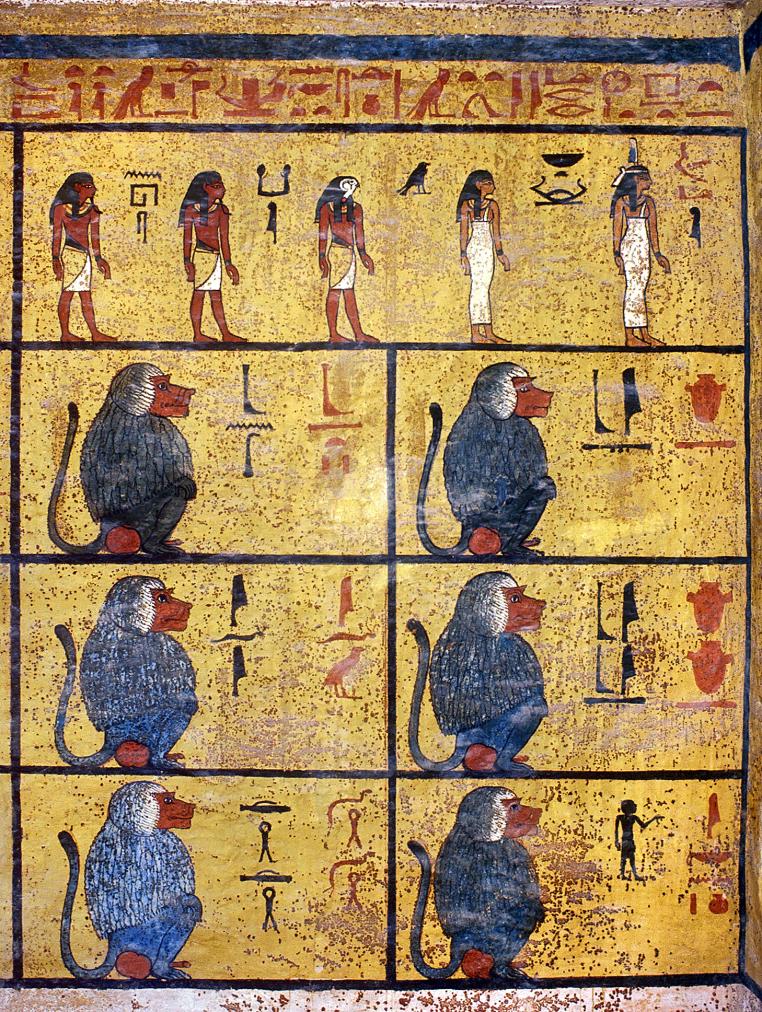
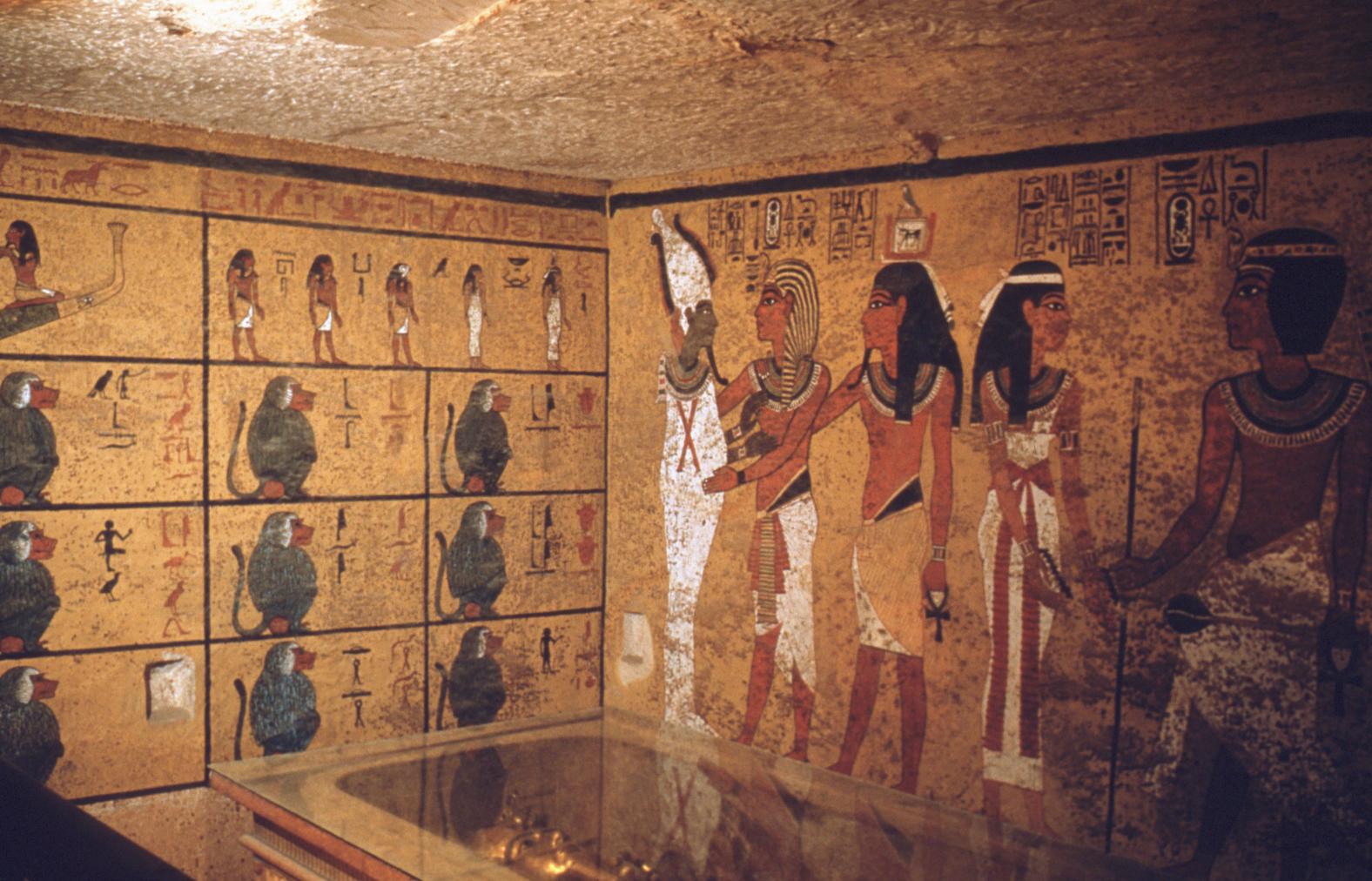
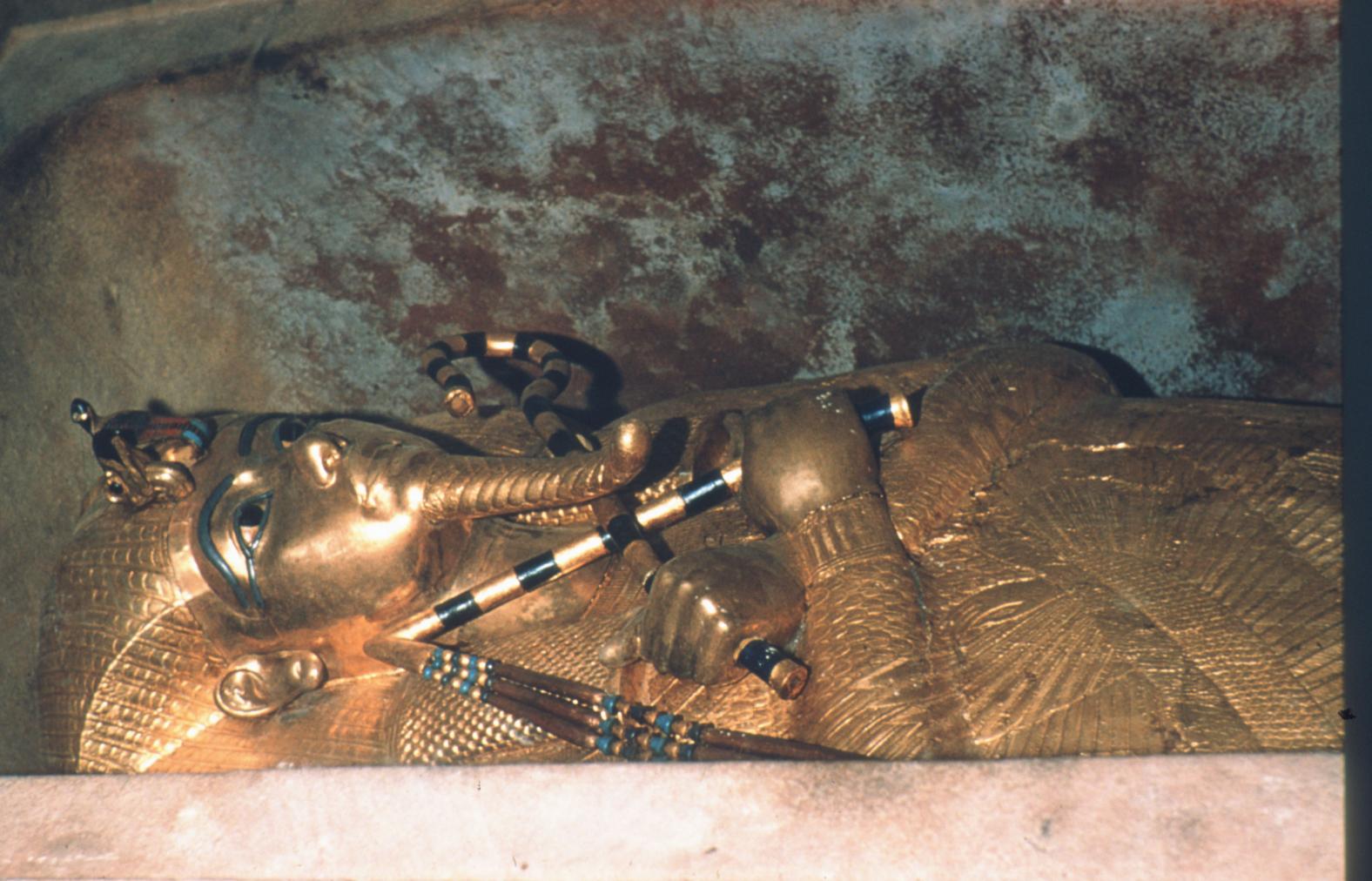
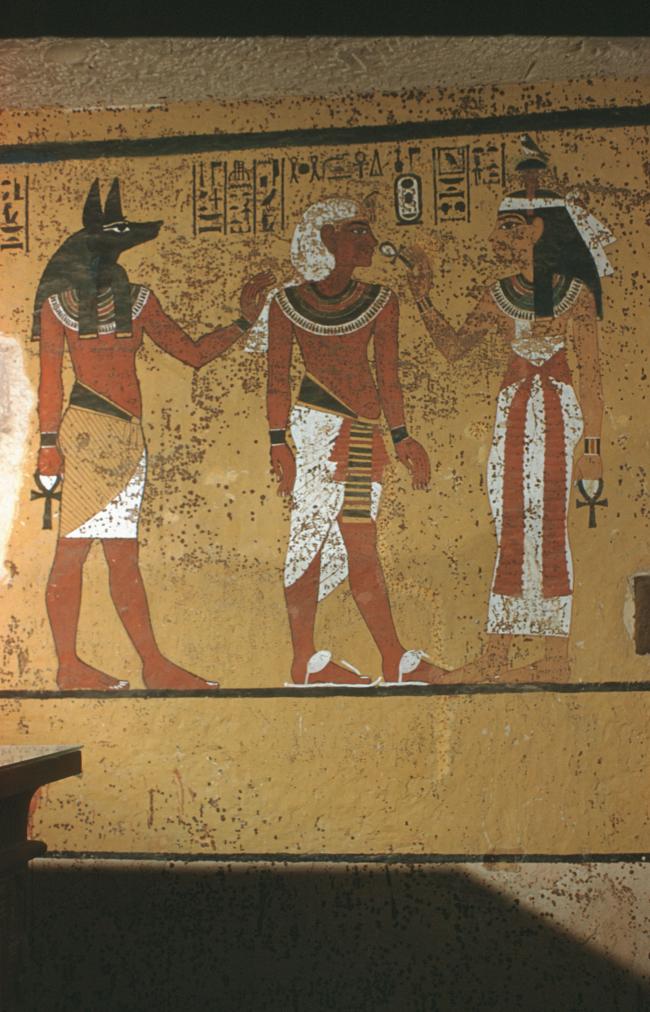
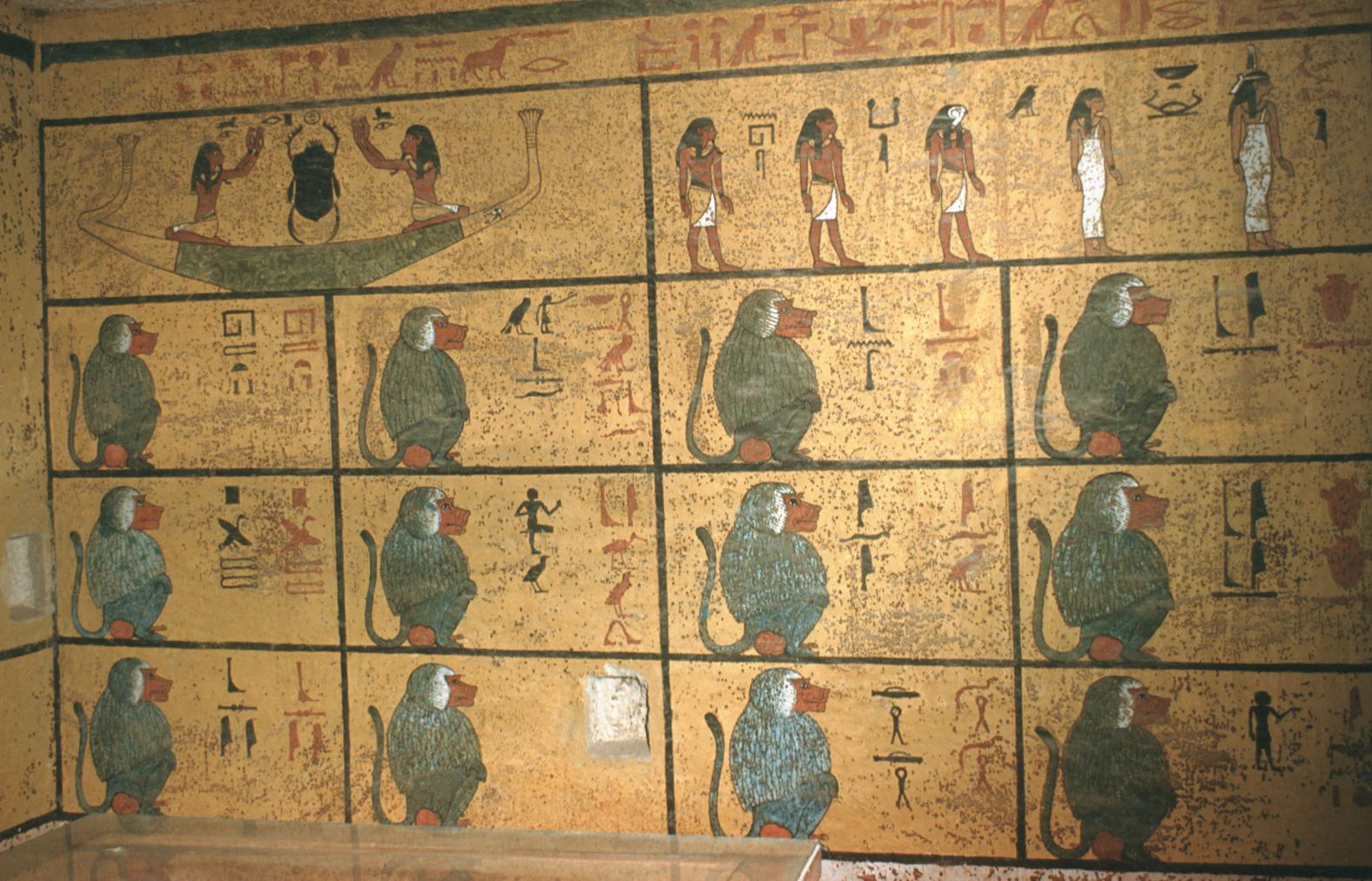
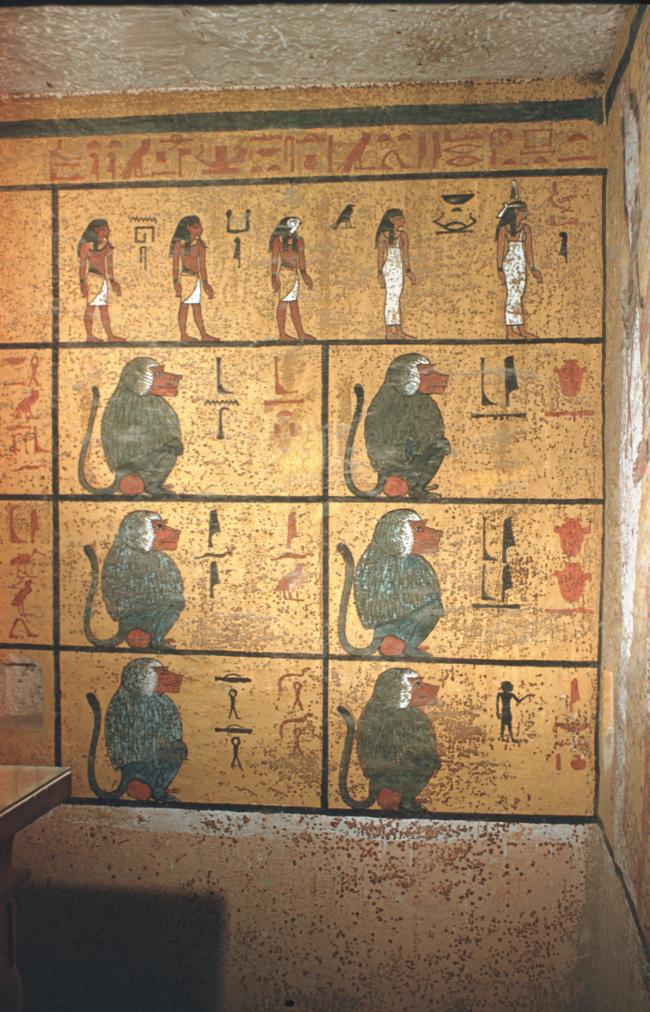
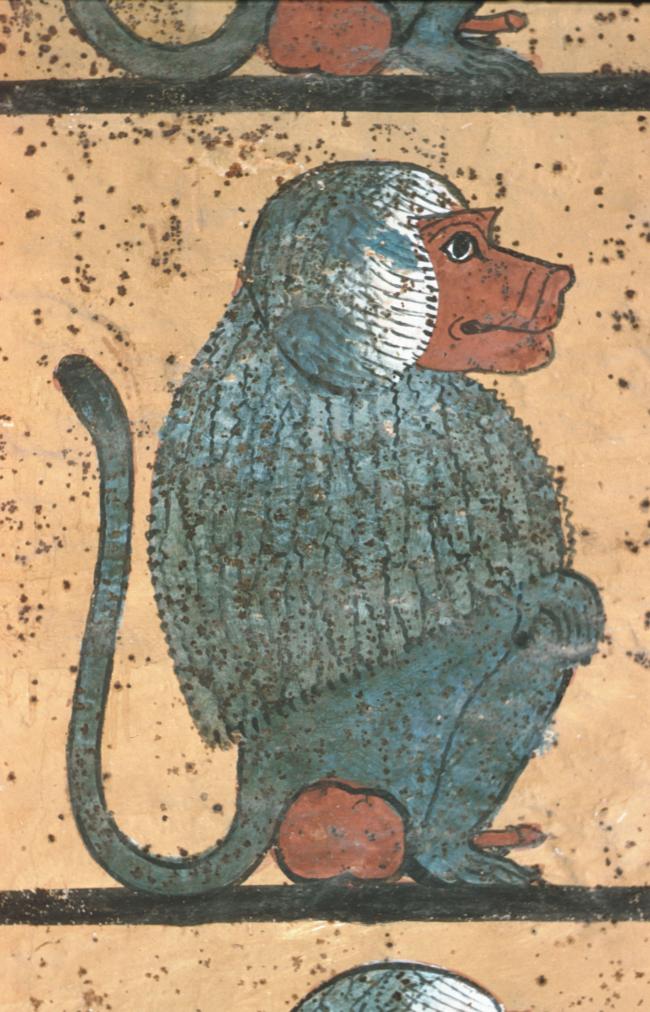
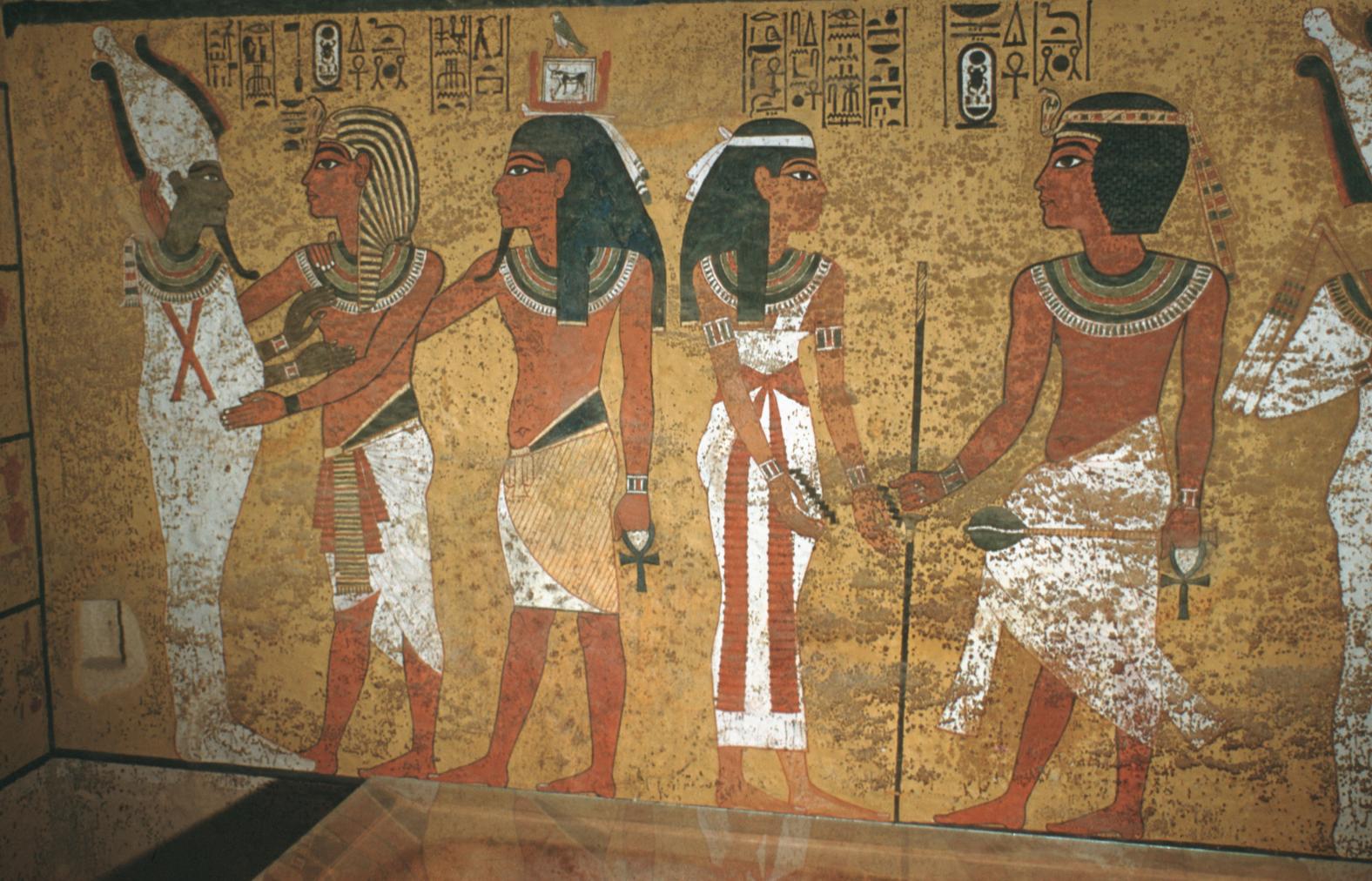
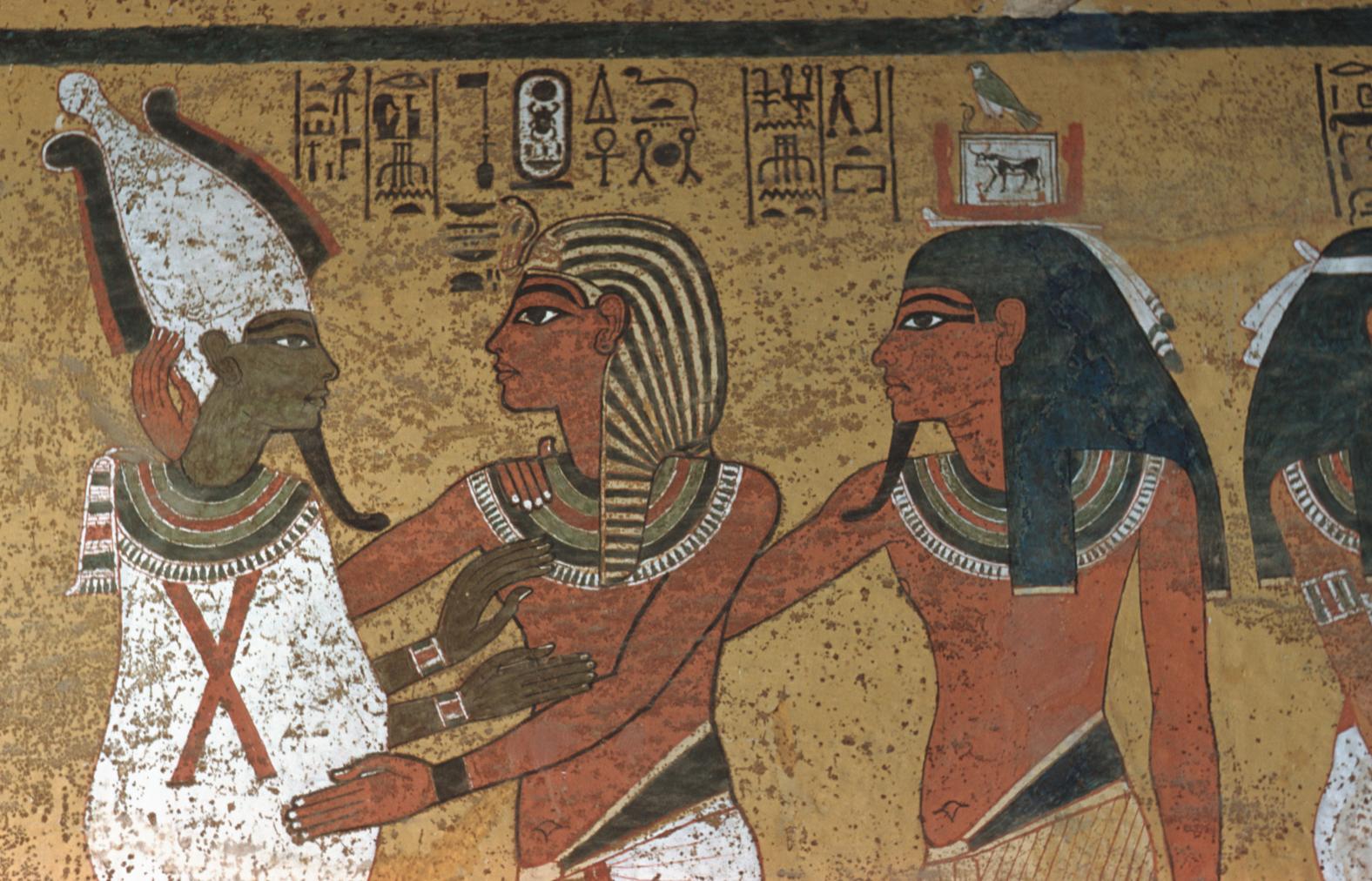
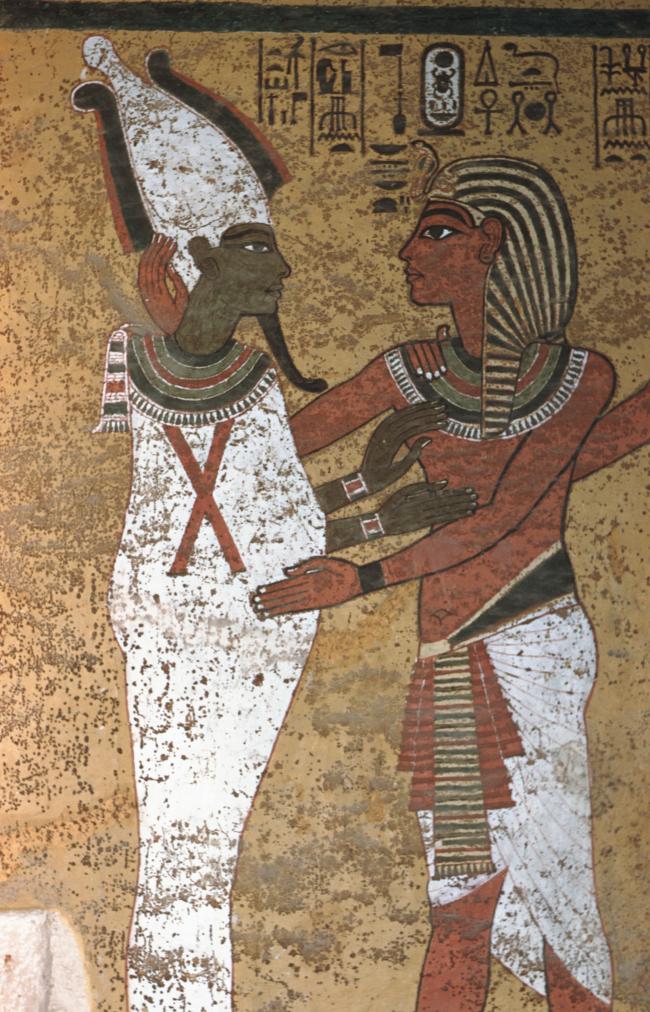
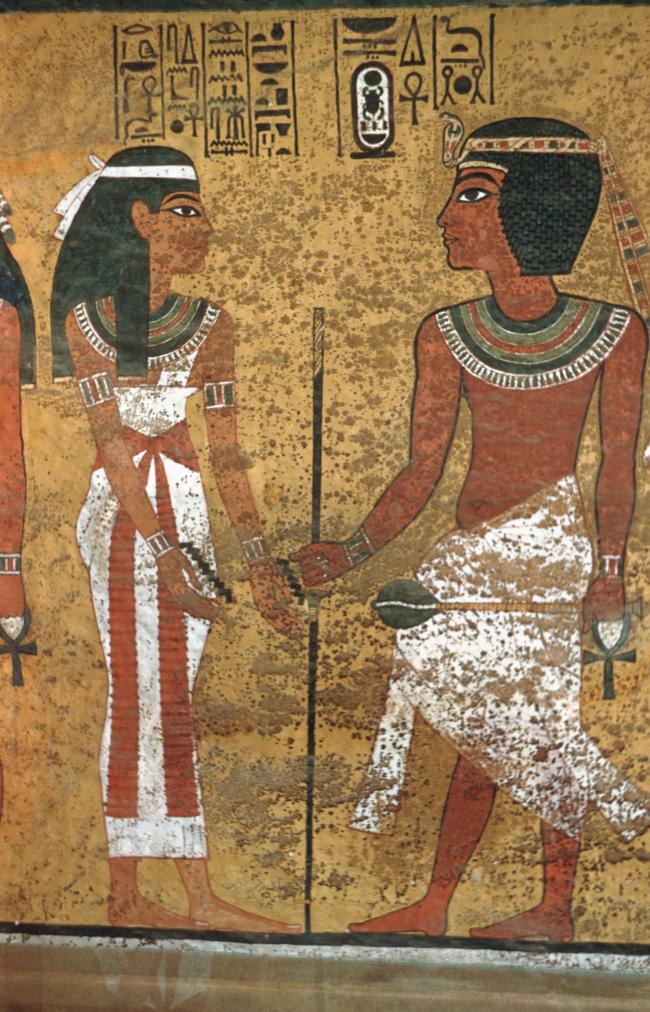
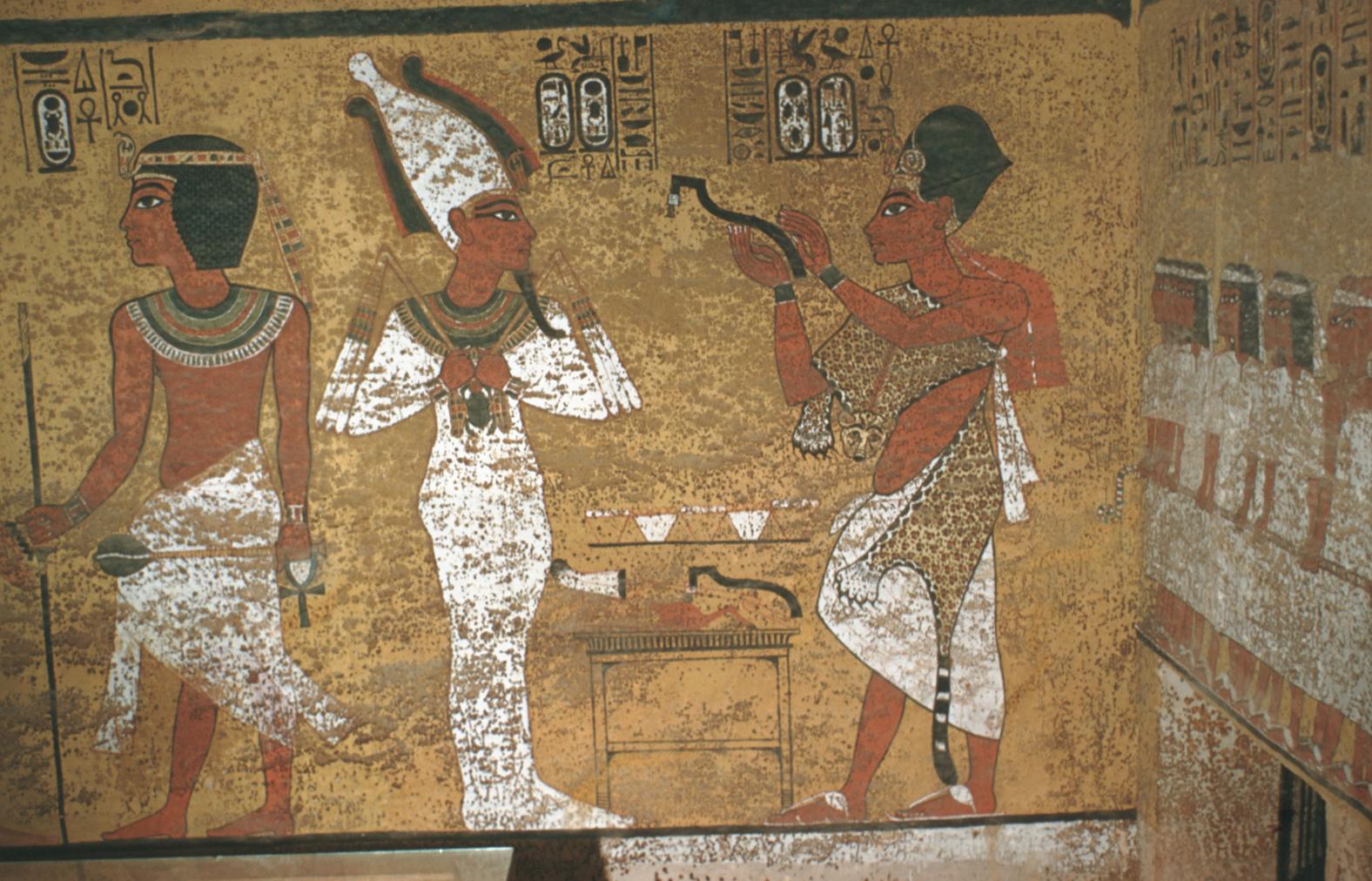
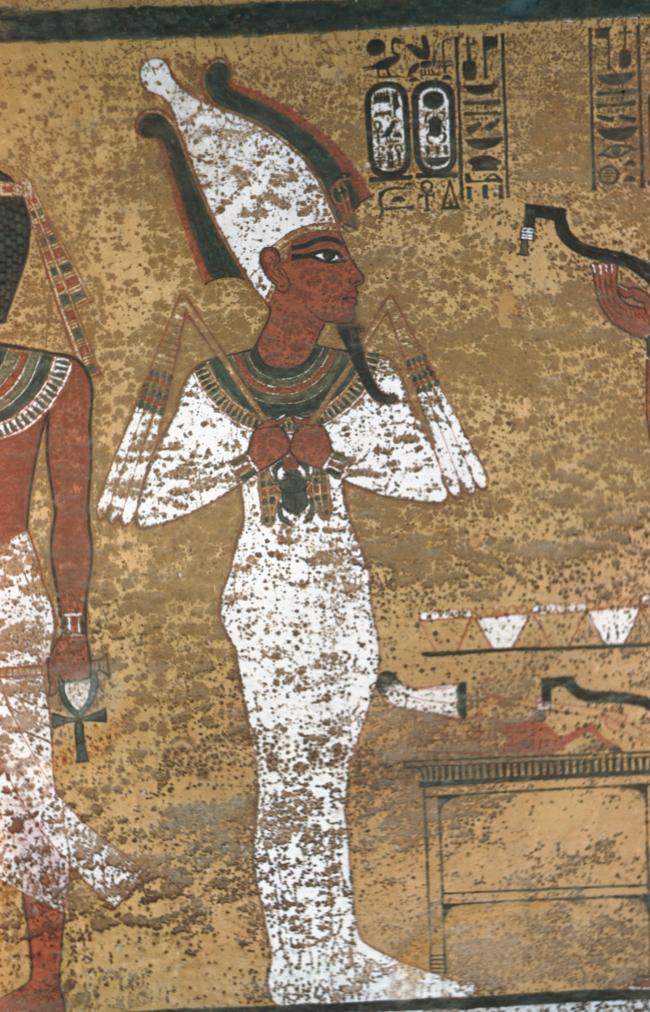
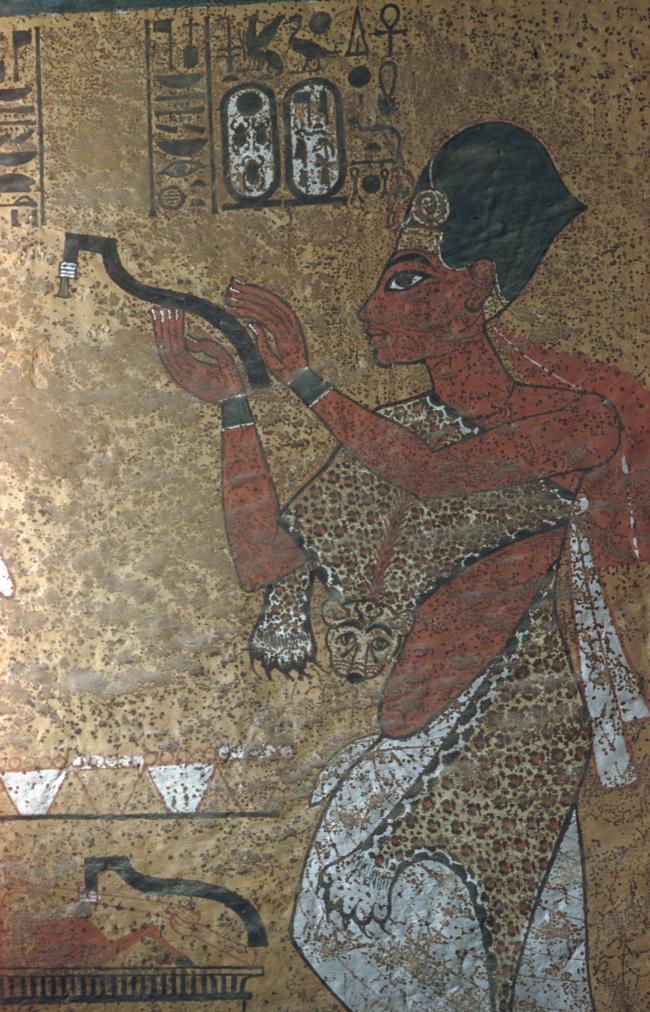
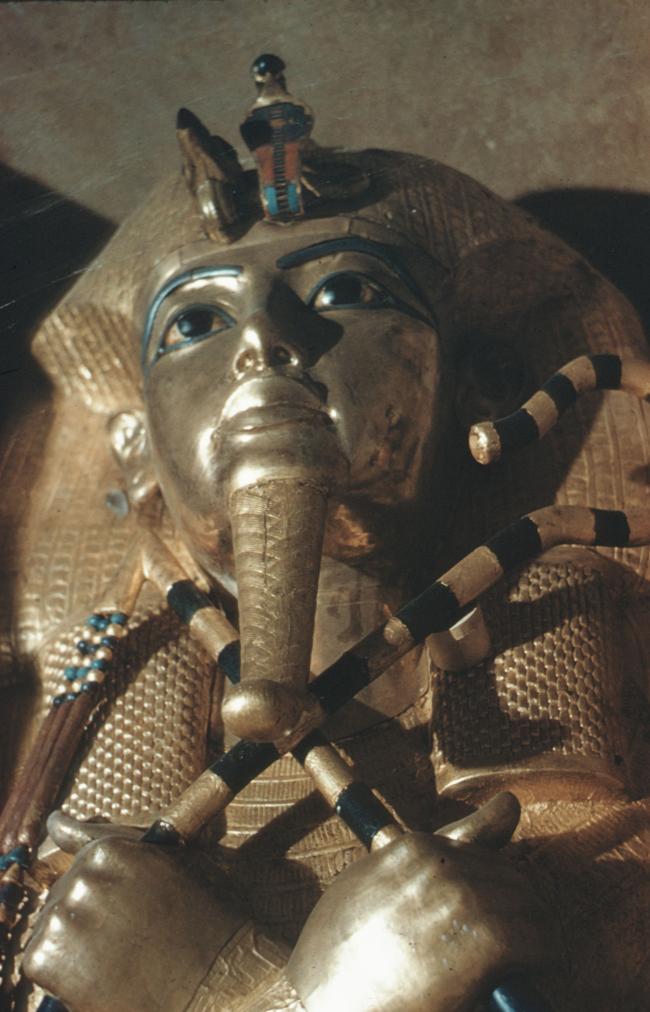
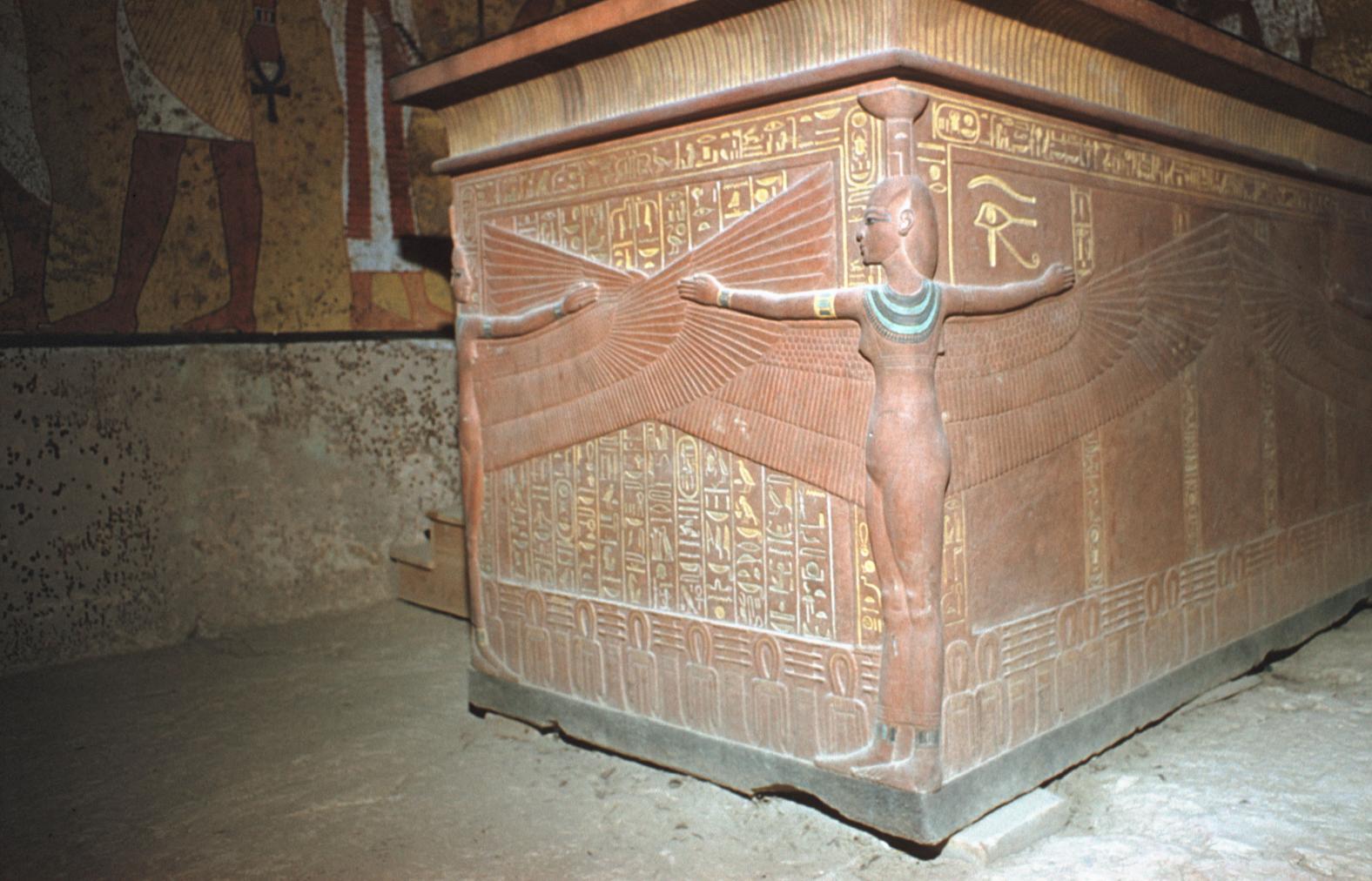
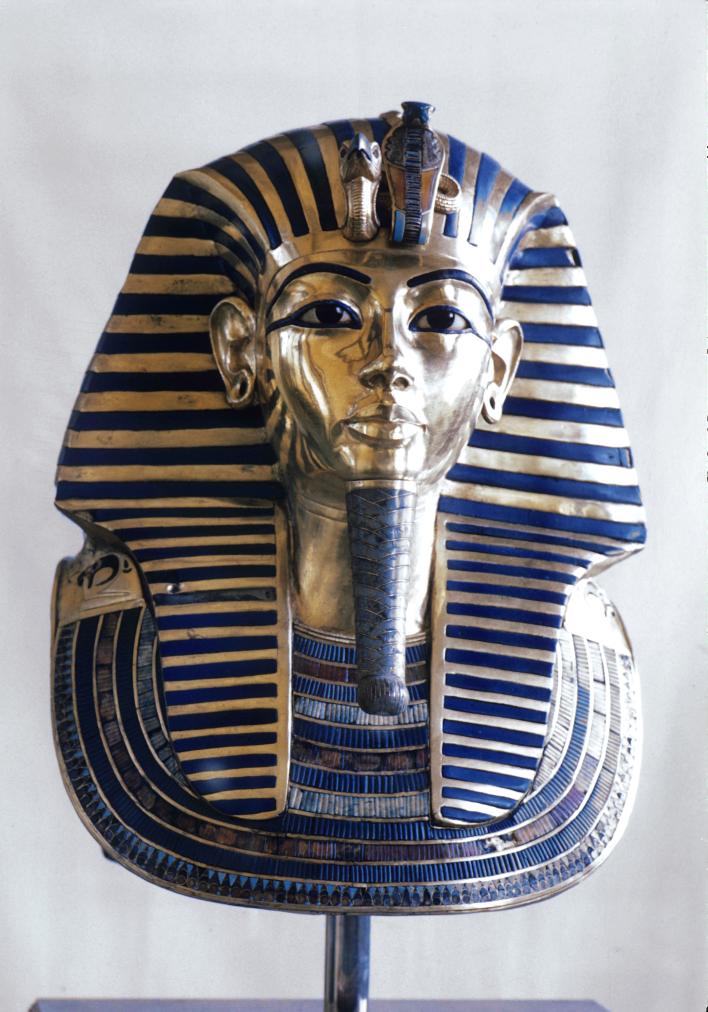
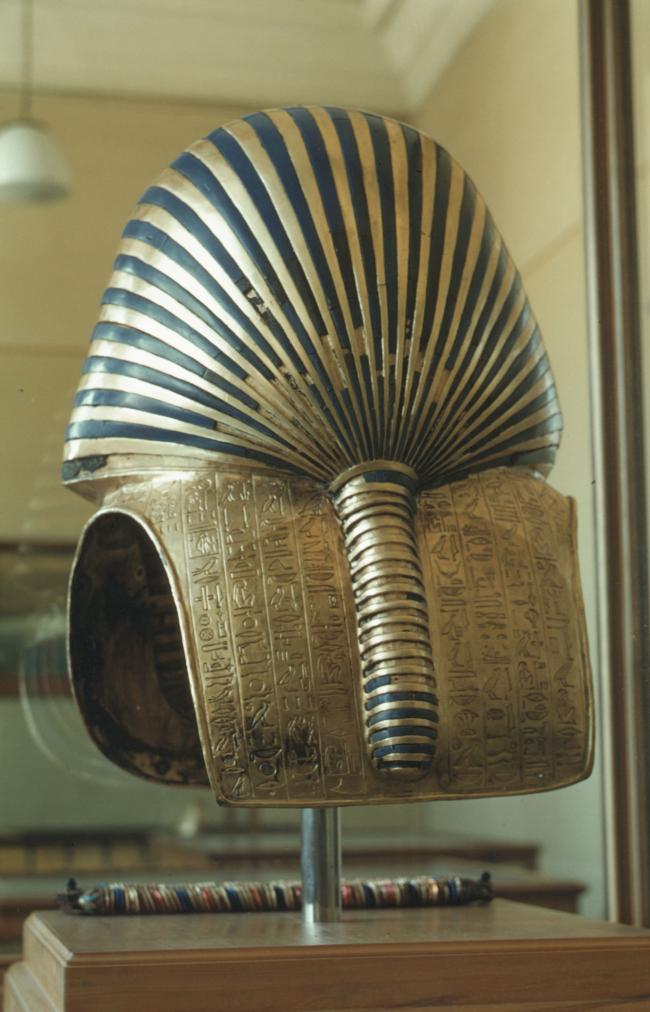
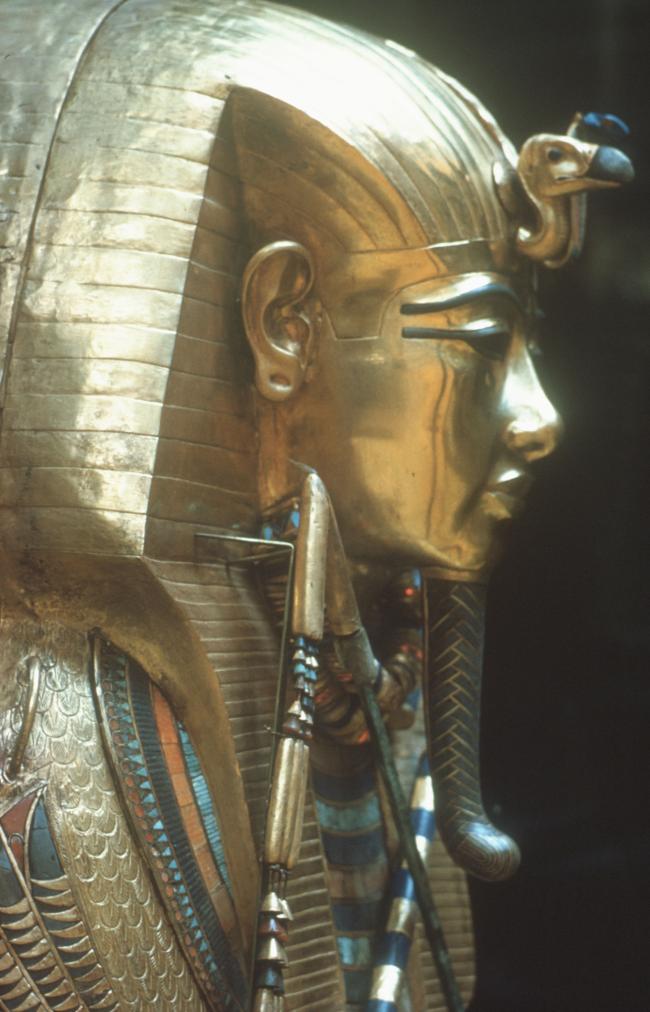
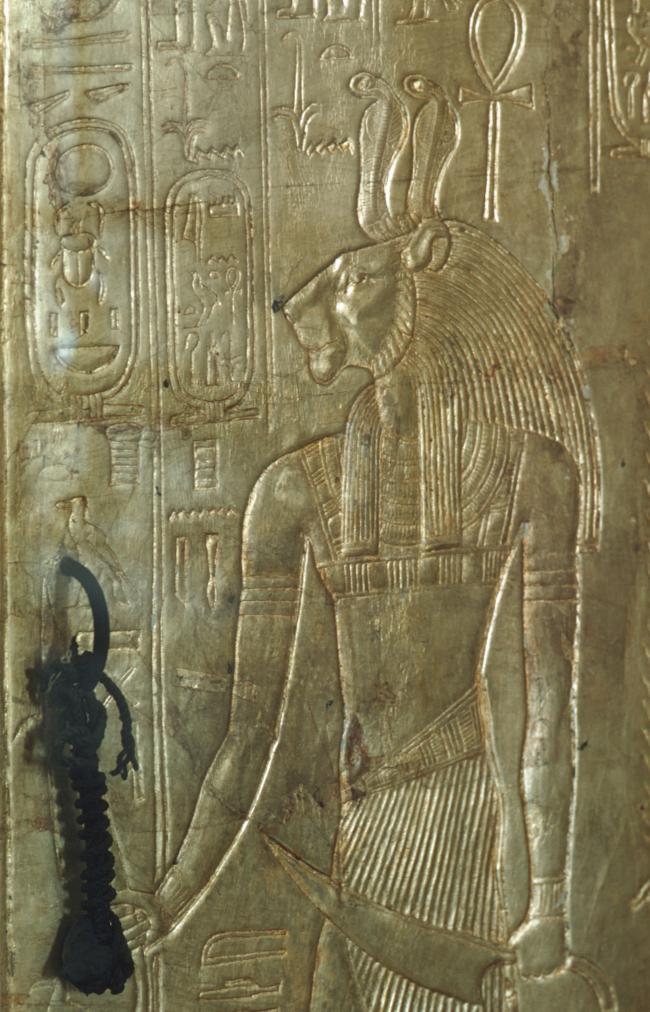
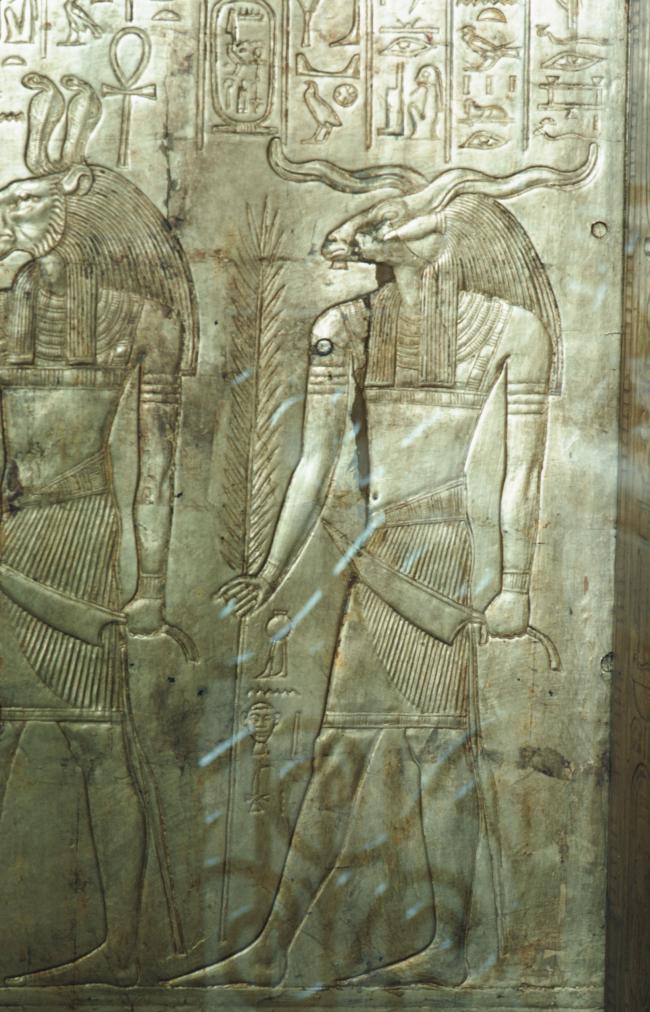
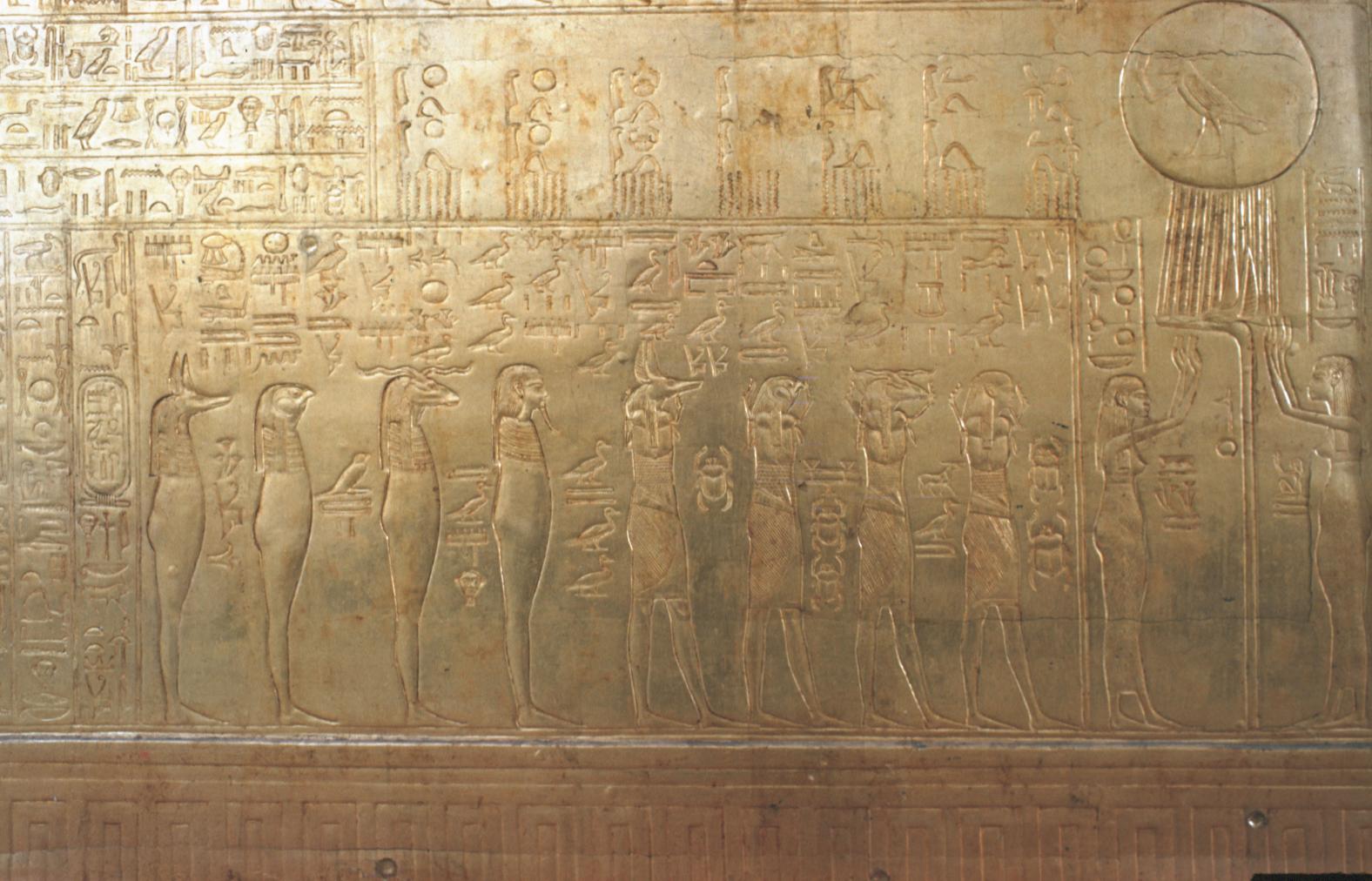
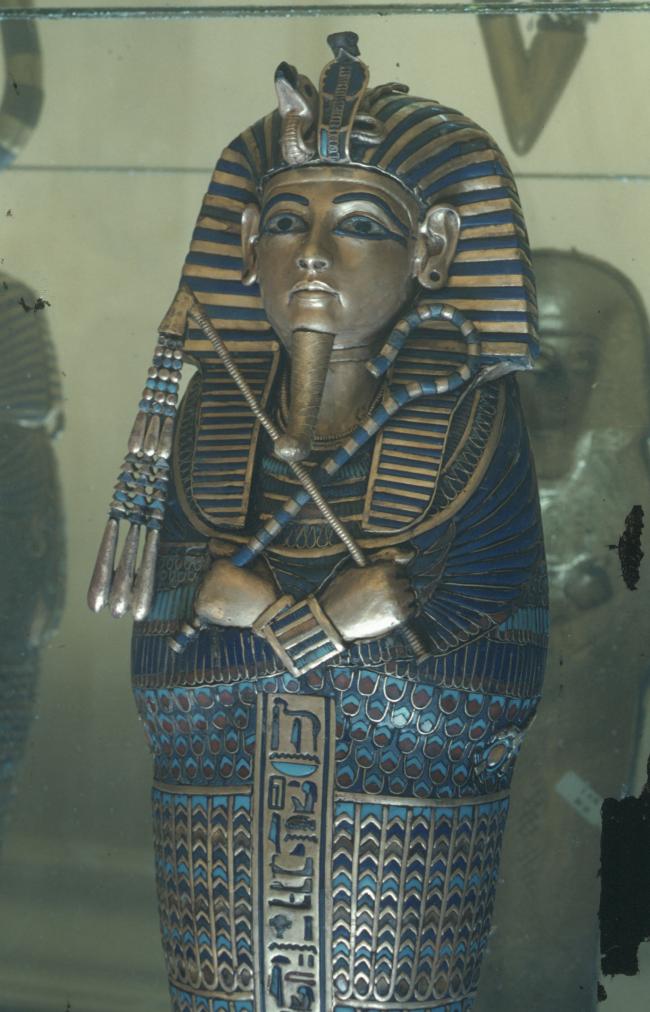
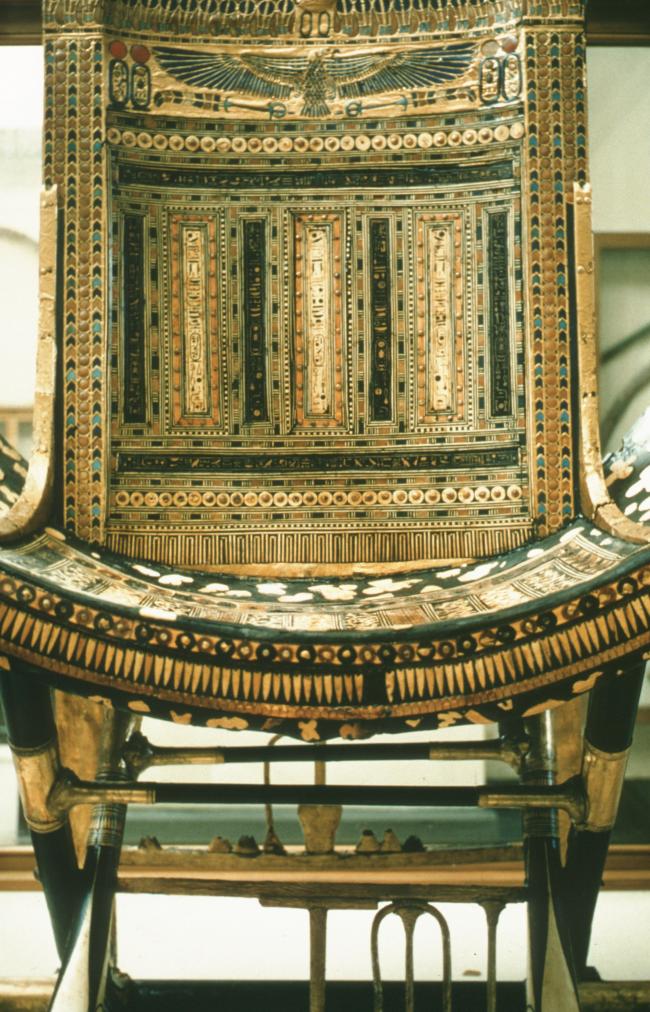
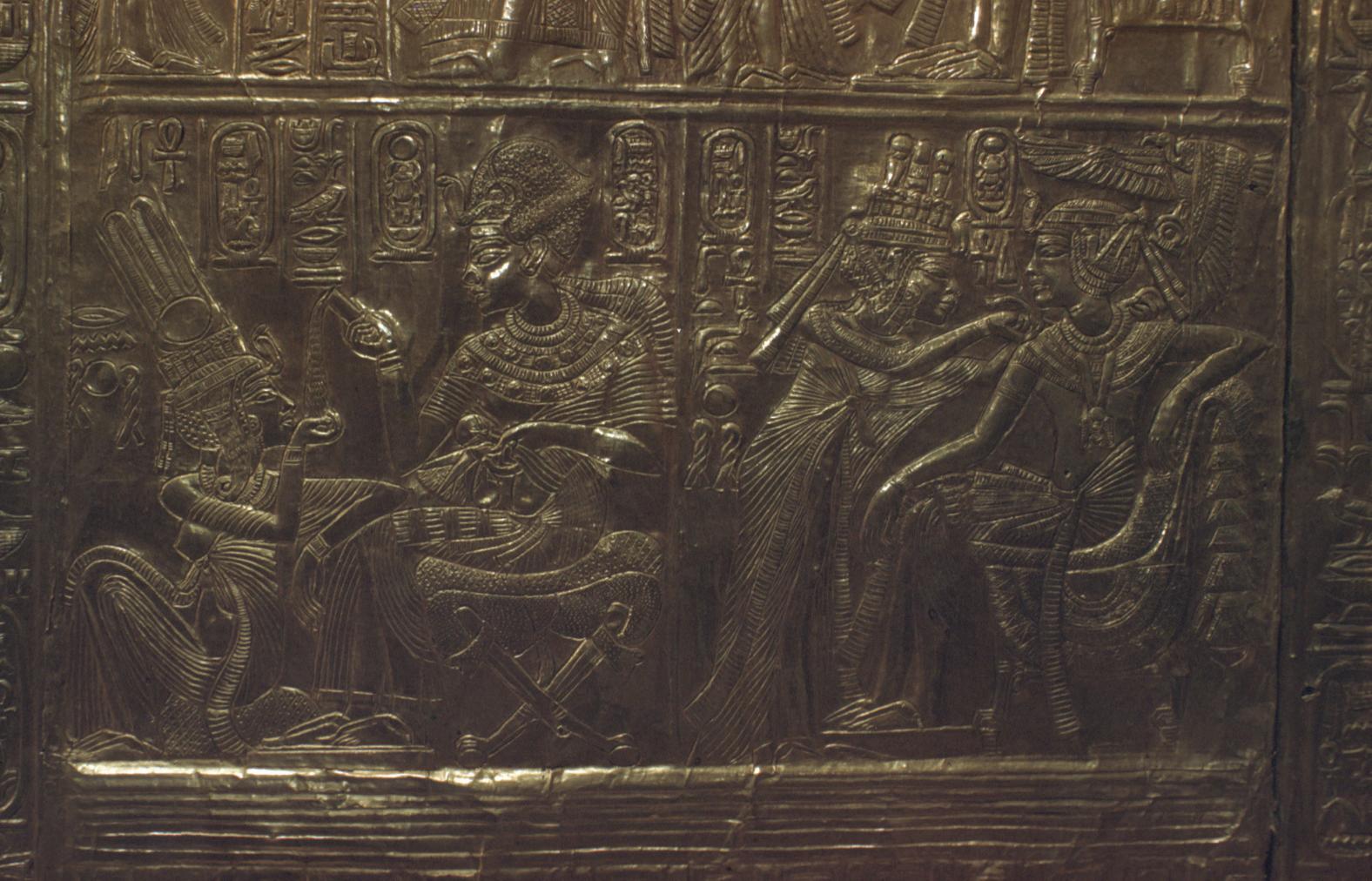
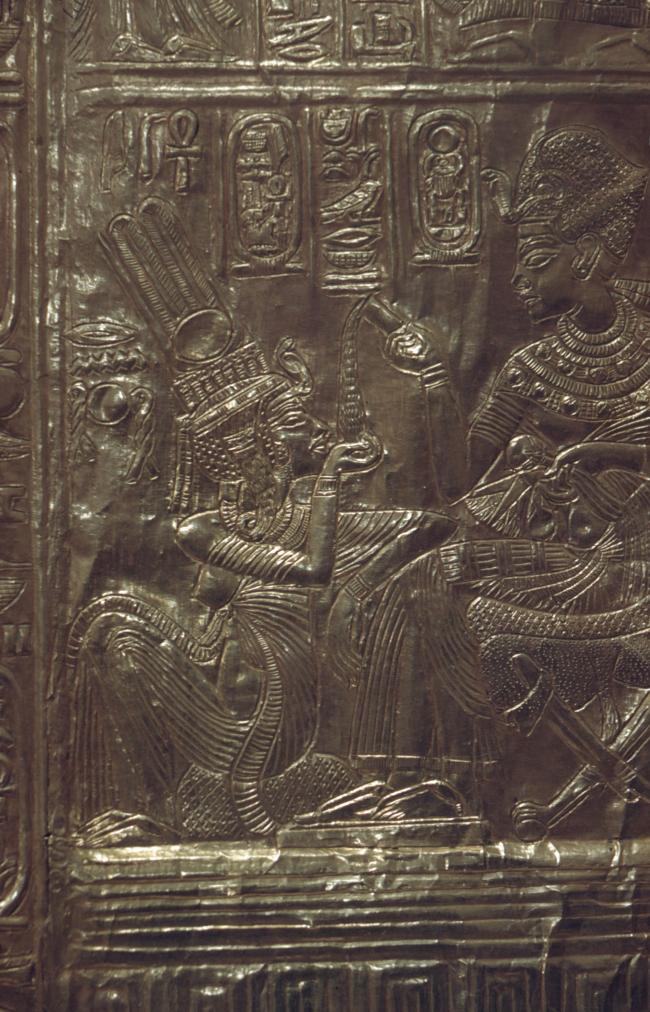
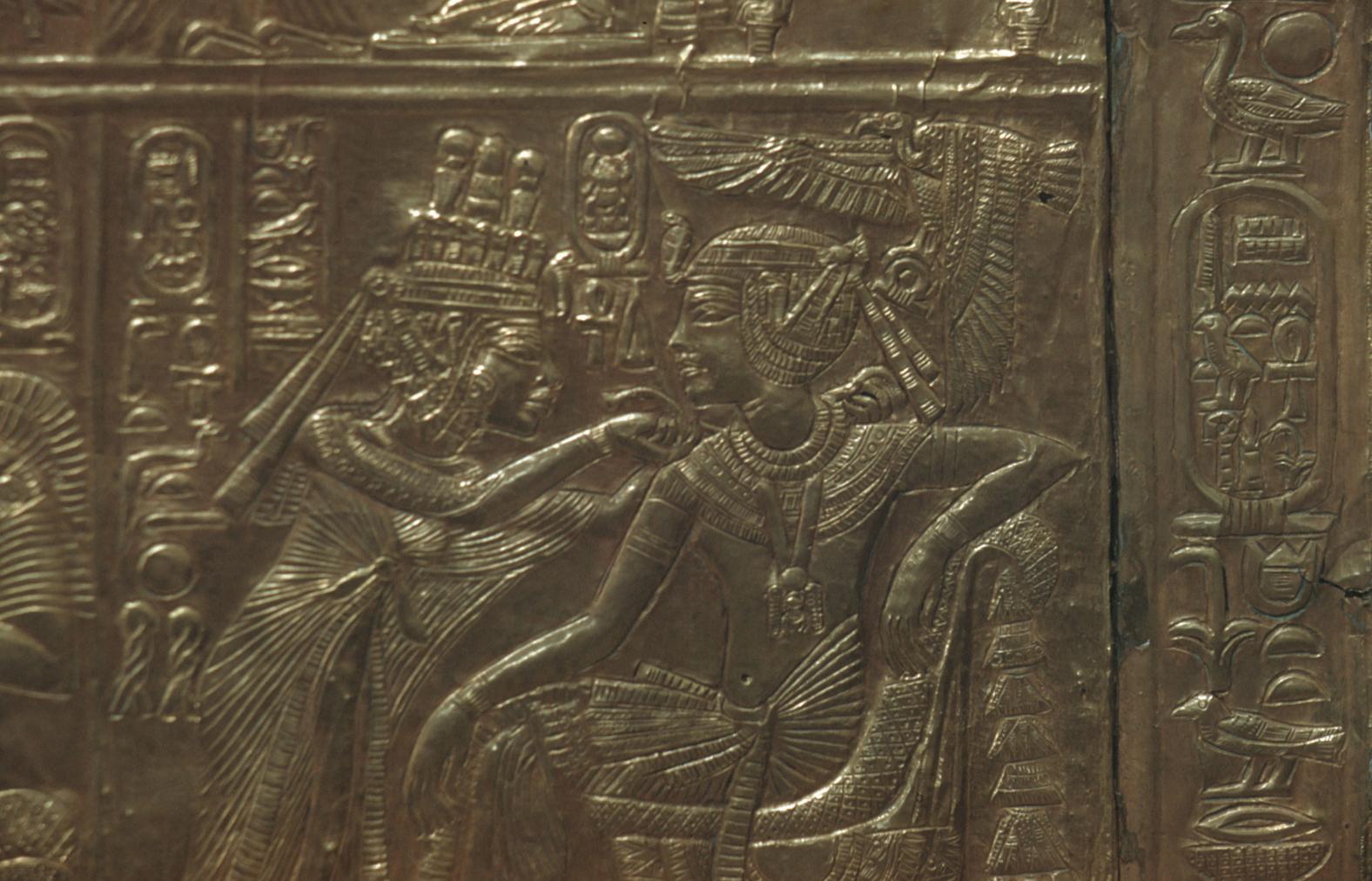
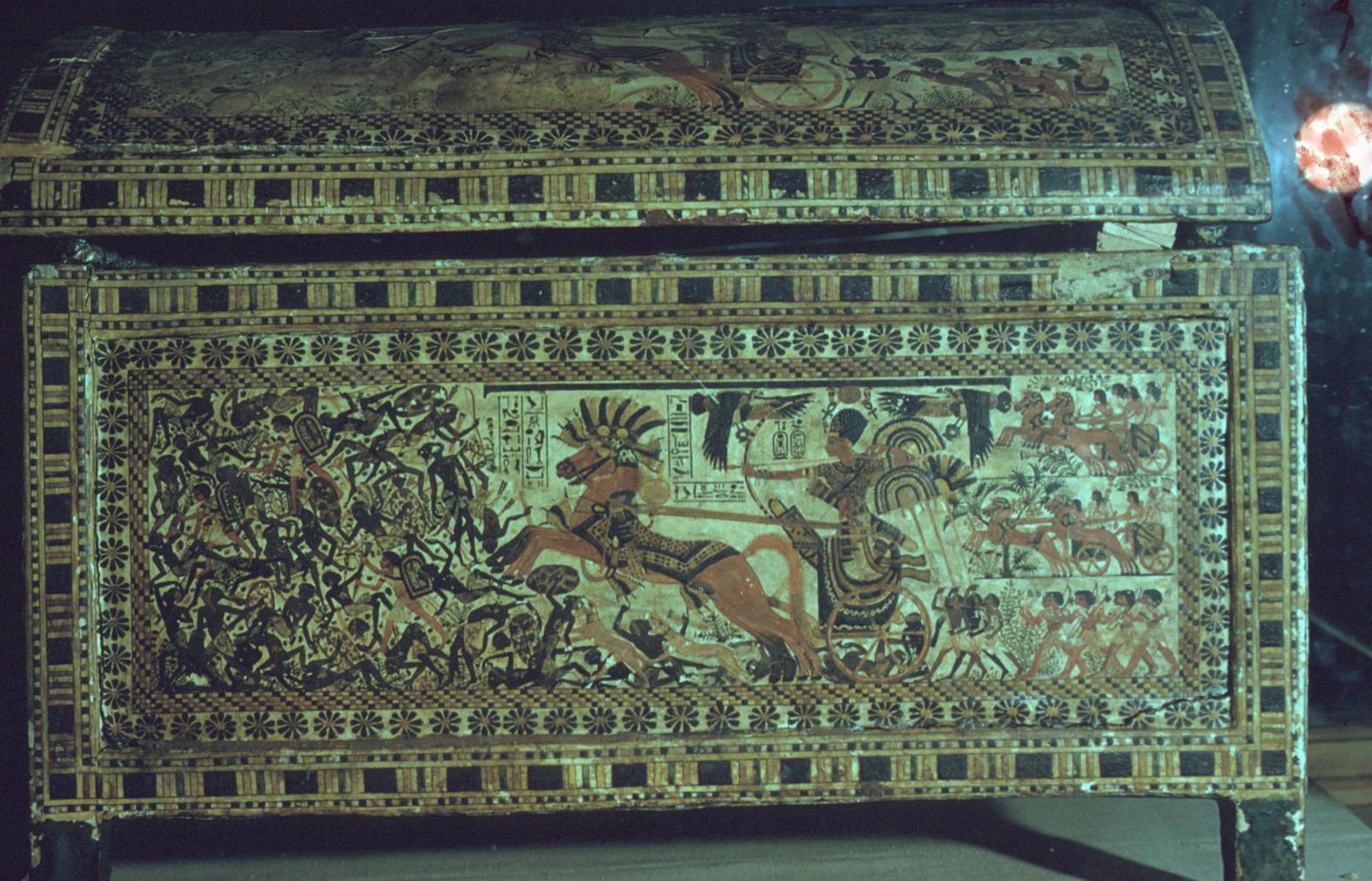
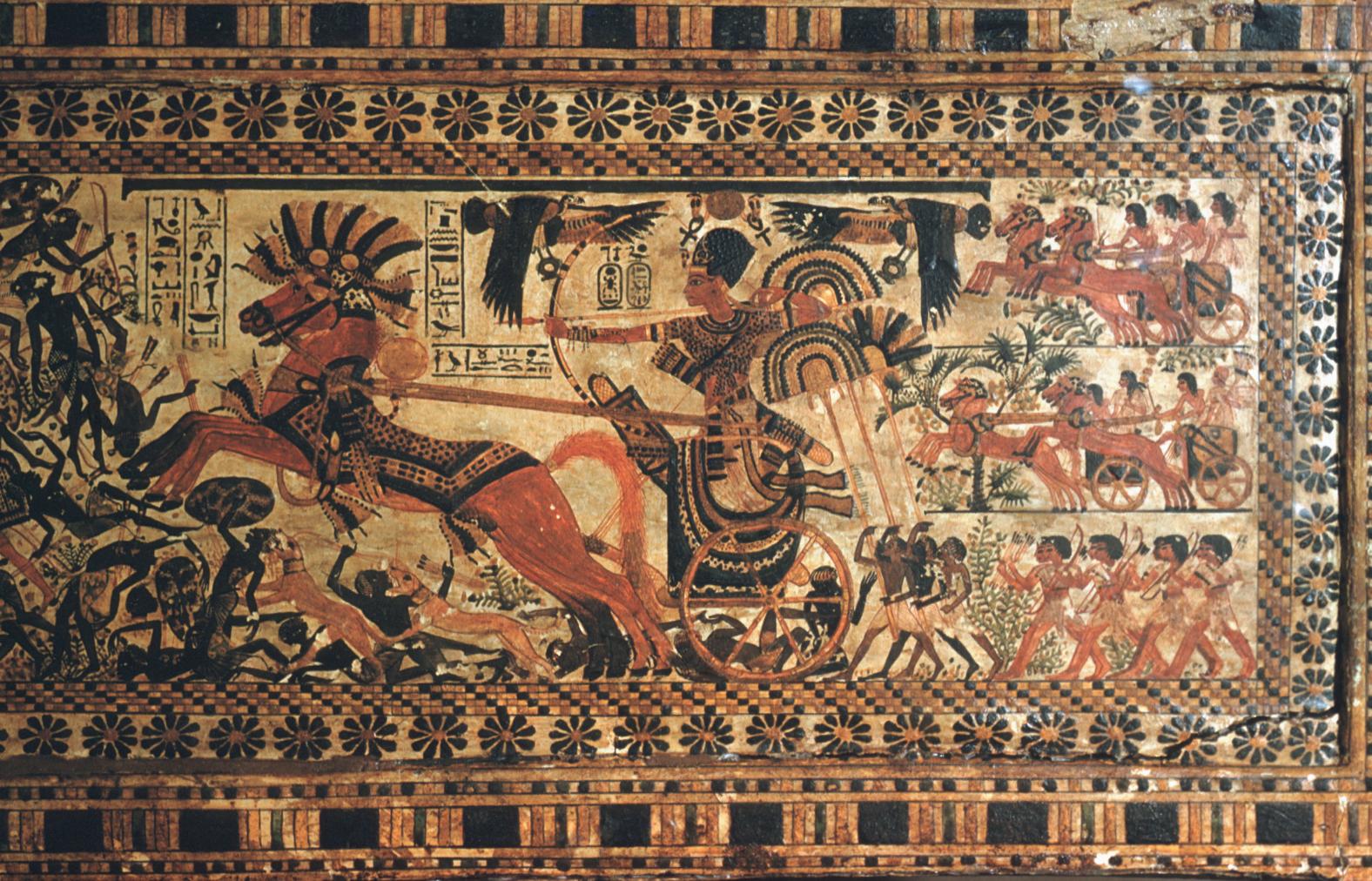
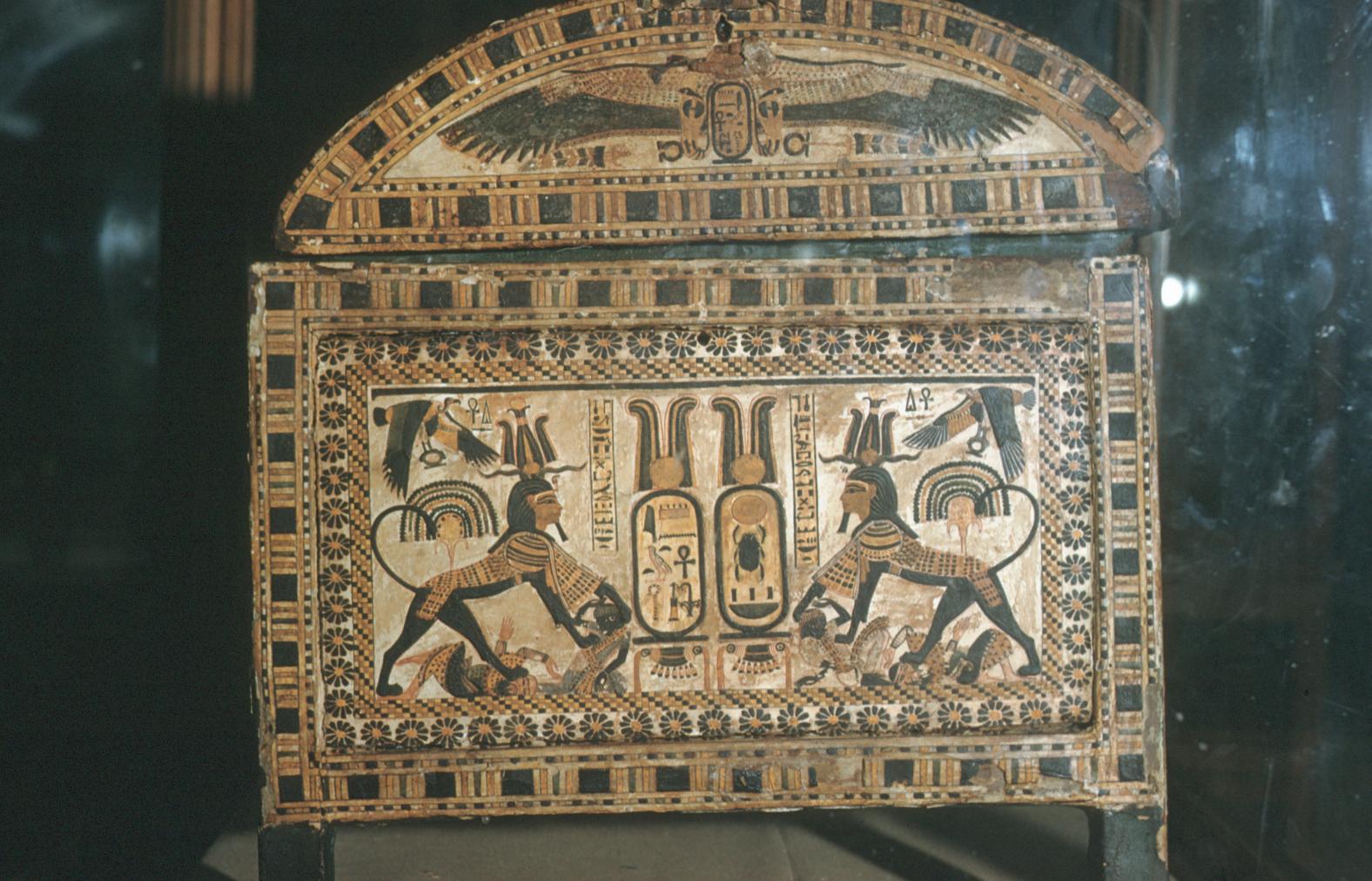
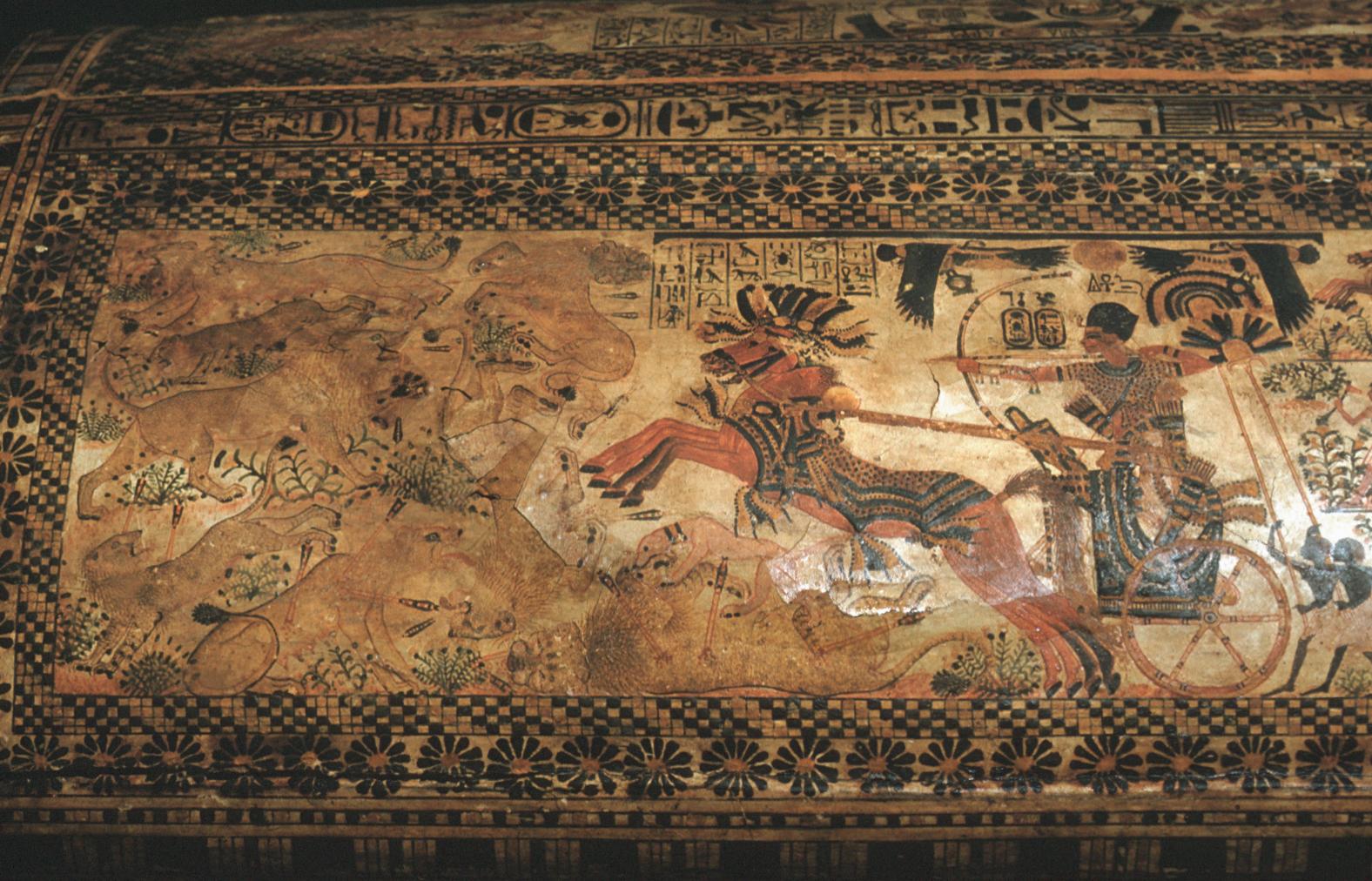
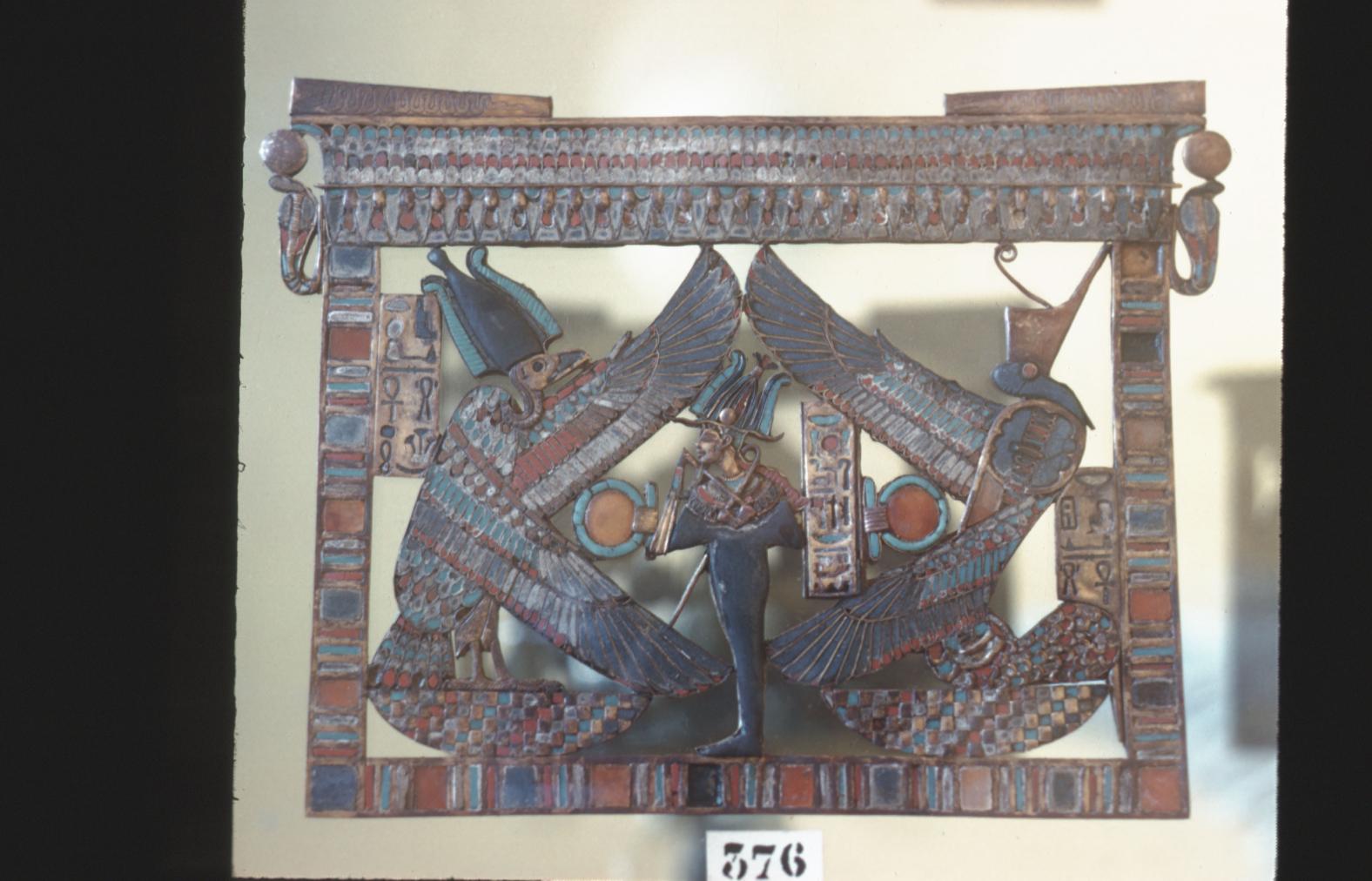
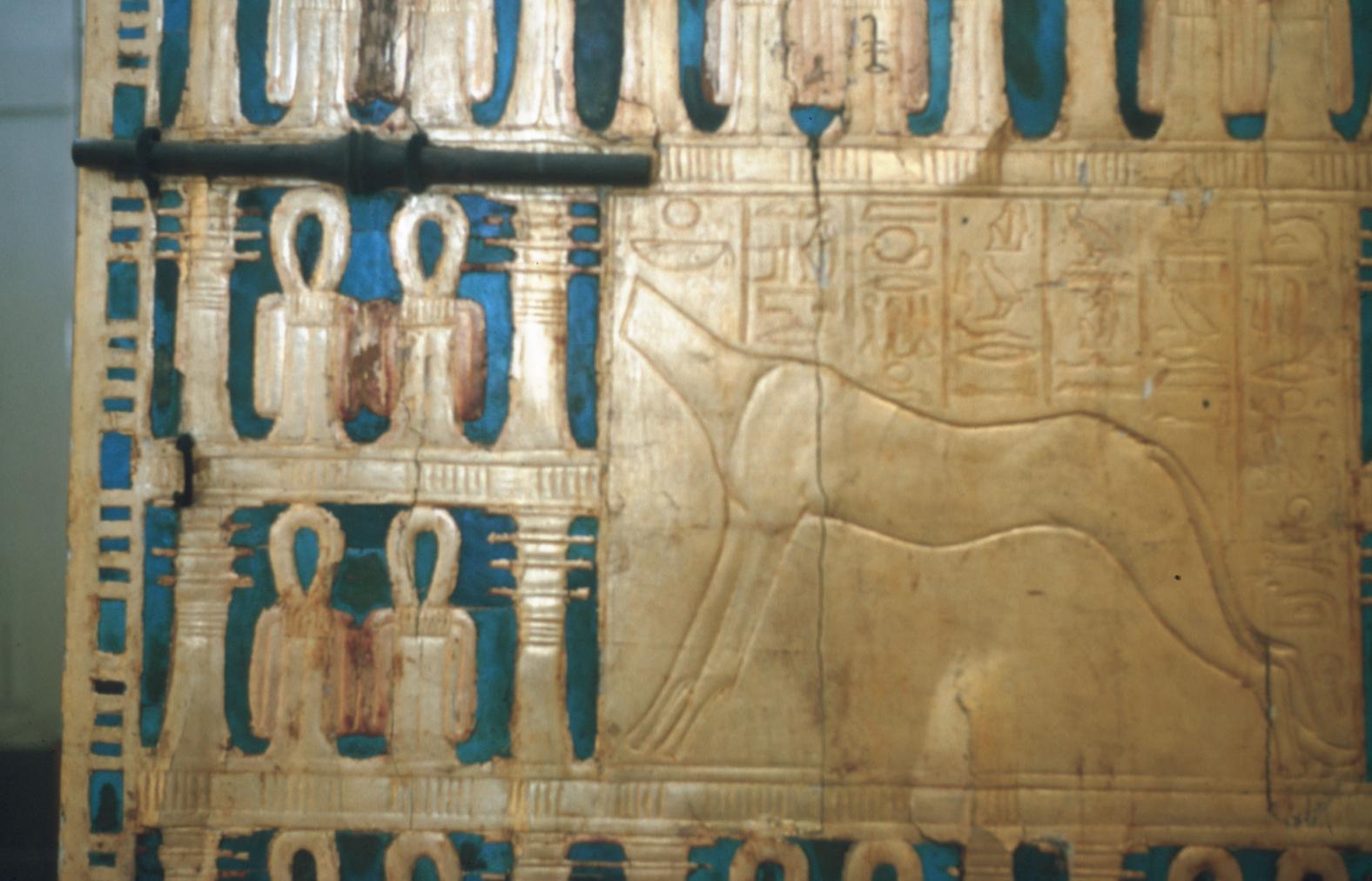
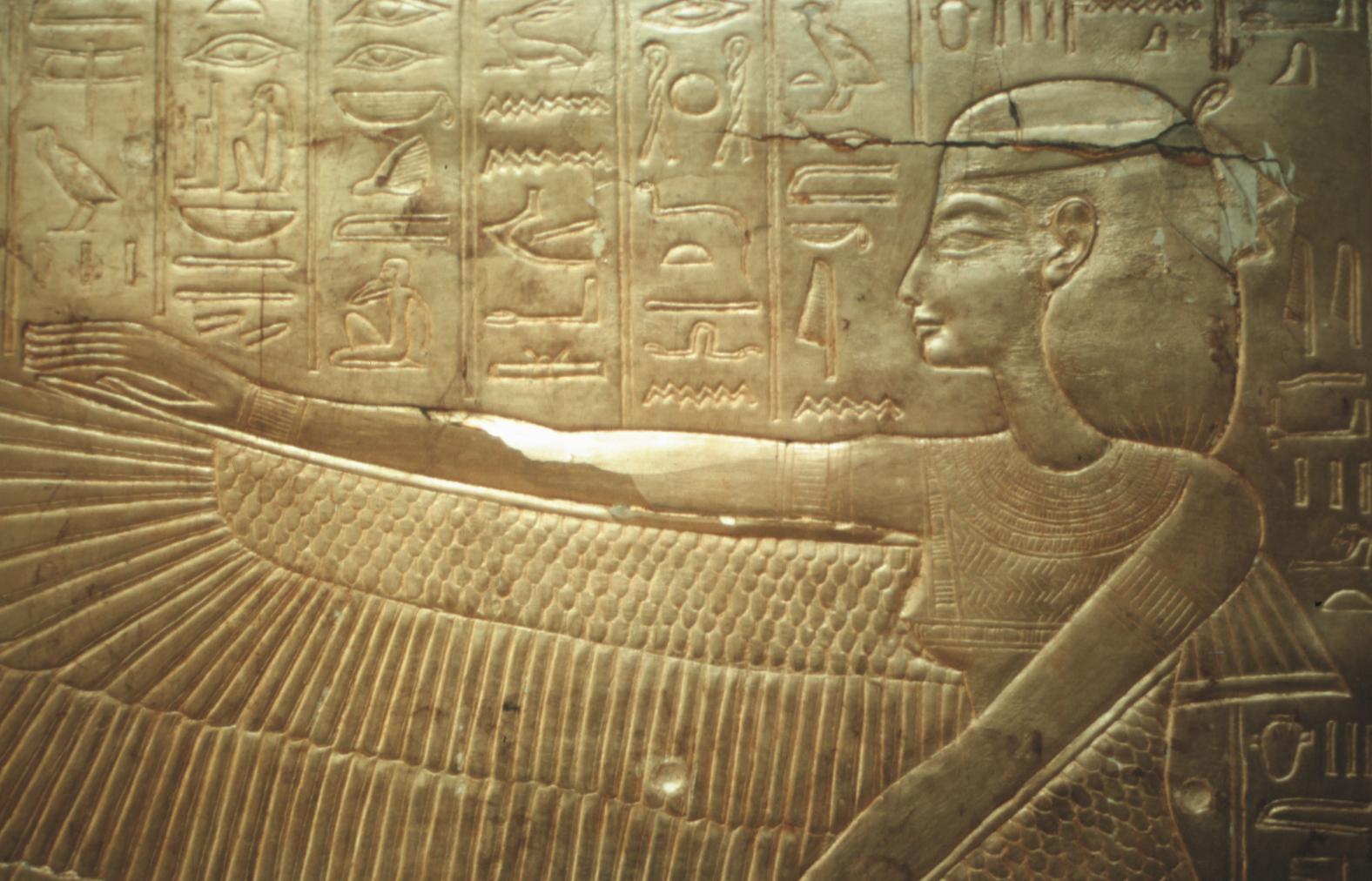
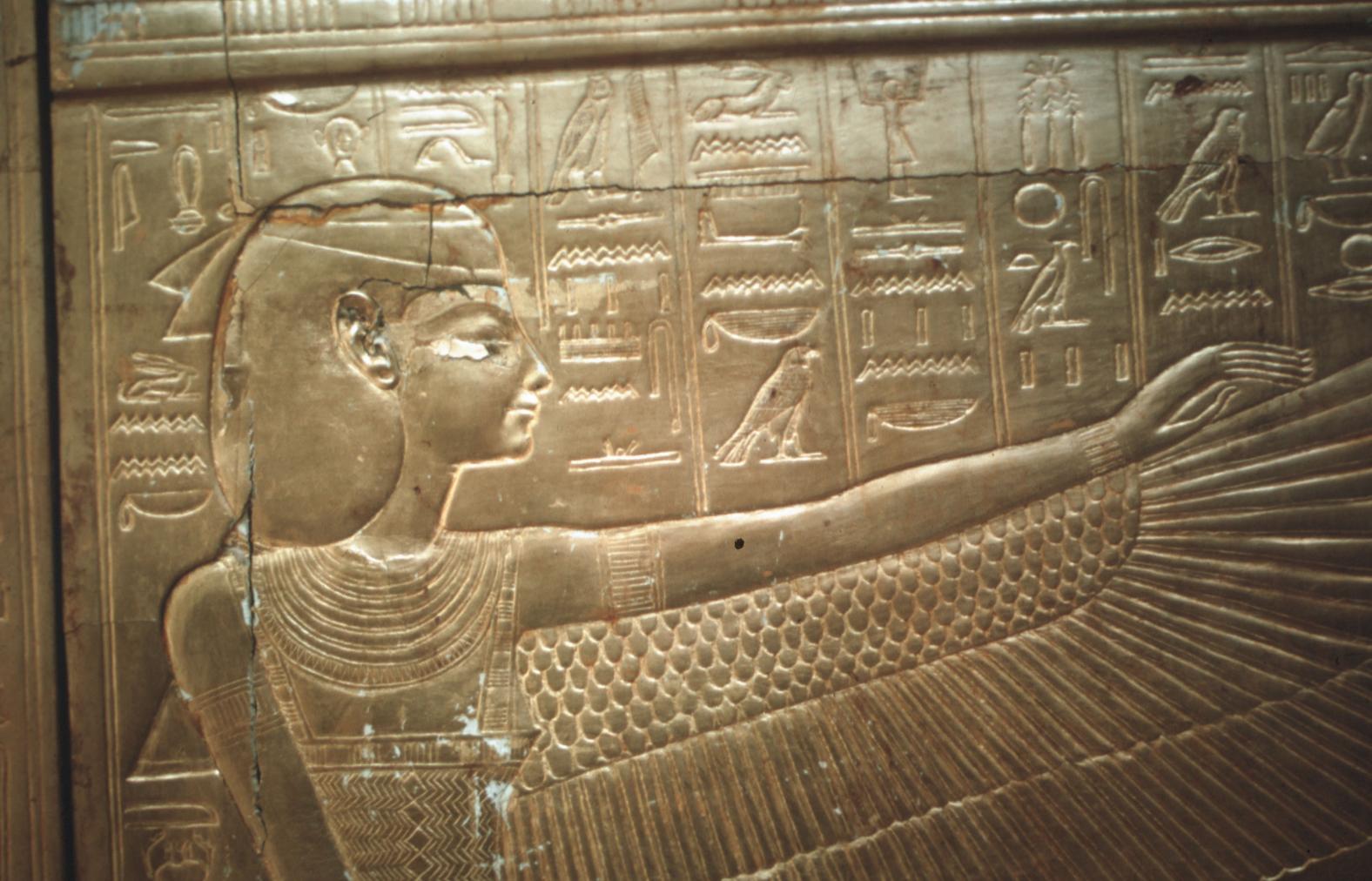
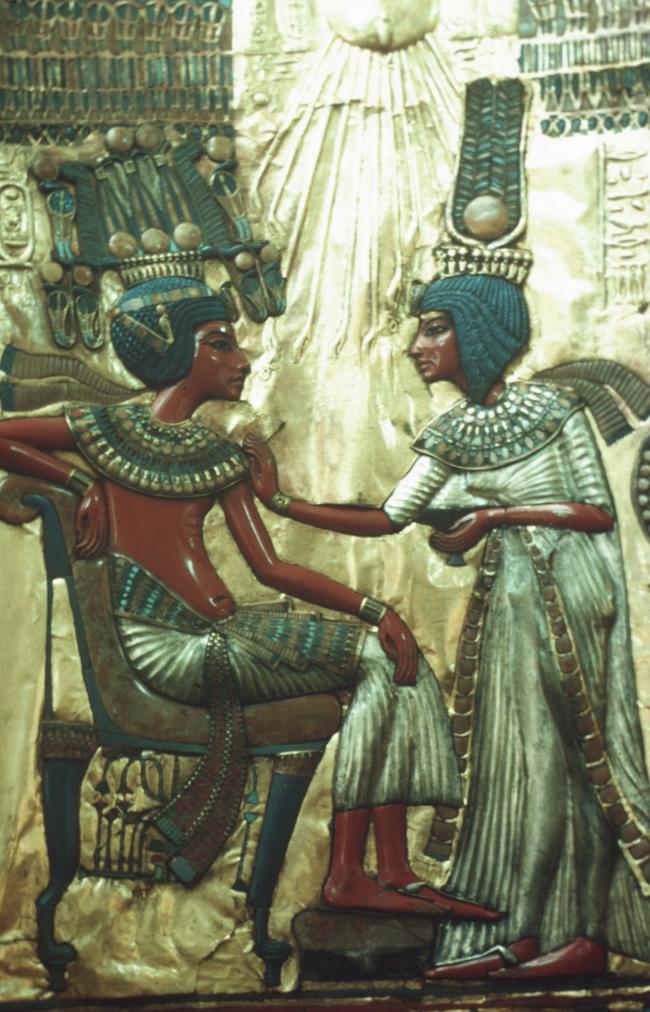
See entire tombThe burial chamber is situated right (north) of chamber I on an east-west axis, and the floor is almost a meter (3 feet) lower than that of the previous chamber. Magical brick niches were cut into each of the four walls of the chamber. The niches were covered by limestone flakes which were then plastered and painted. The chamber held three hundred objects in addition to four shrines inside of which were the sarcophagus, three coffins, burial mask and mummy of the king. Only this chamber was decorated. The background for the scenes was a golden yellow; the figures are in a non-traditional style. The human figures on every wall except the front (south) are laid out using the twenty-square grid during the Amarna Period. The south wall more closely fits the eighteen-square grid pattern of traditional art.
Chamber plan:
RectangularRelationship to main tomb axis:
ParallelChamber layout:
Flat floor, no pillarsFloor:
One levelCeiling:
Flat
Porter and Moss designation:
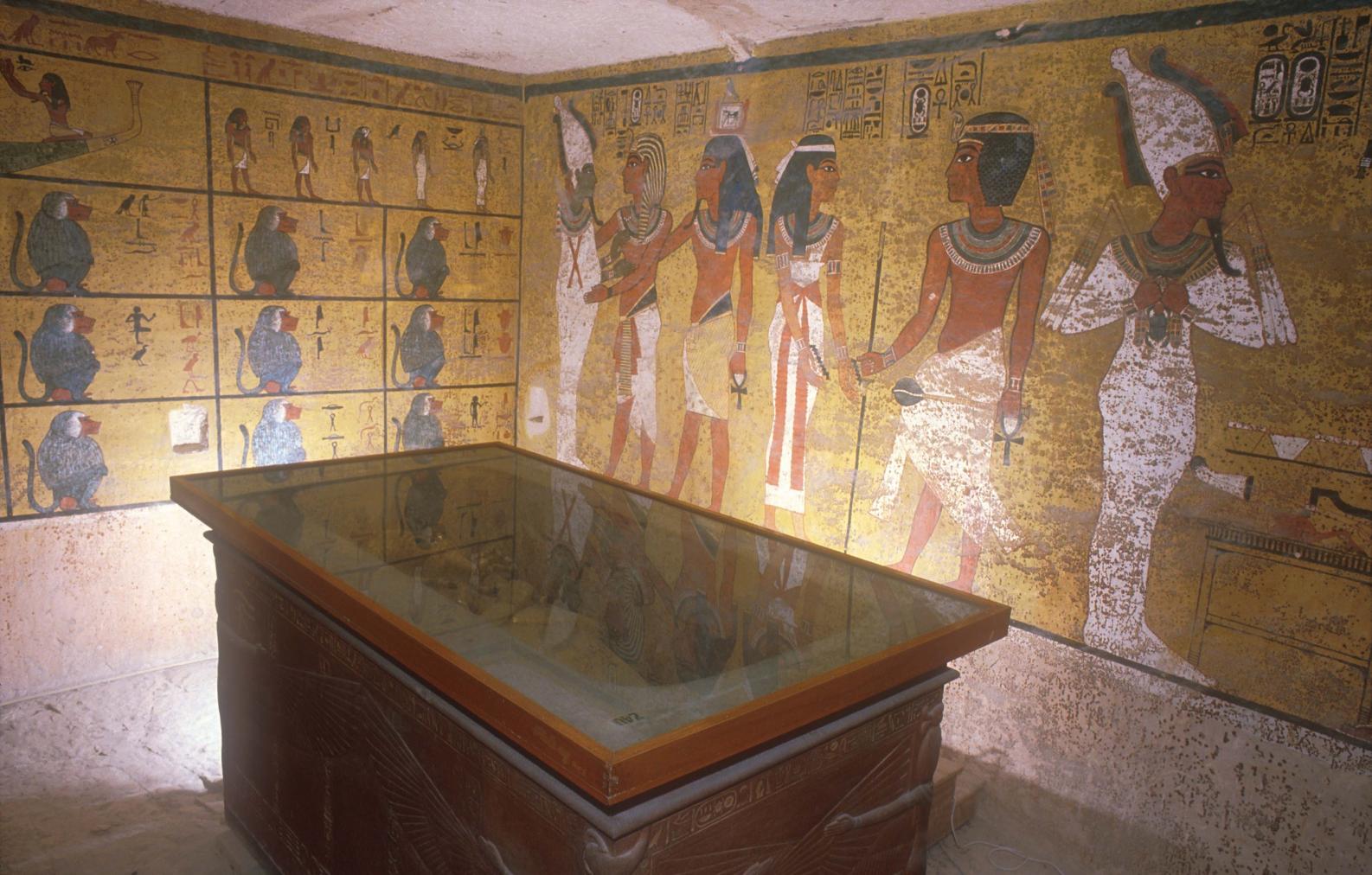
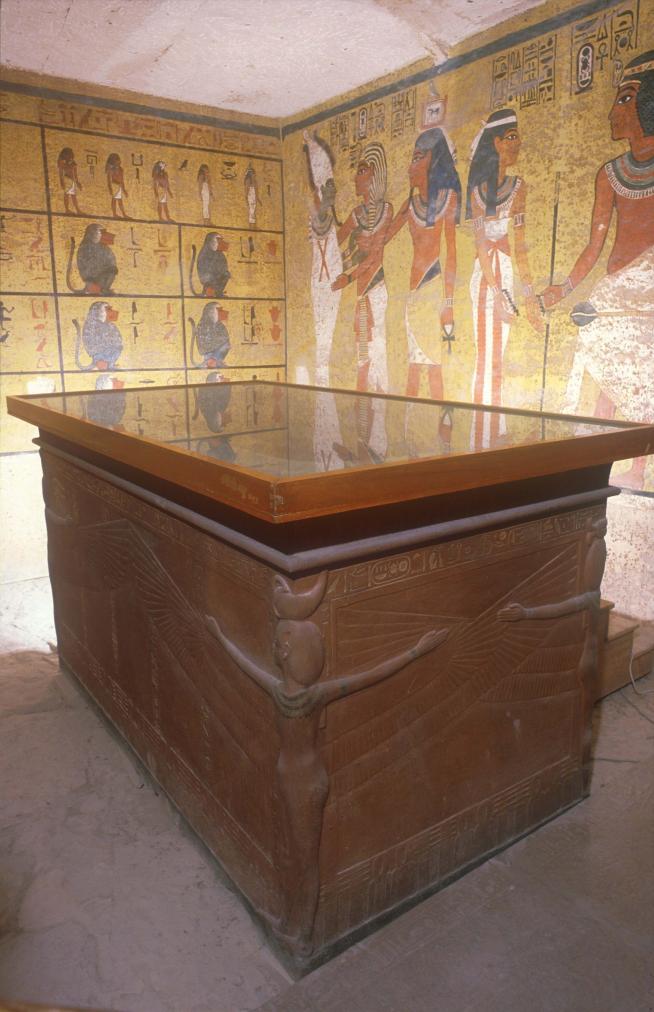
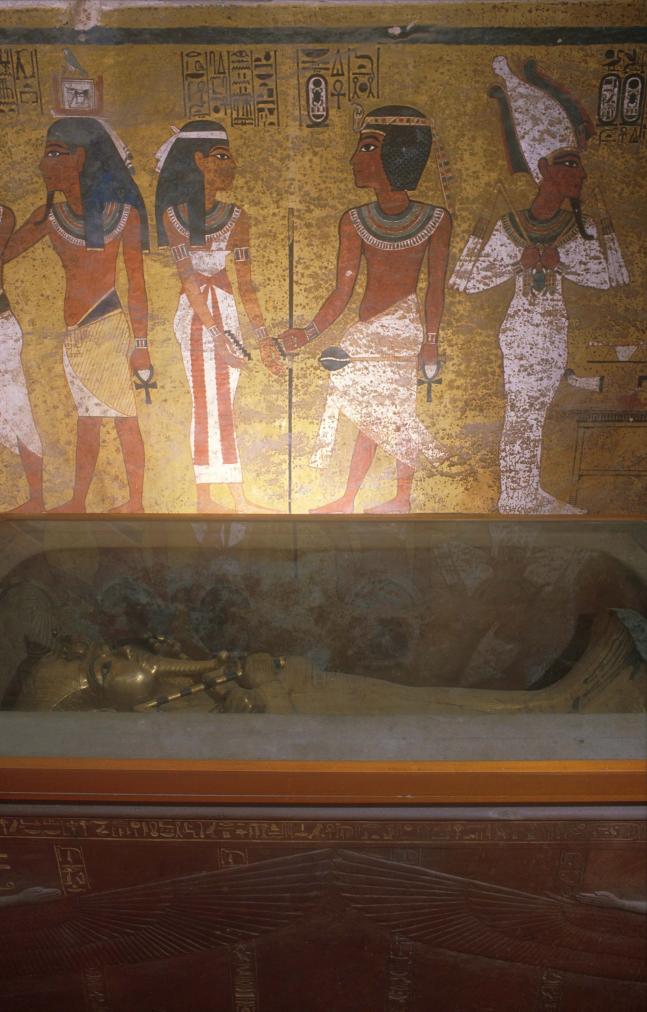
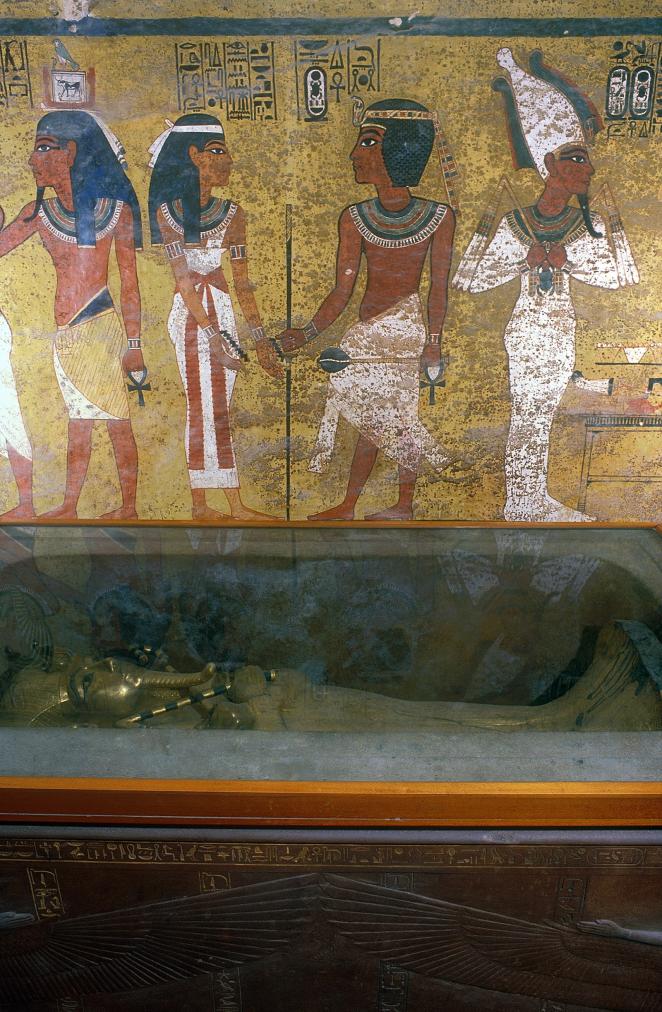
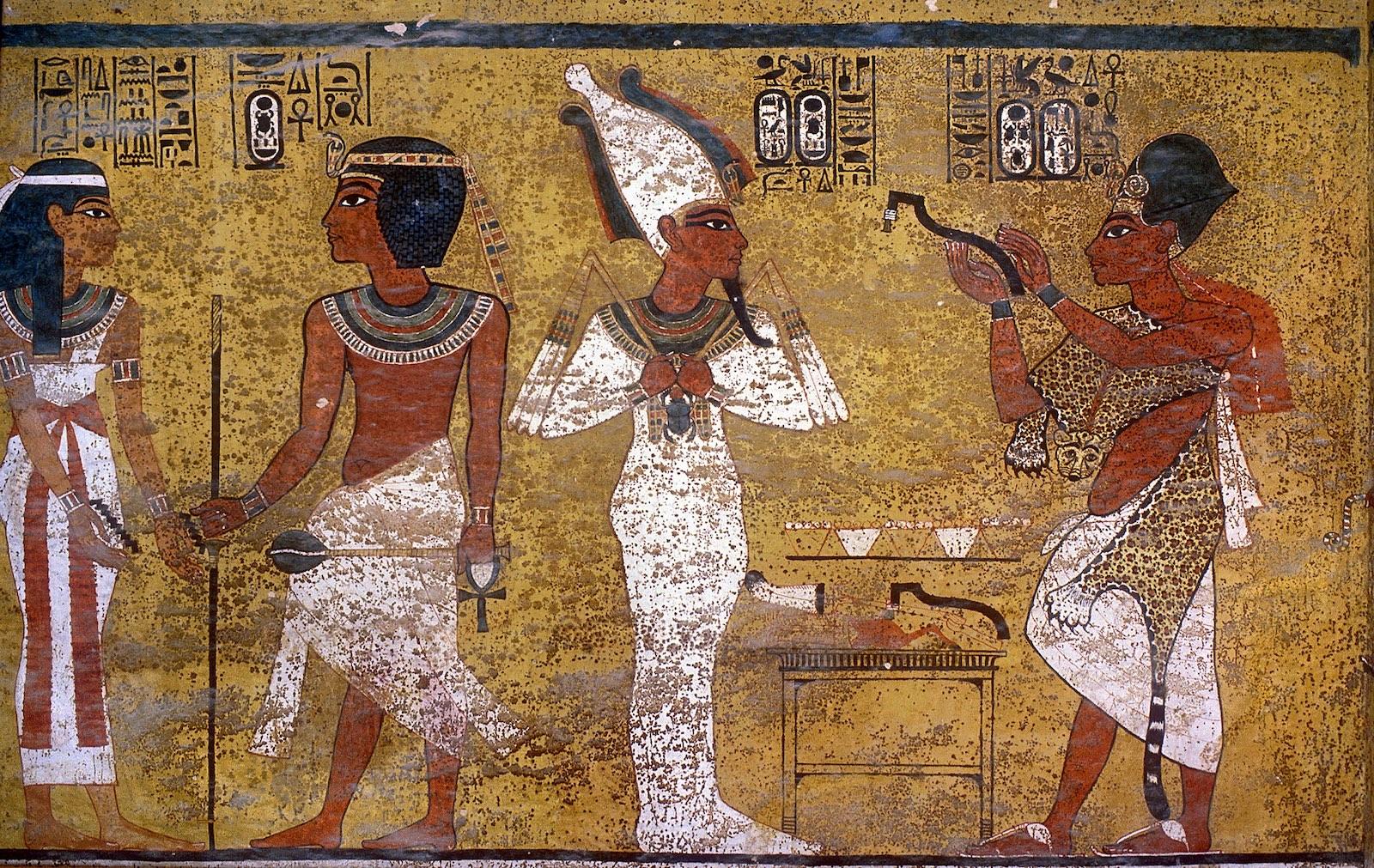









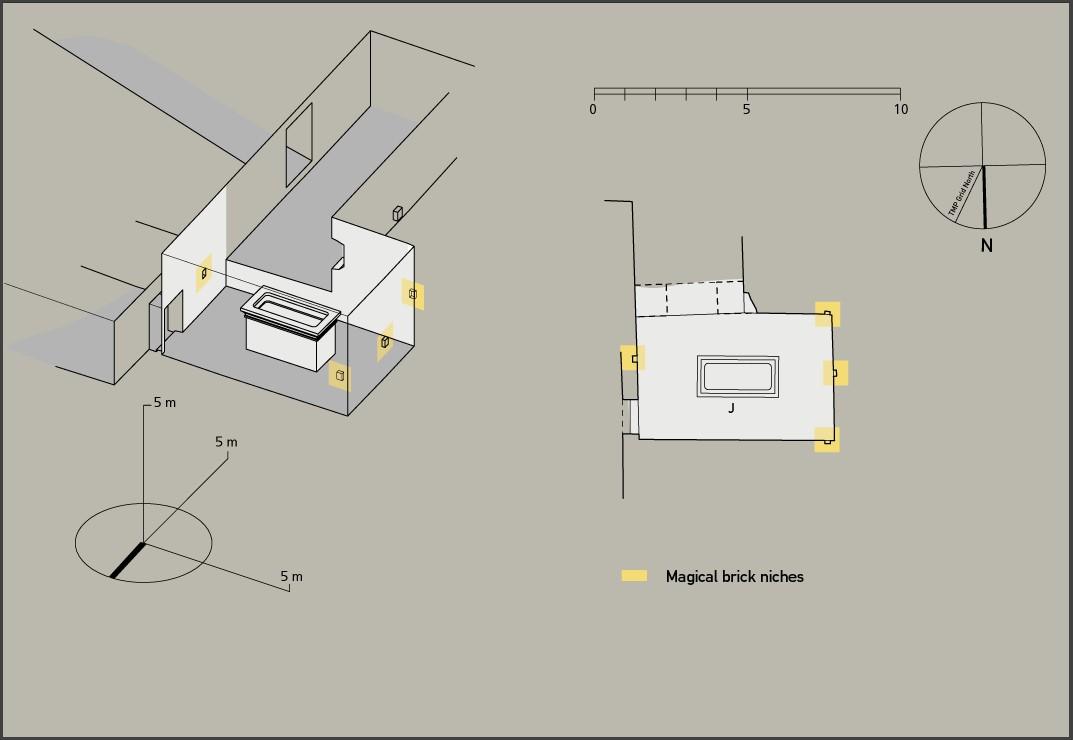


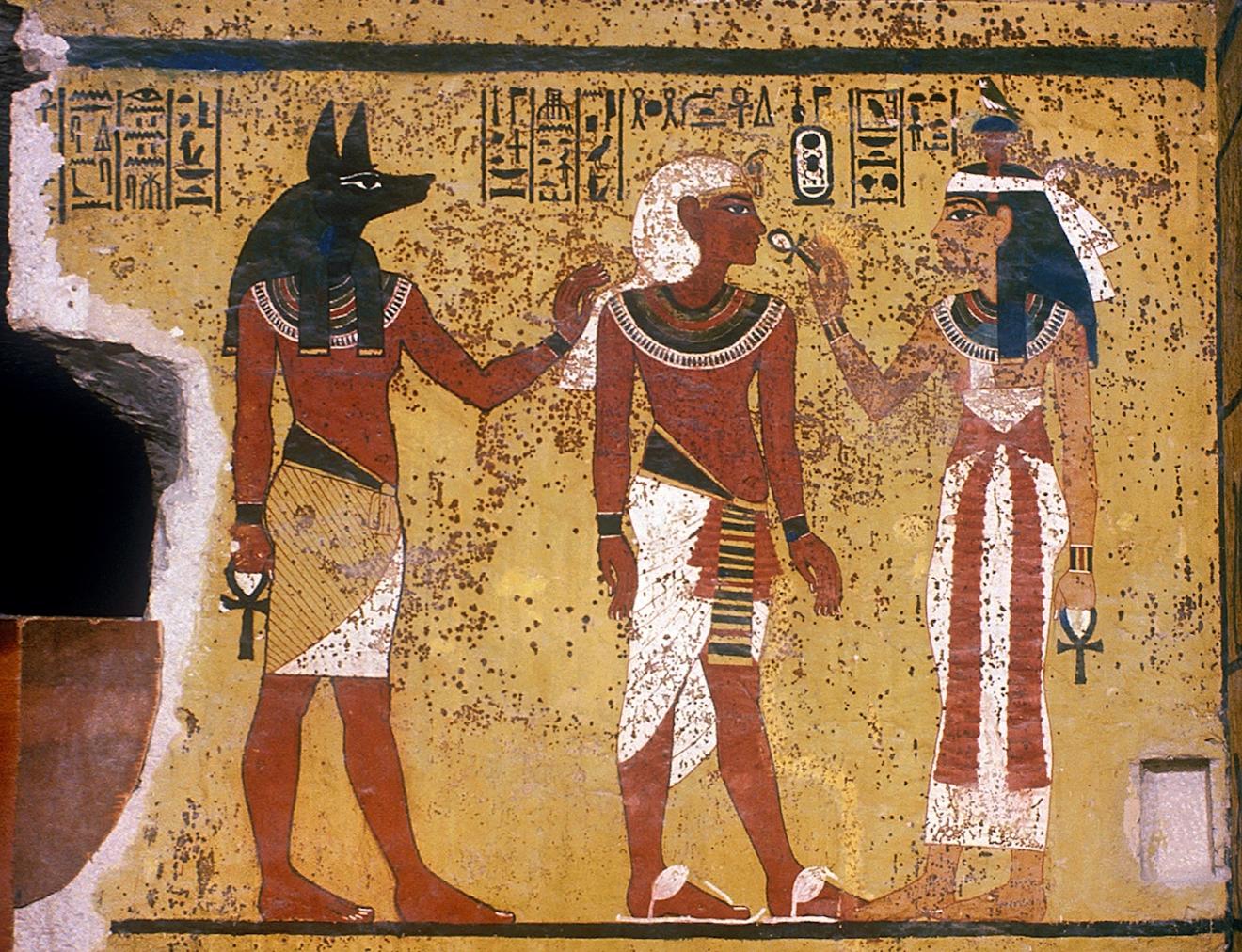





















Gate J
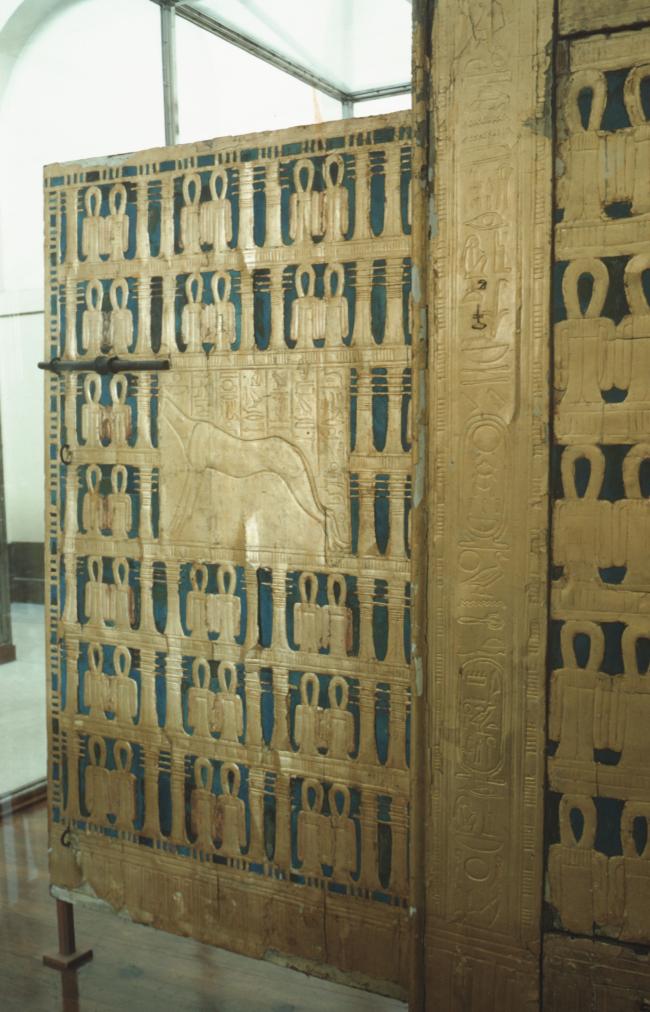
See entire tombA partition wall of rubble covered with plaster was constructed at the right (north) end of chamber I to close off the large opening into the burial chamber J. A gate, with wood beams laid on top as the lintel, was made in the center of this wall, and after the burial, it was blocked with rubble and covered with plaster bearing impressions of the necropolis seal. The excavators first entered the burial chamber through a resealed hole made by tomb robbers in the lower right of the gate. Eventually it was necessary for Carter to remove the blocking and dismantle the partition wall in order to remove the larger burial equipment. For this reason, it was impossible for the Theban Mapping Project to obtain measurements of this gate.
Porter and Moss designation:
Gate Ja
See entire tombThis low doorway was never blocked. There is a step down from burial chamber J to side chamber Ja in the gate.
Porter and Moss designation:
Side chamber Ja
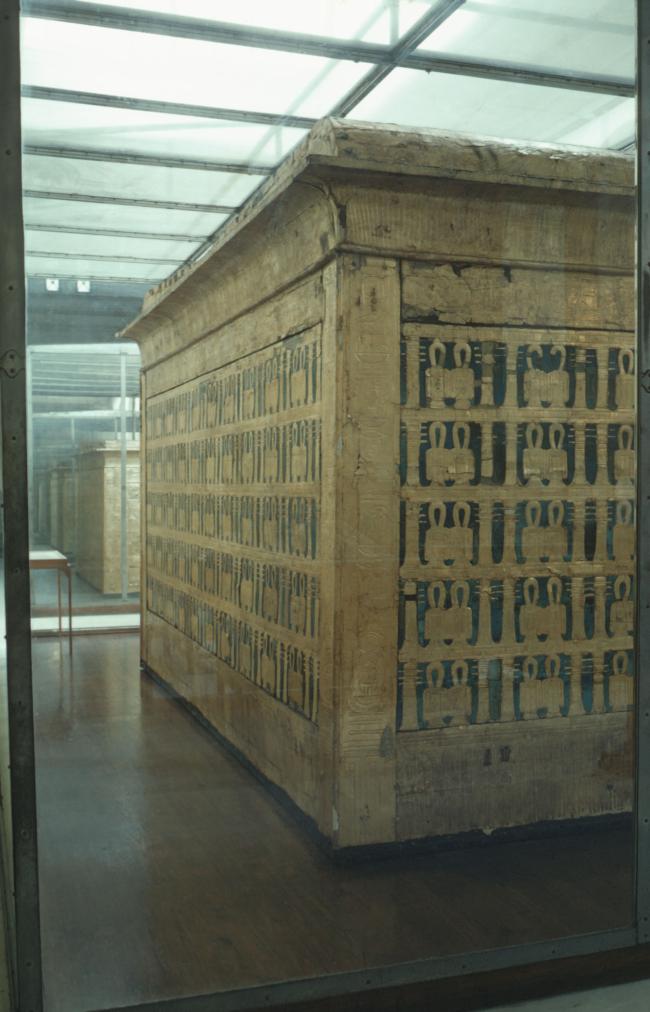
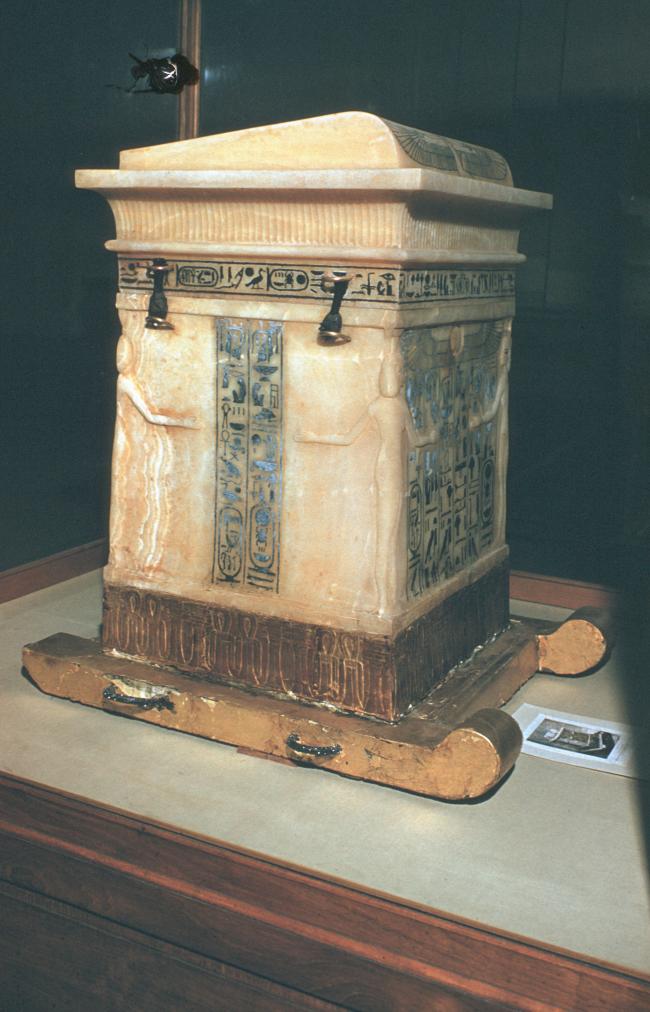
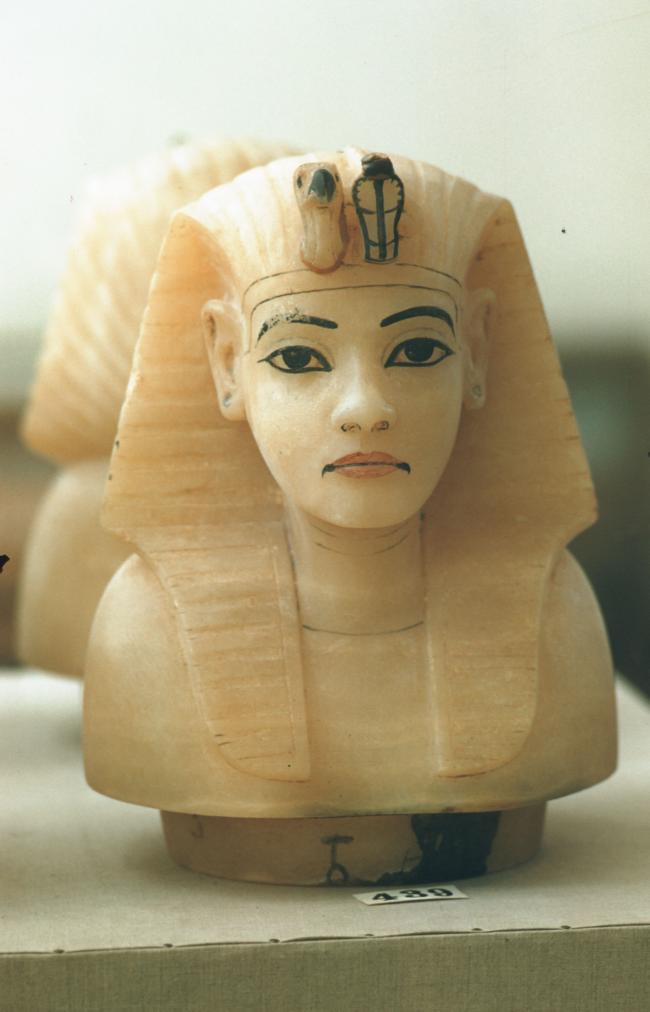
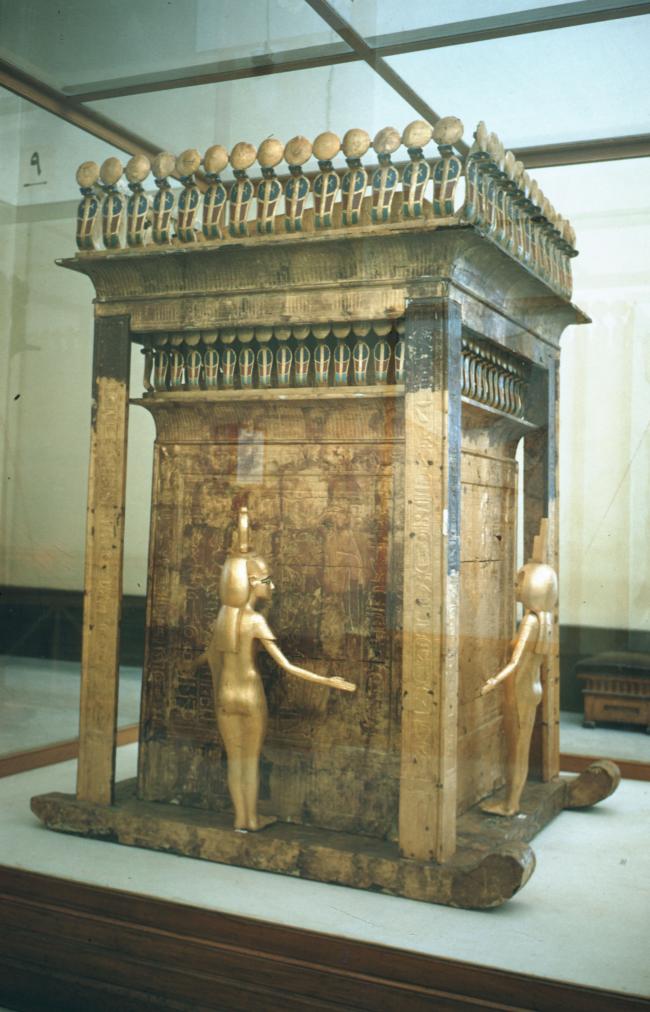
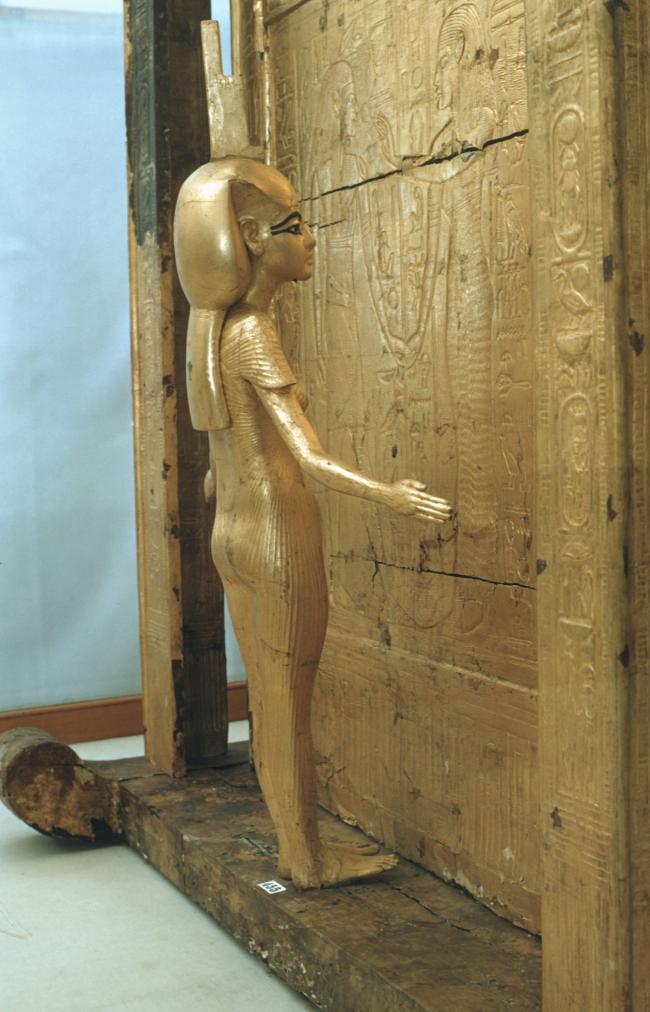
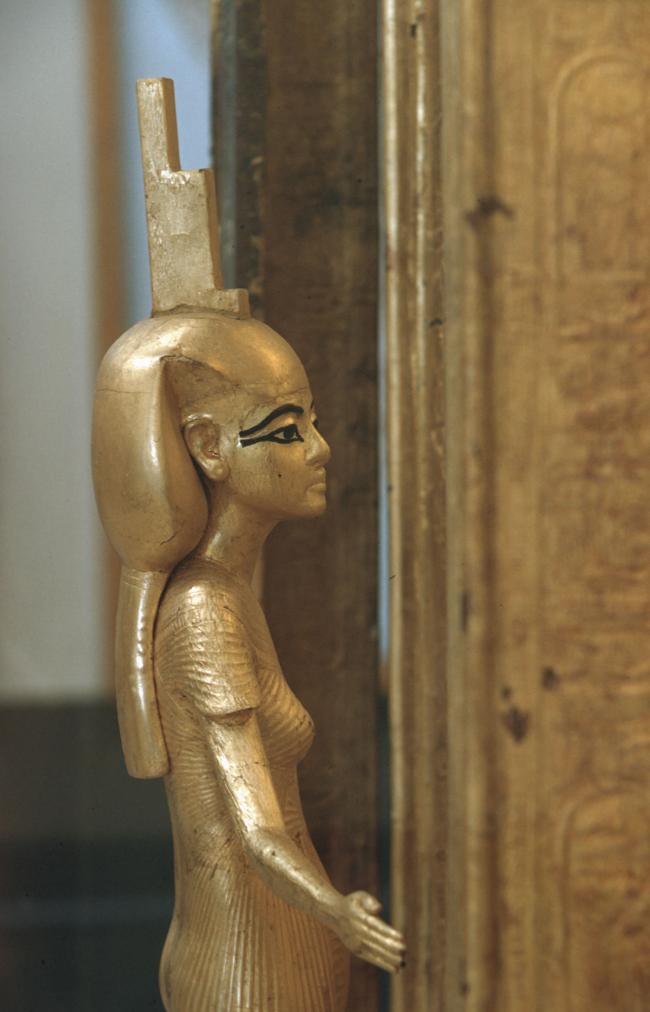
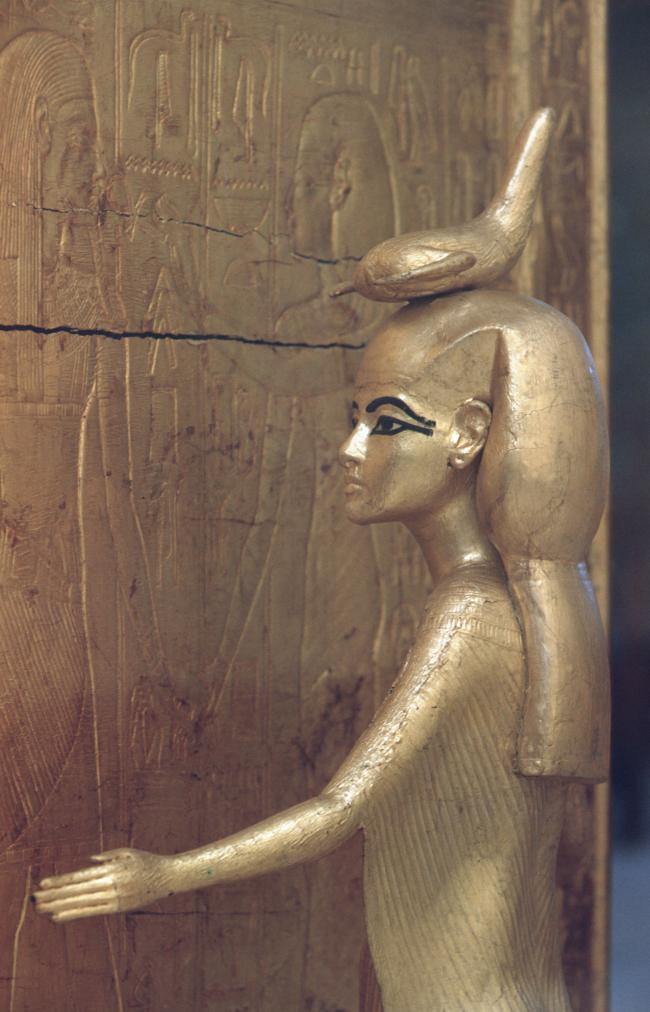
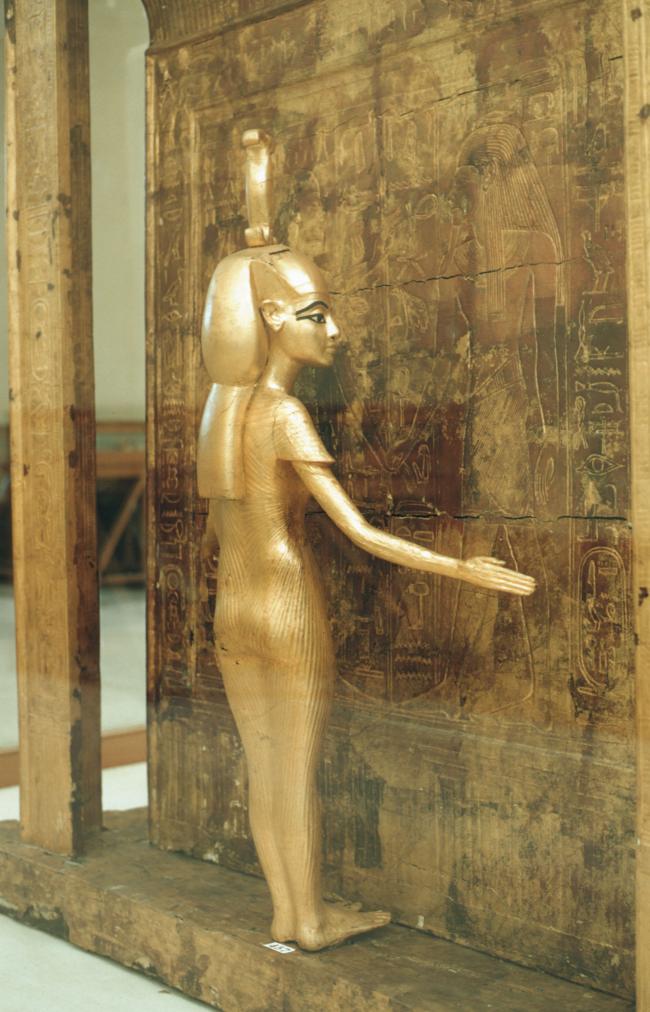
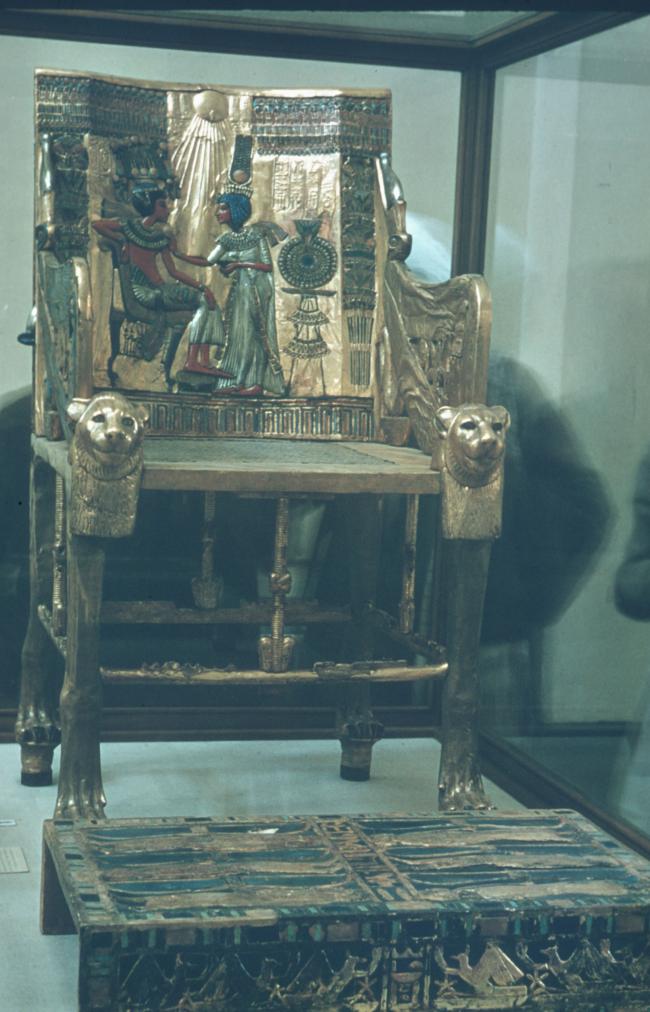
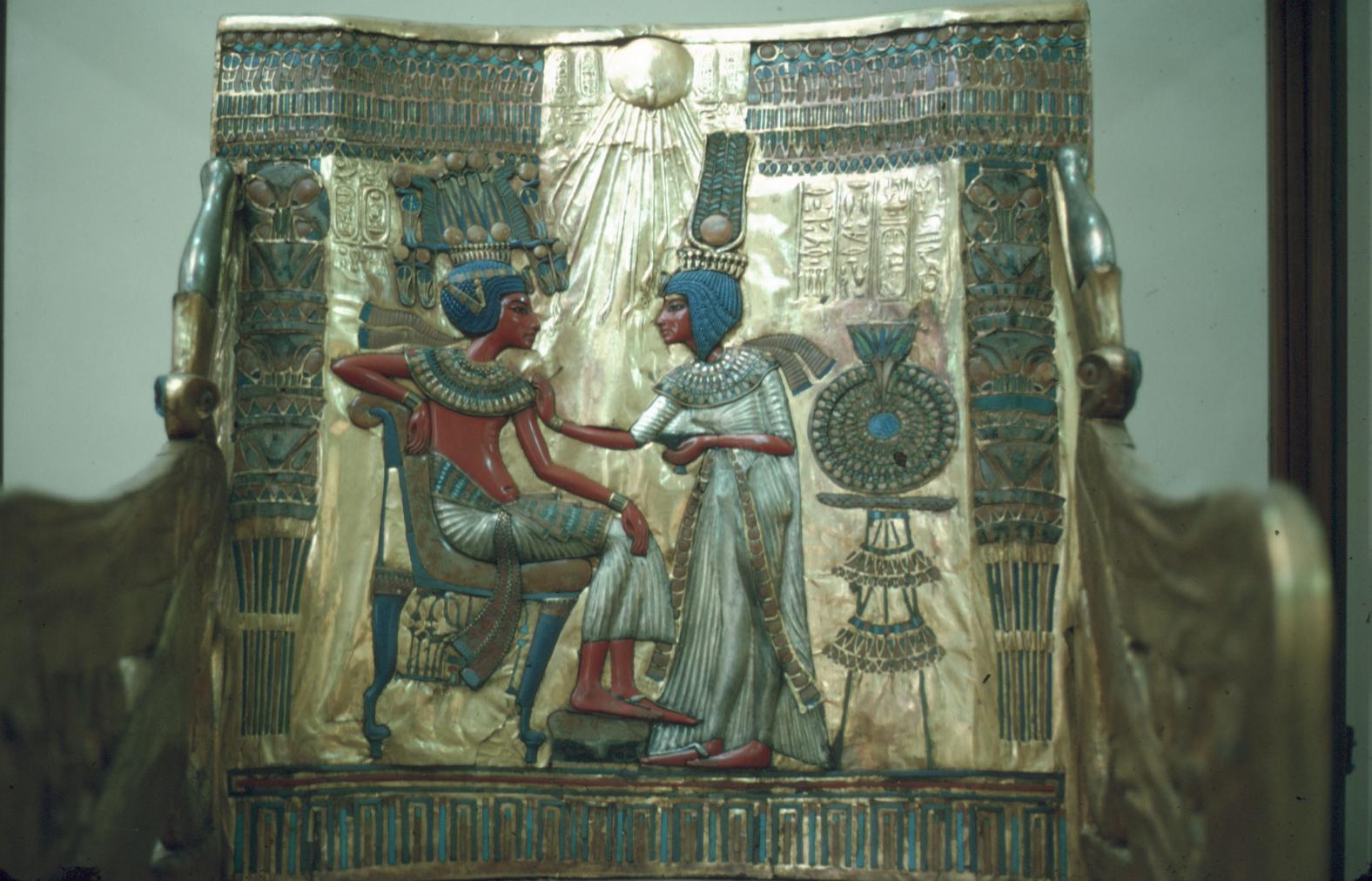
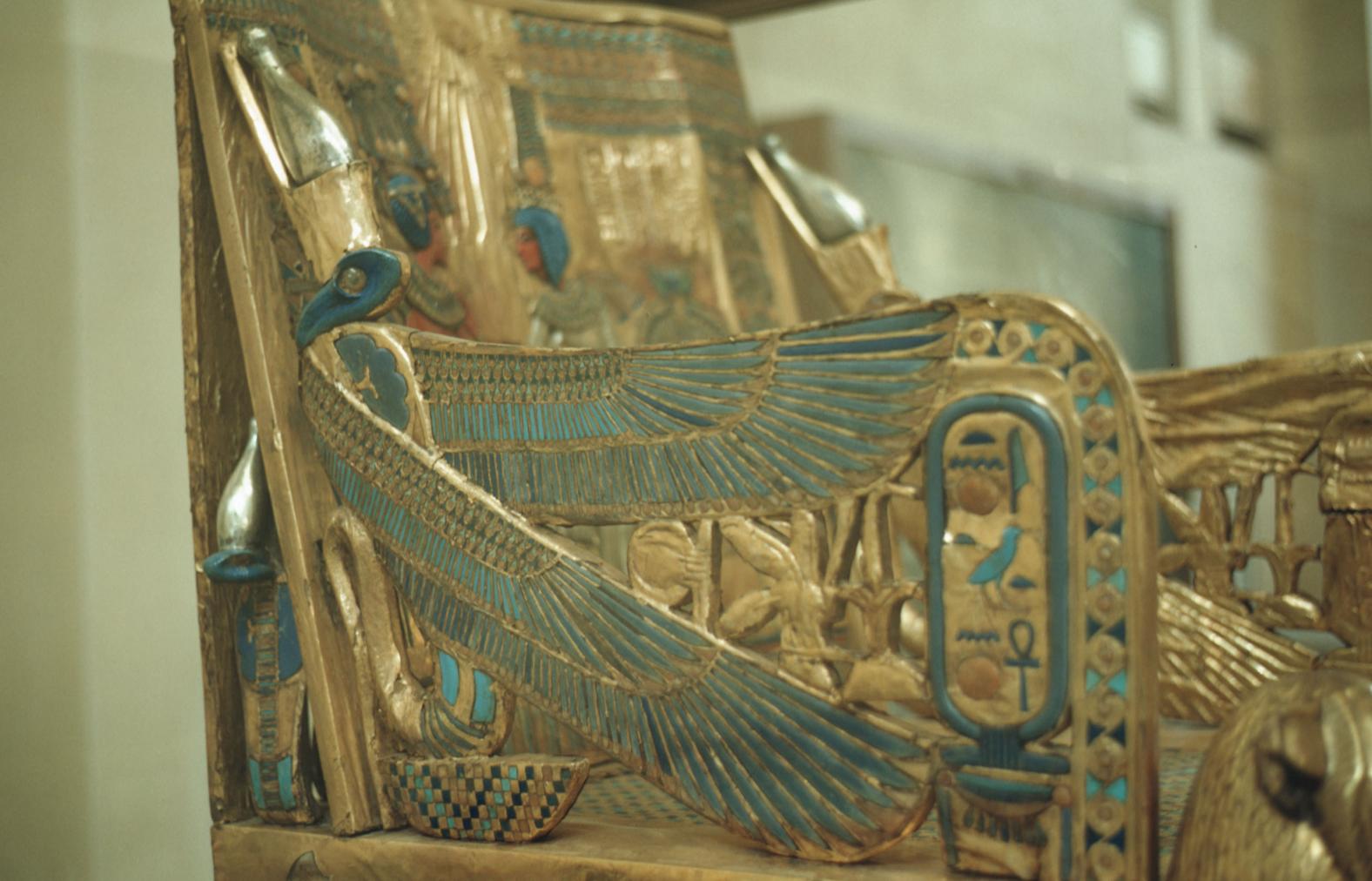
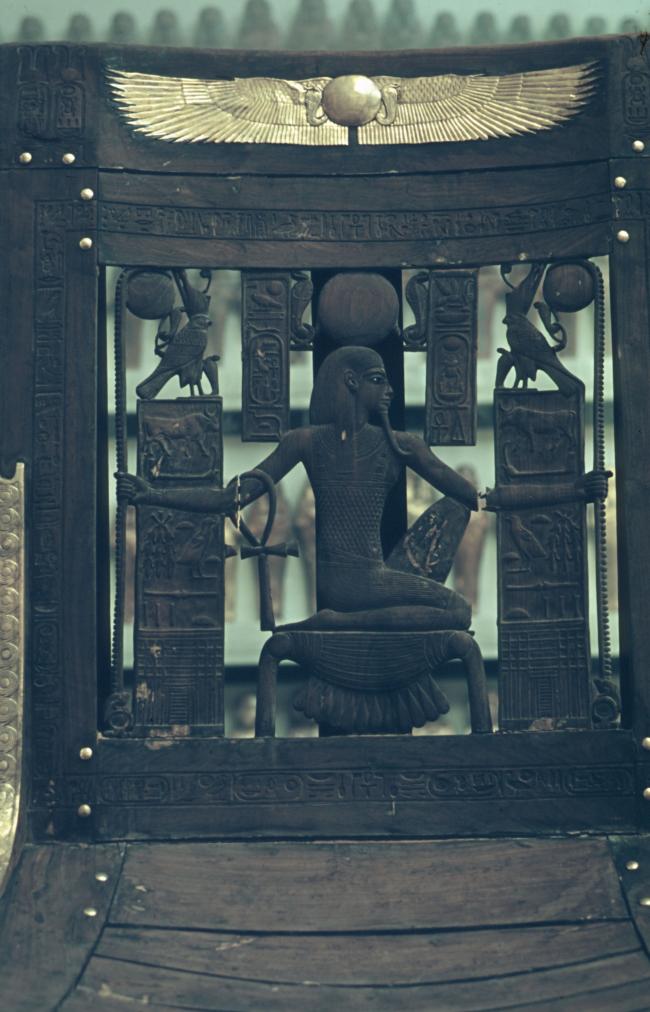
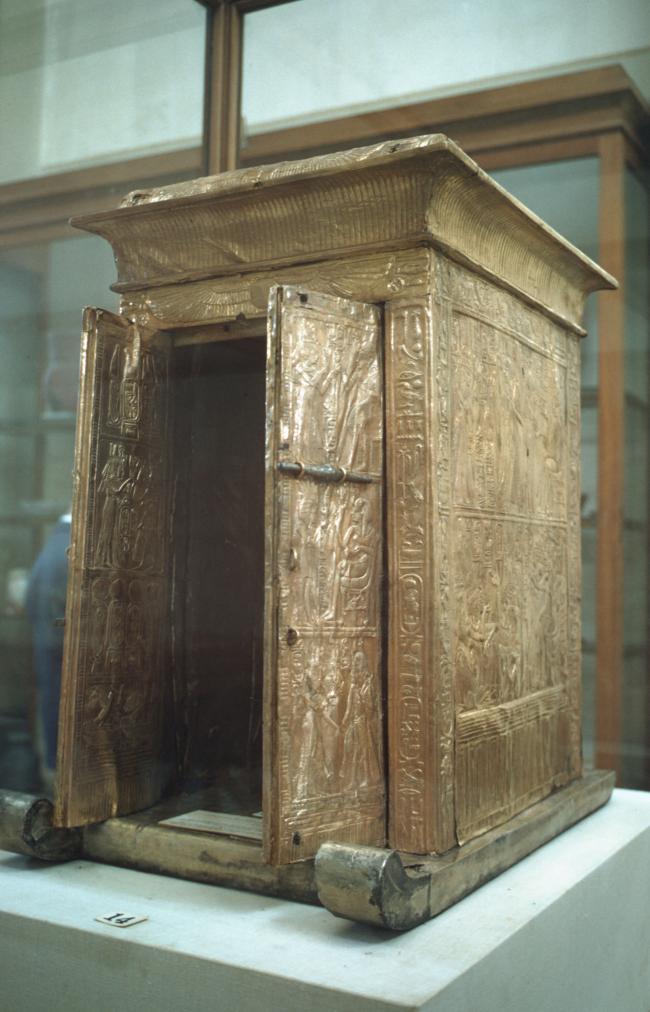
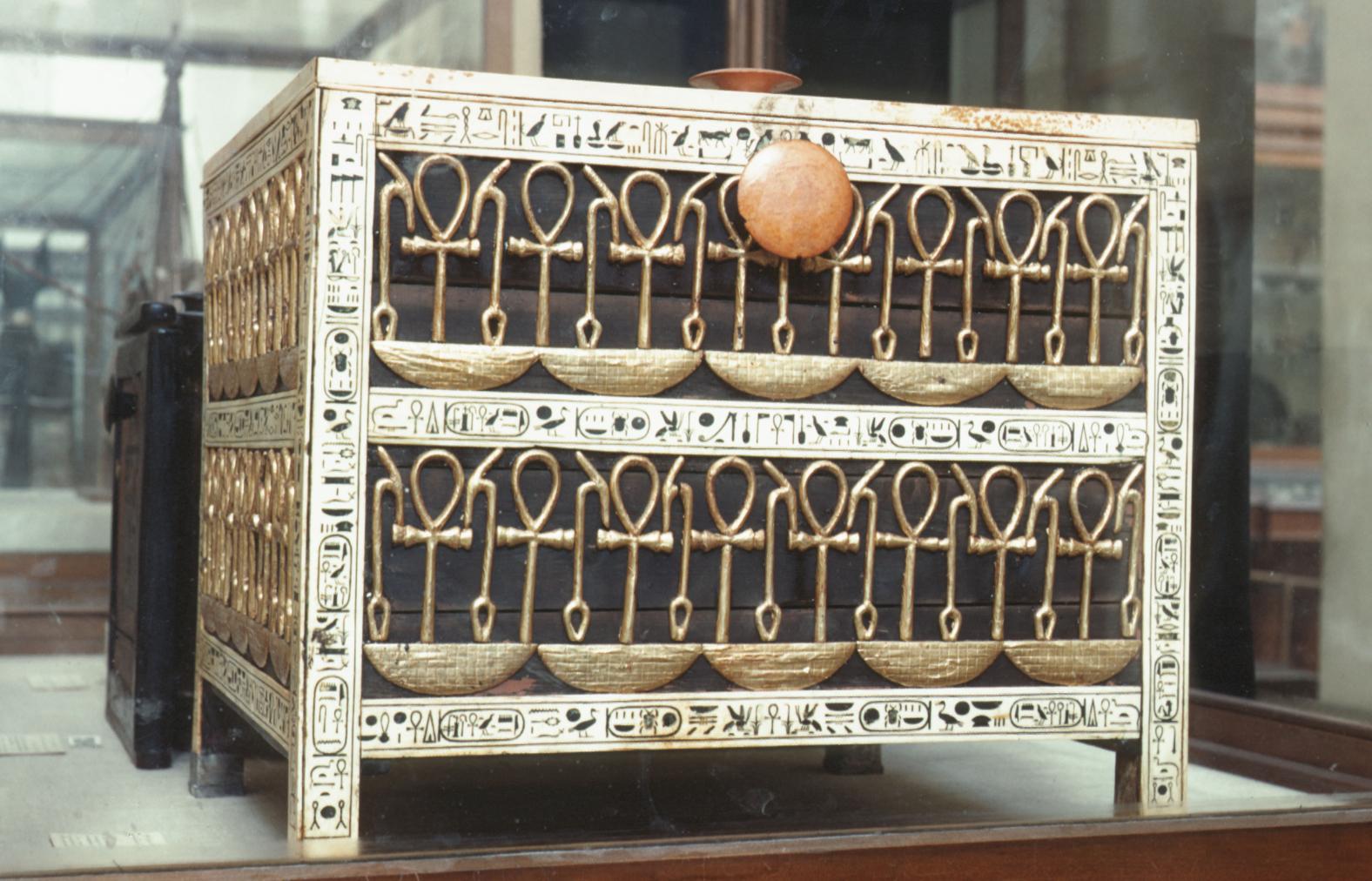
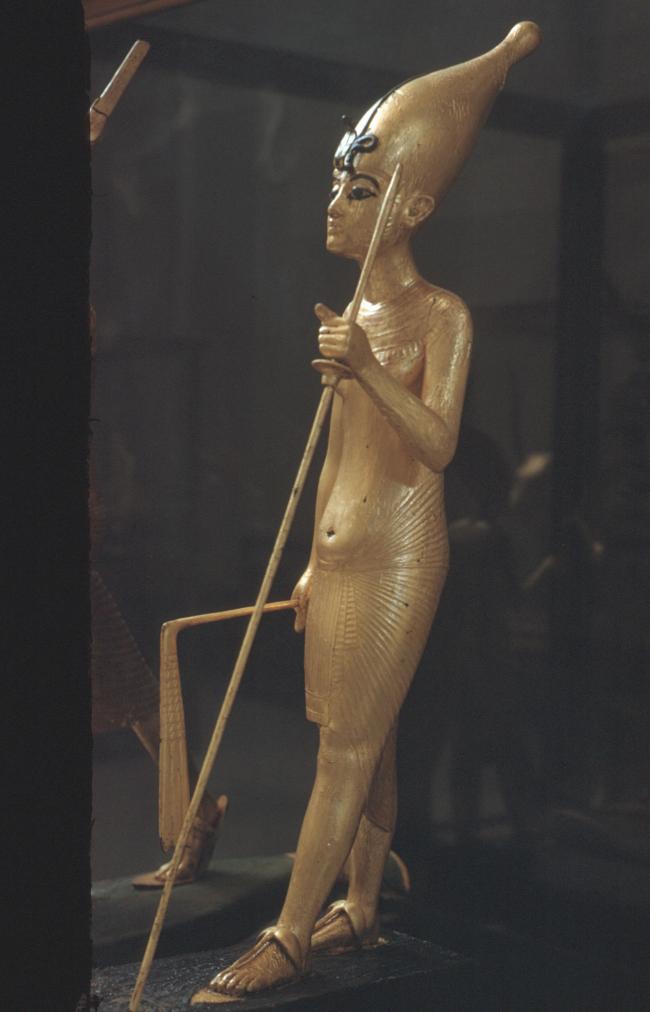
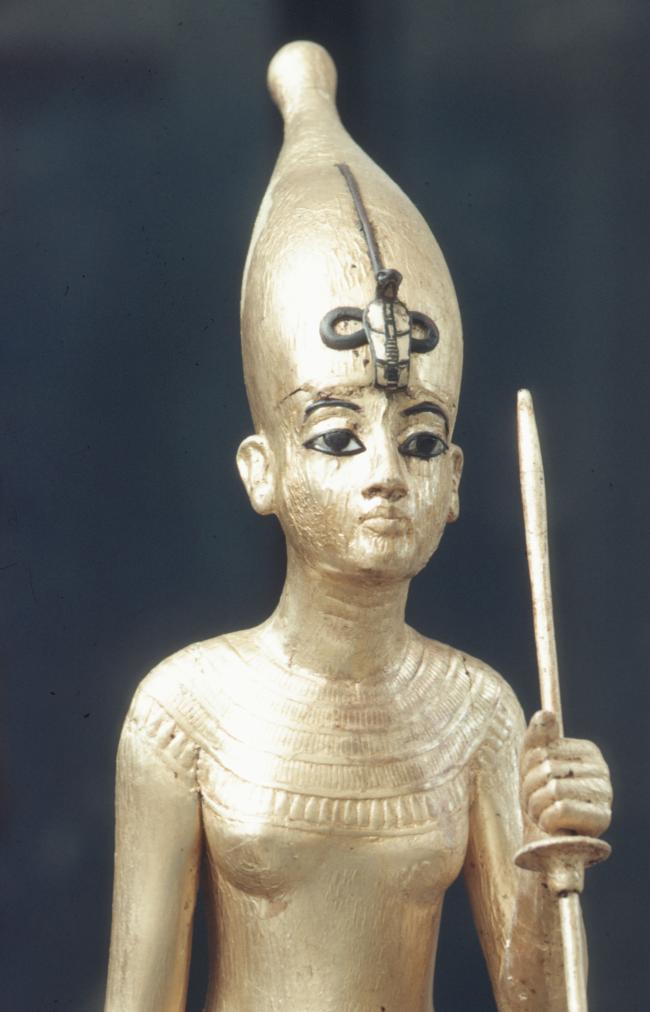
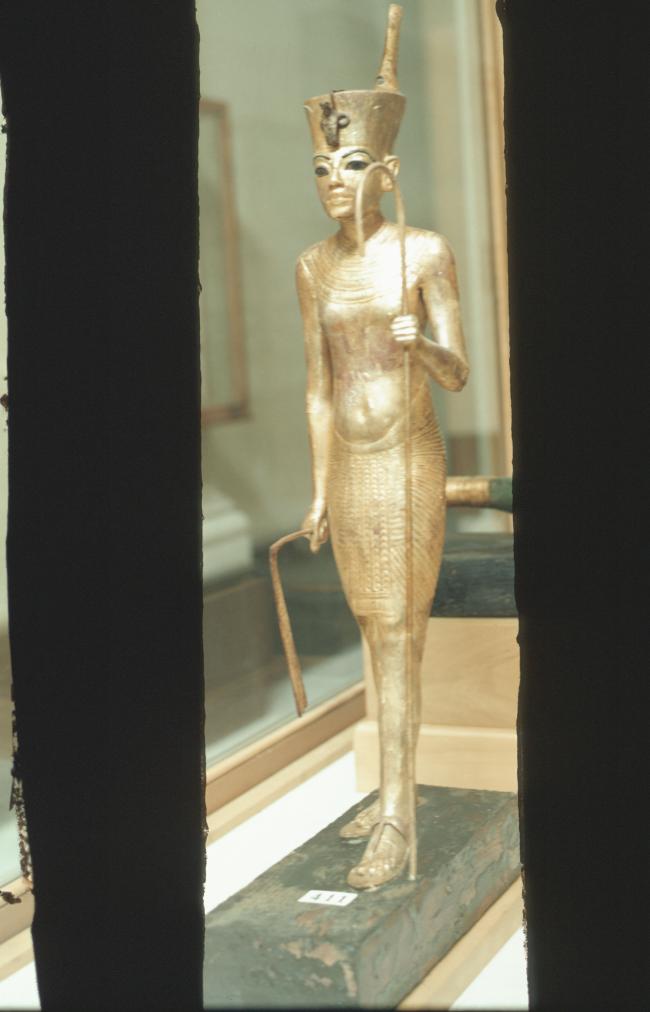
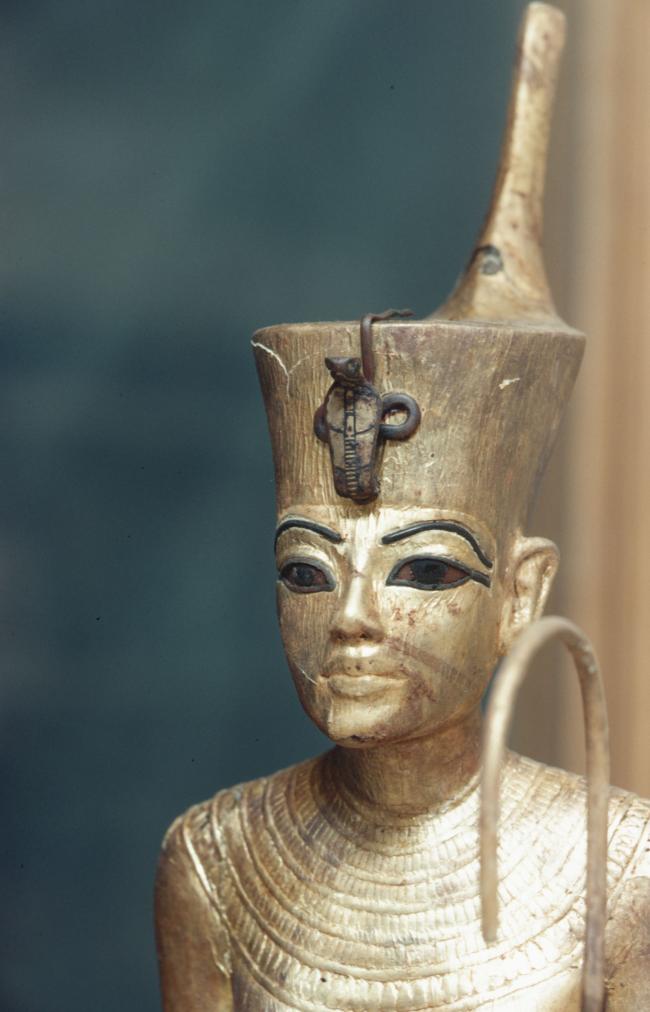
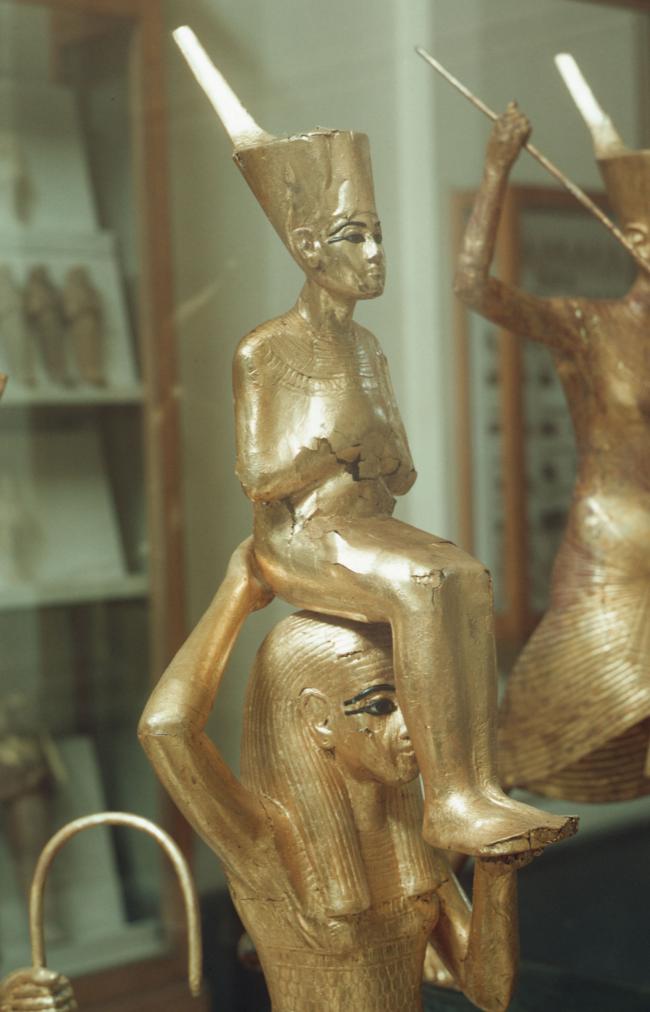
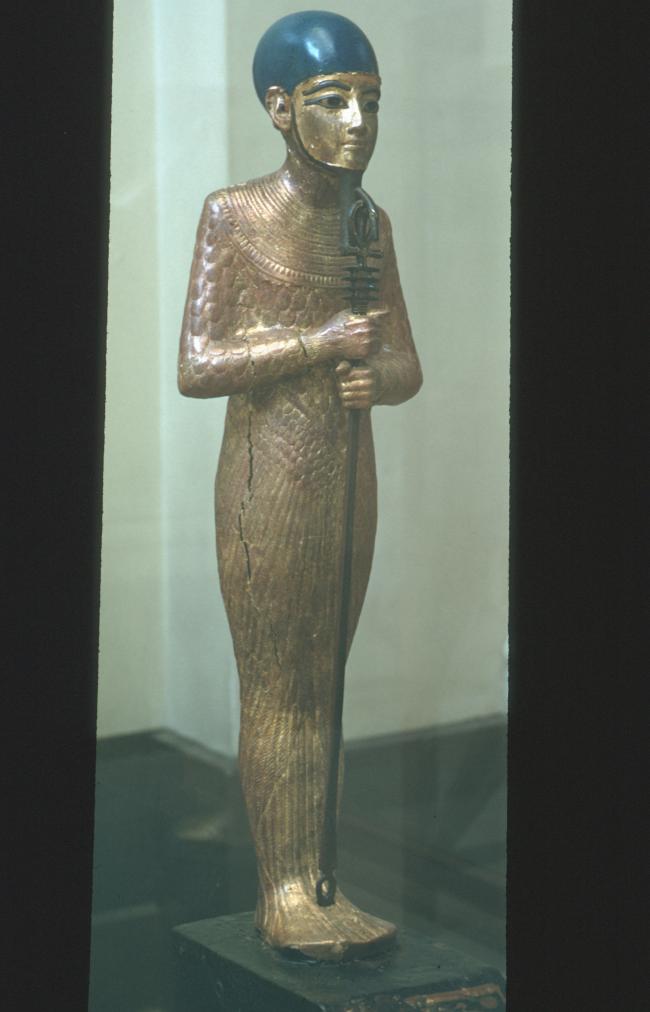
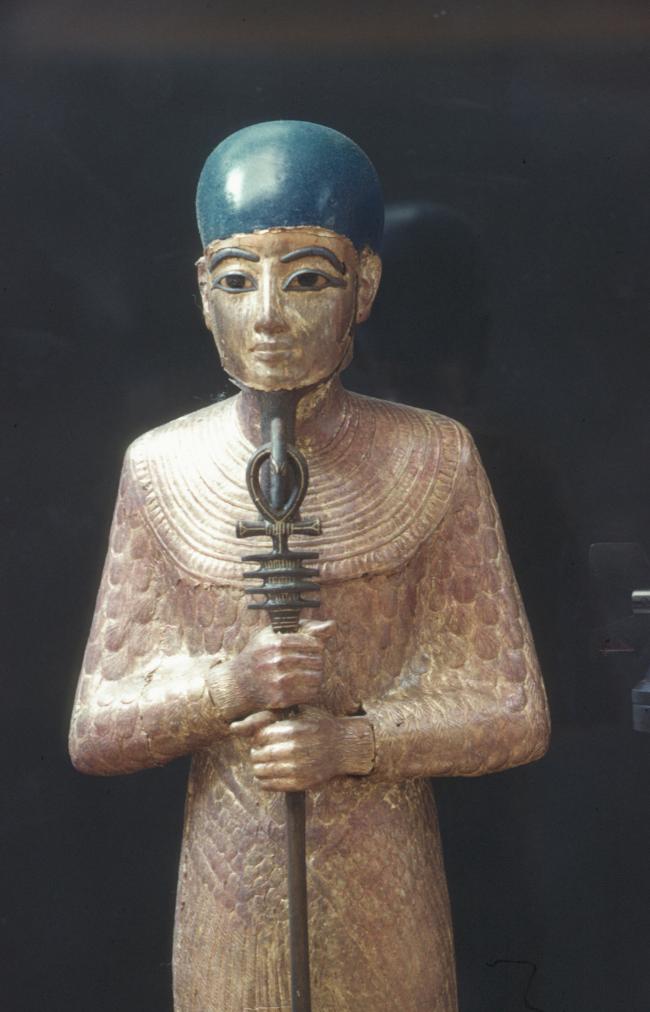
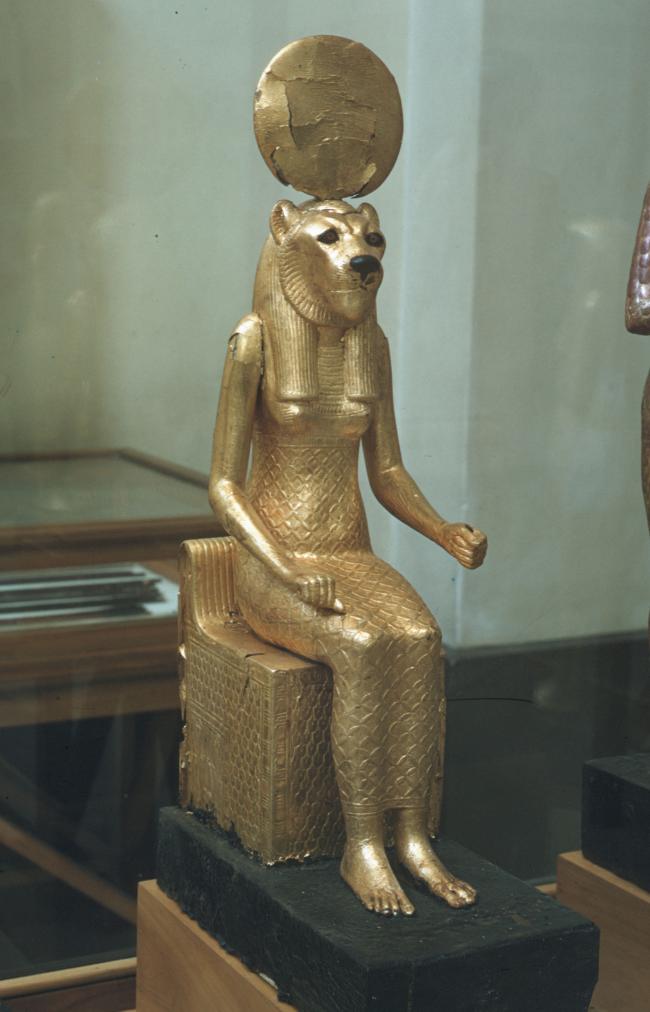
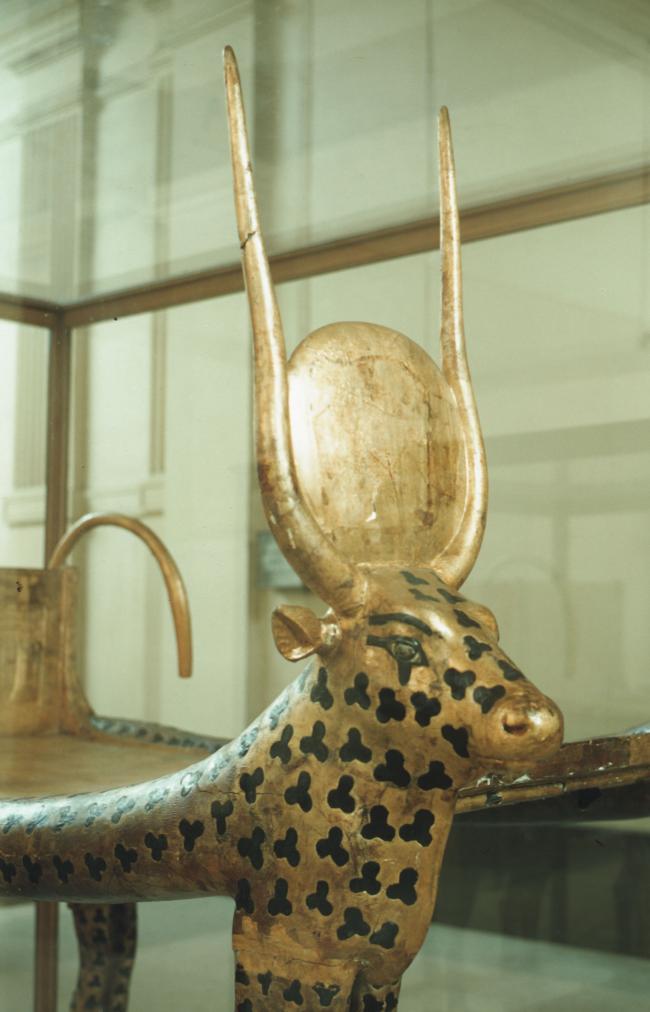
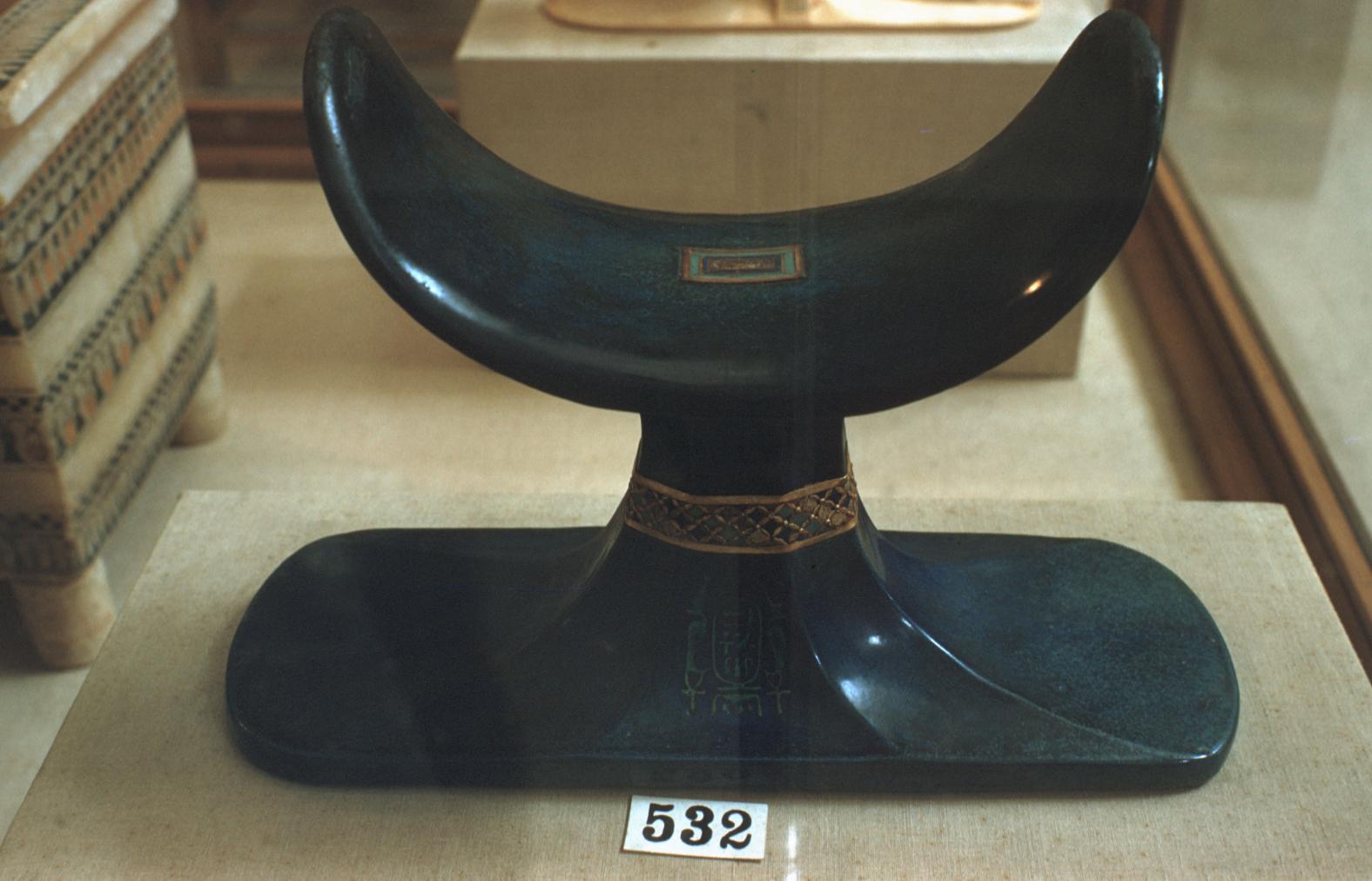
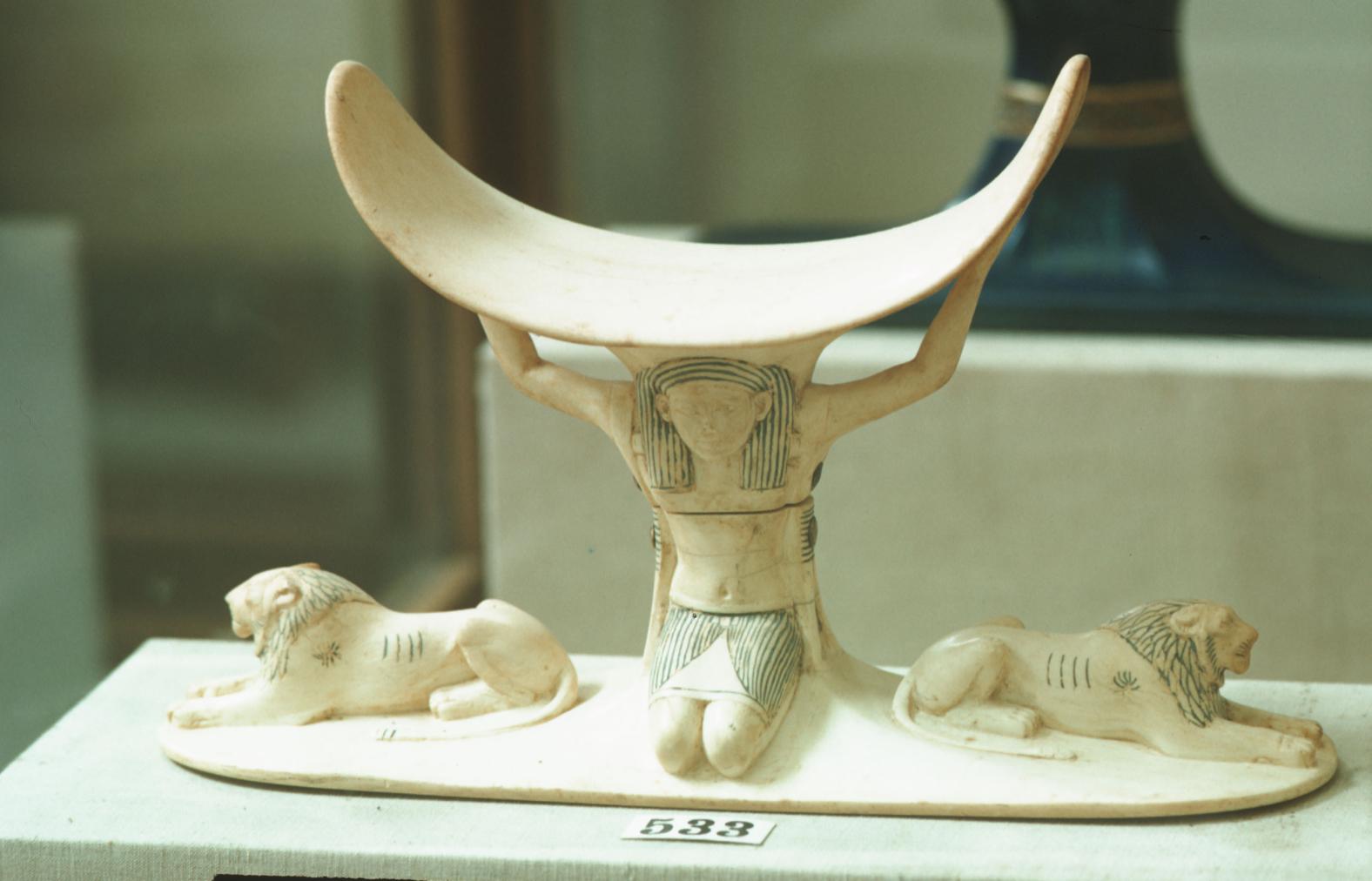
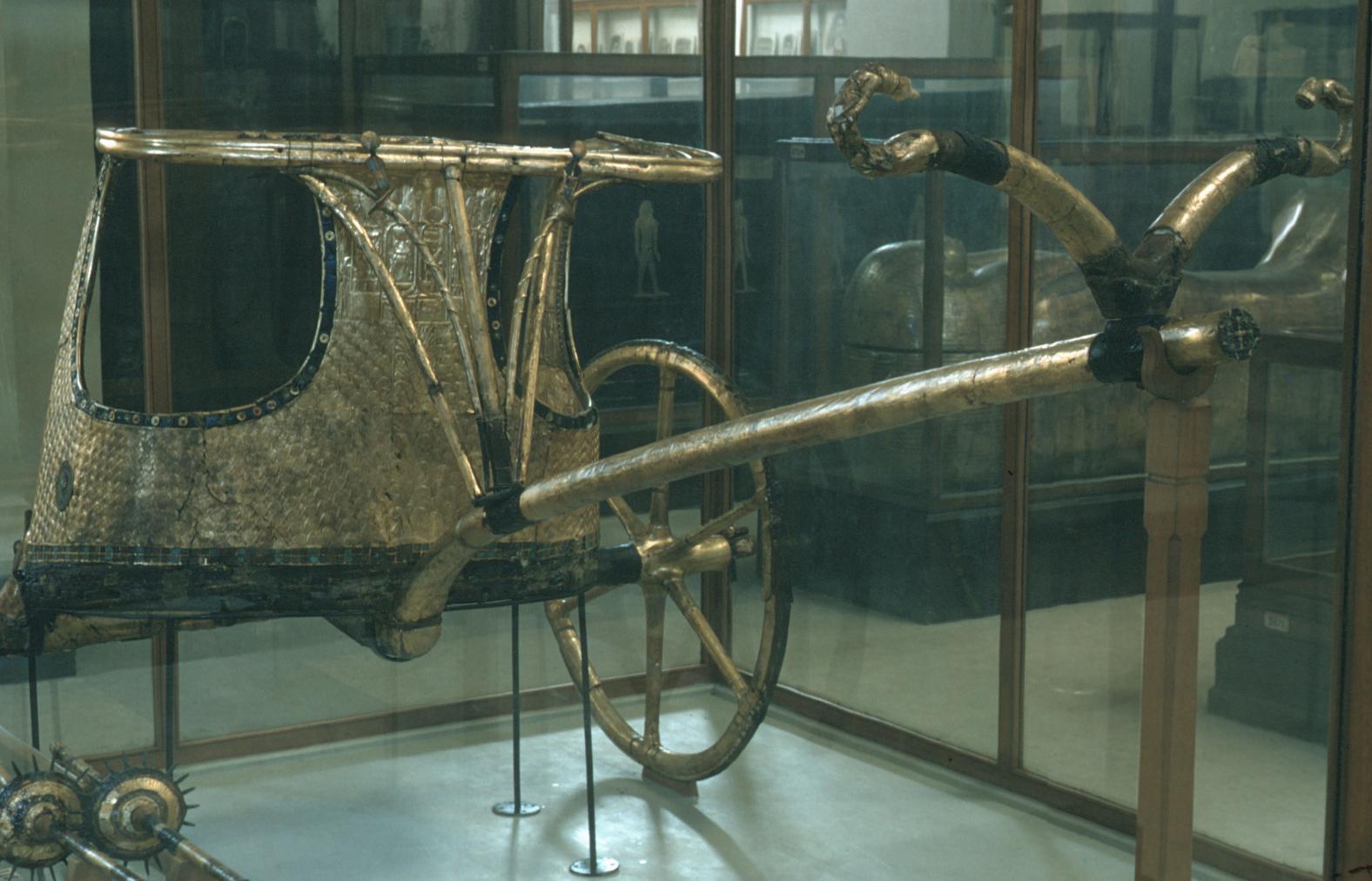
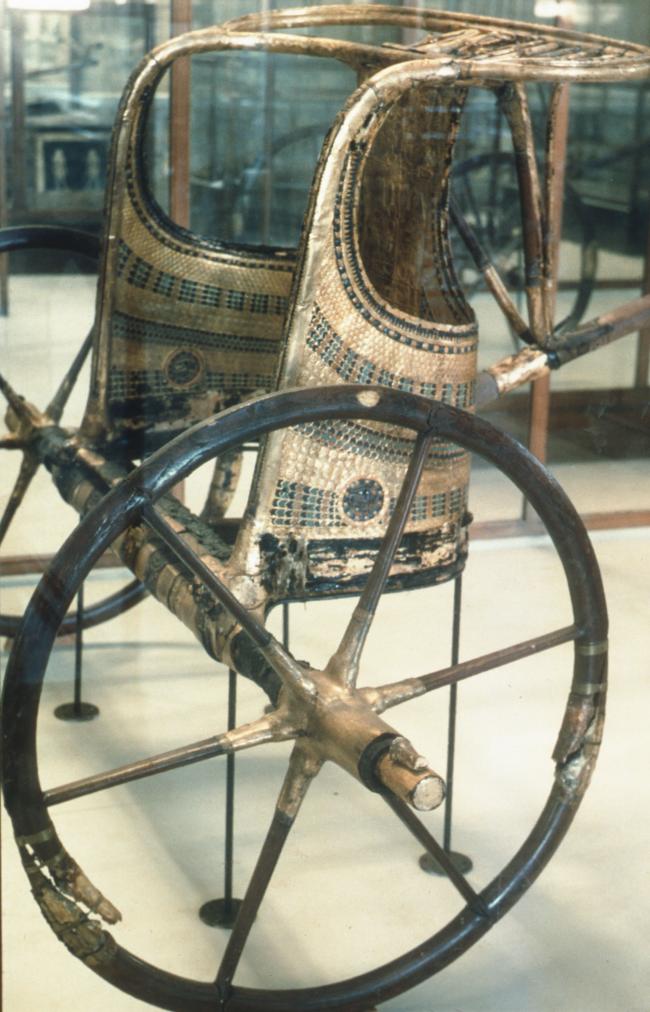
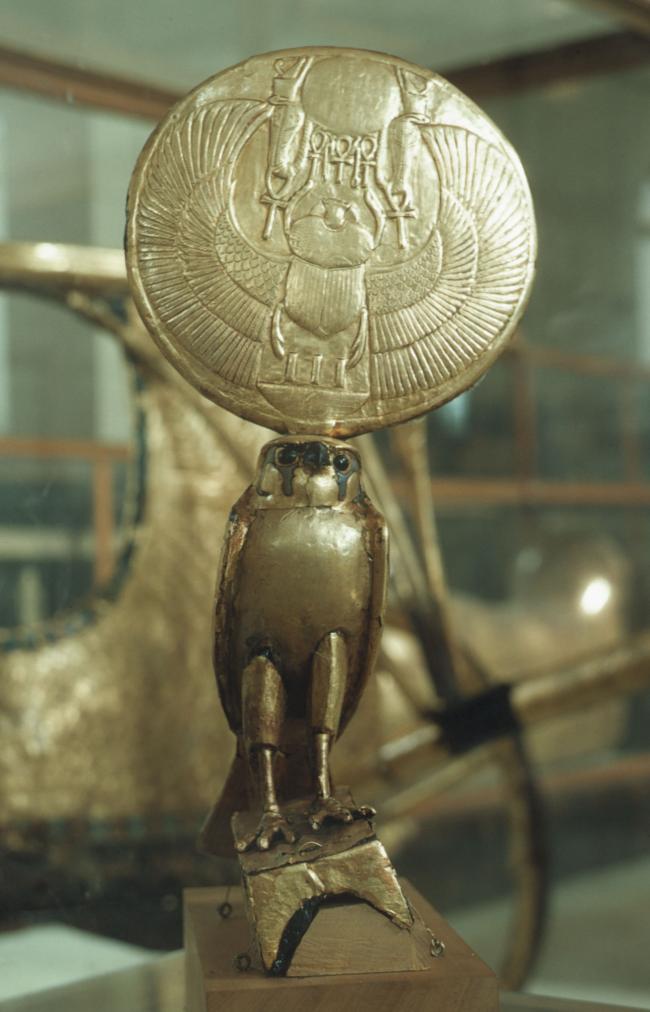
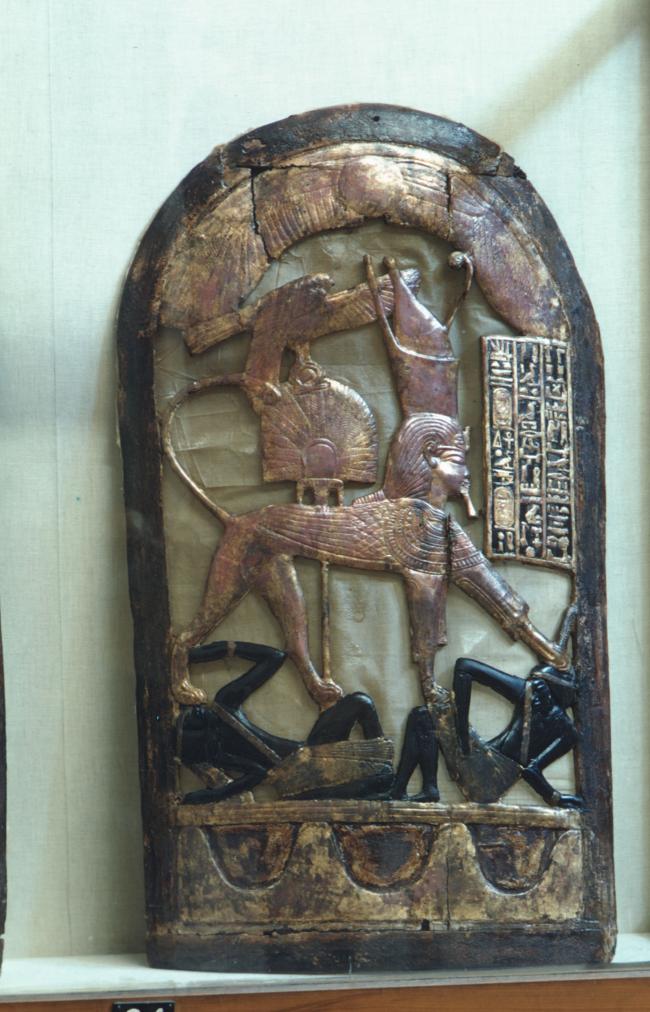
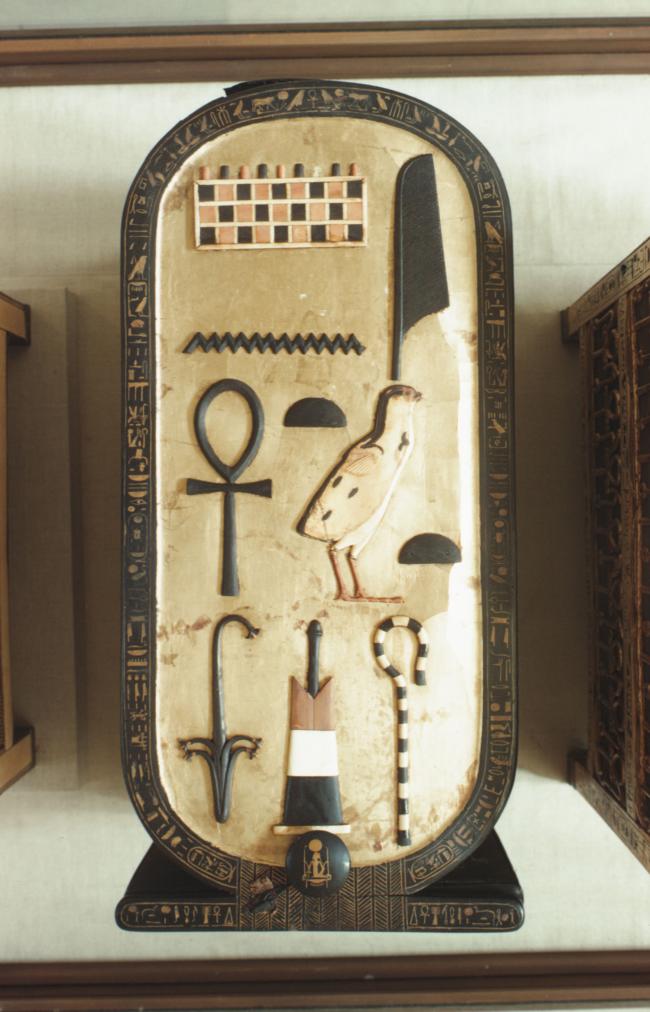
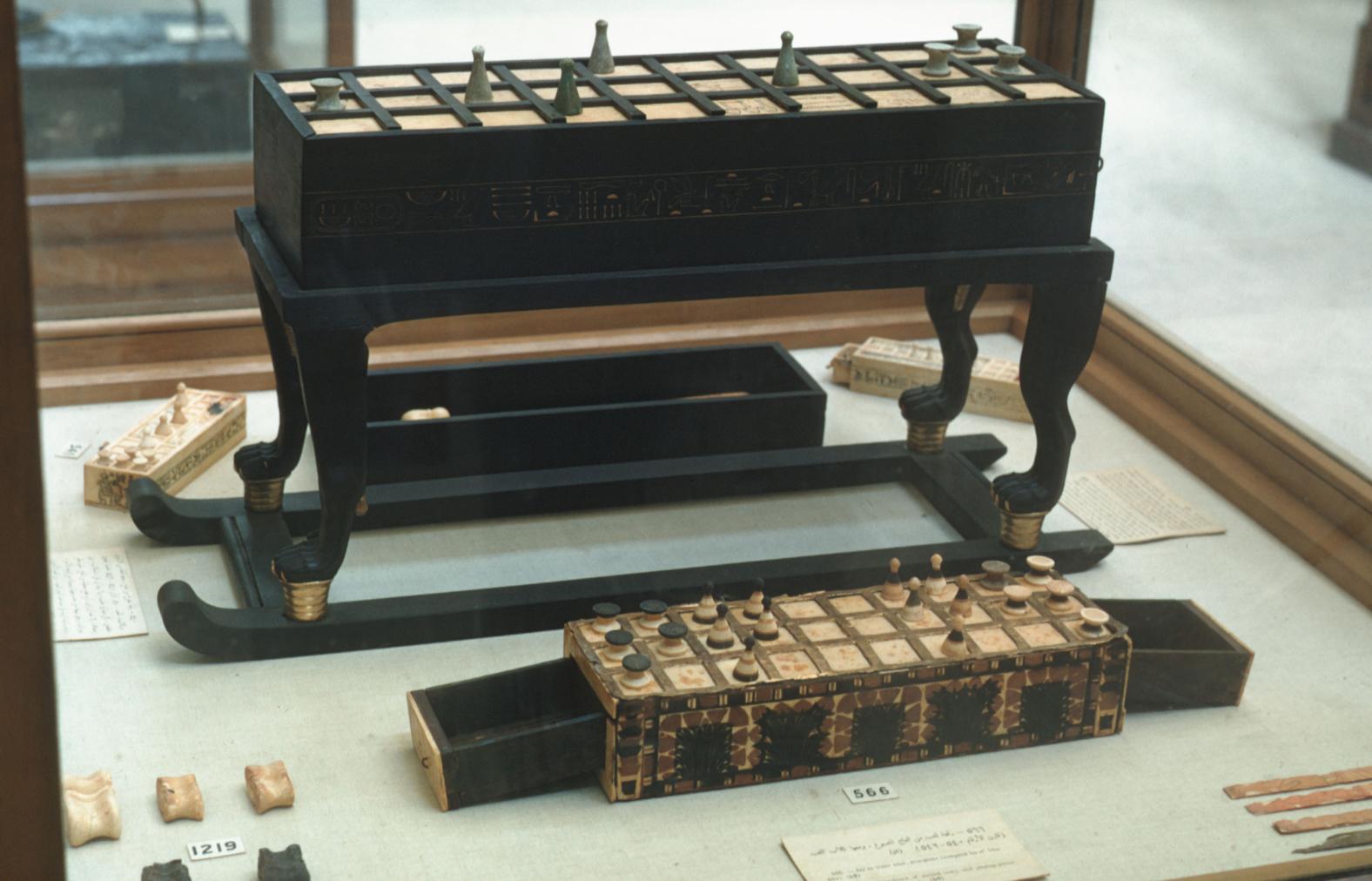
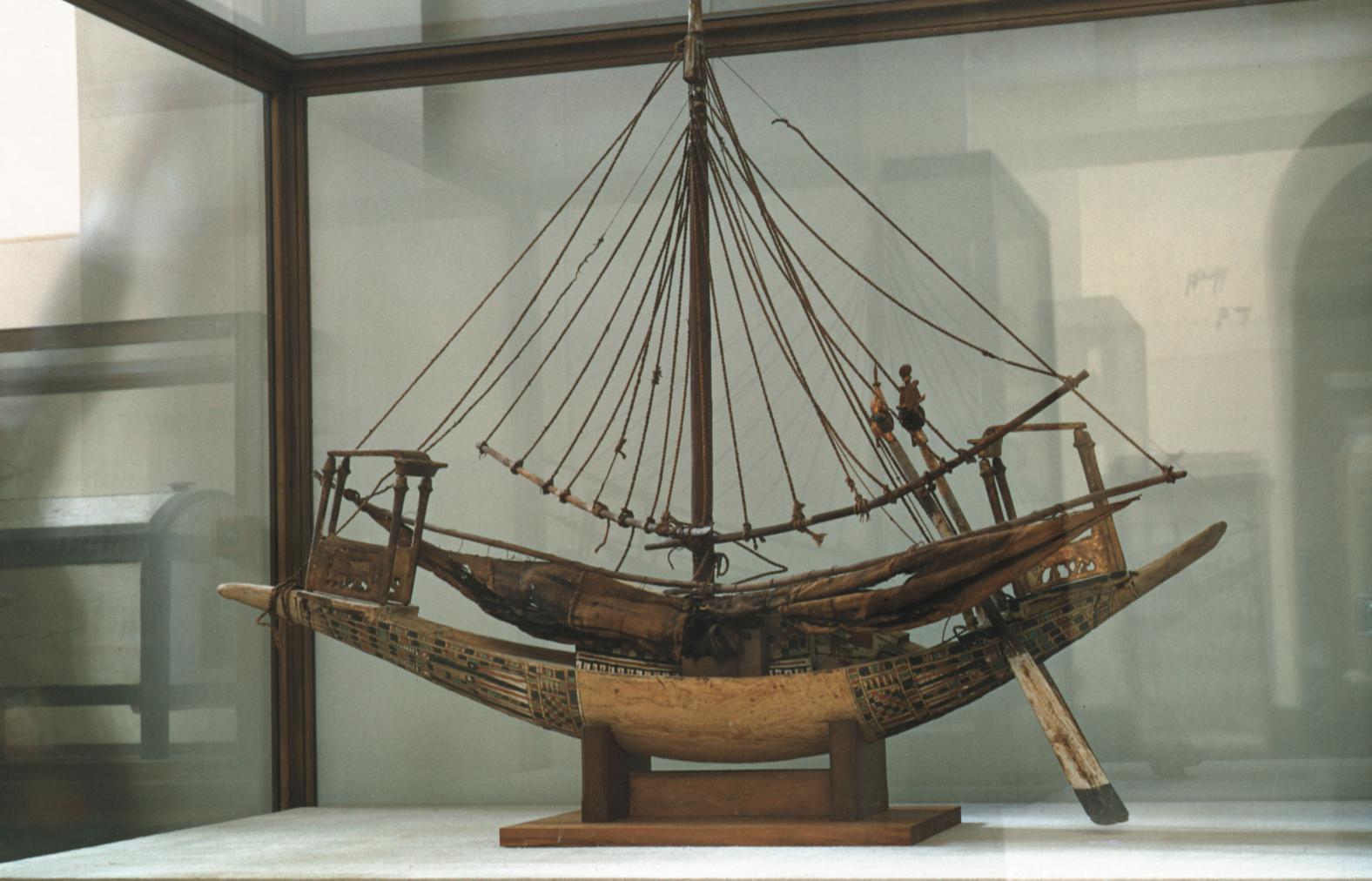
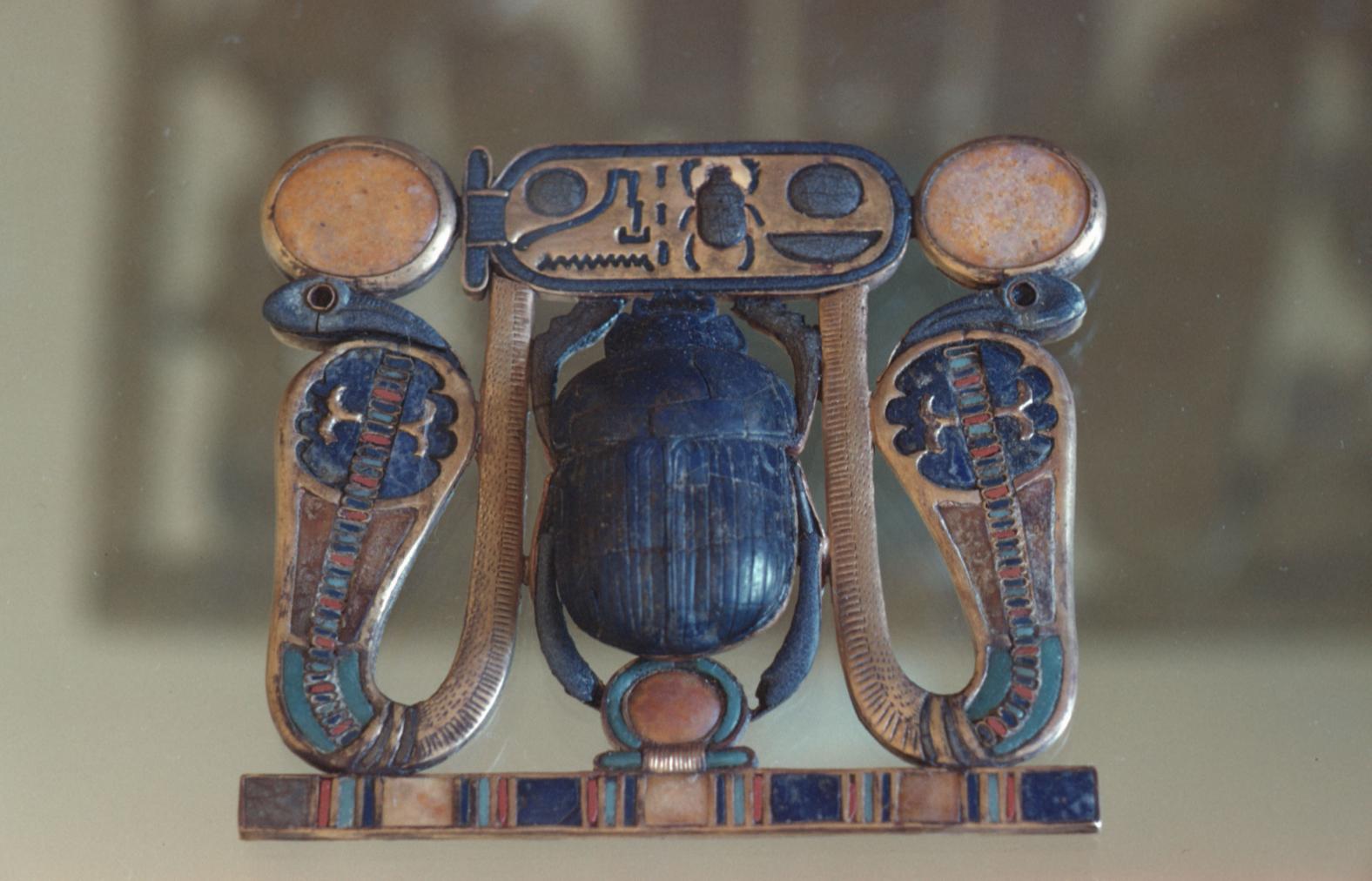
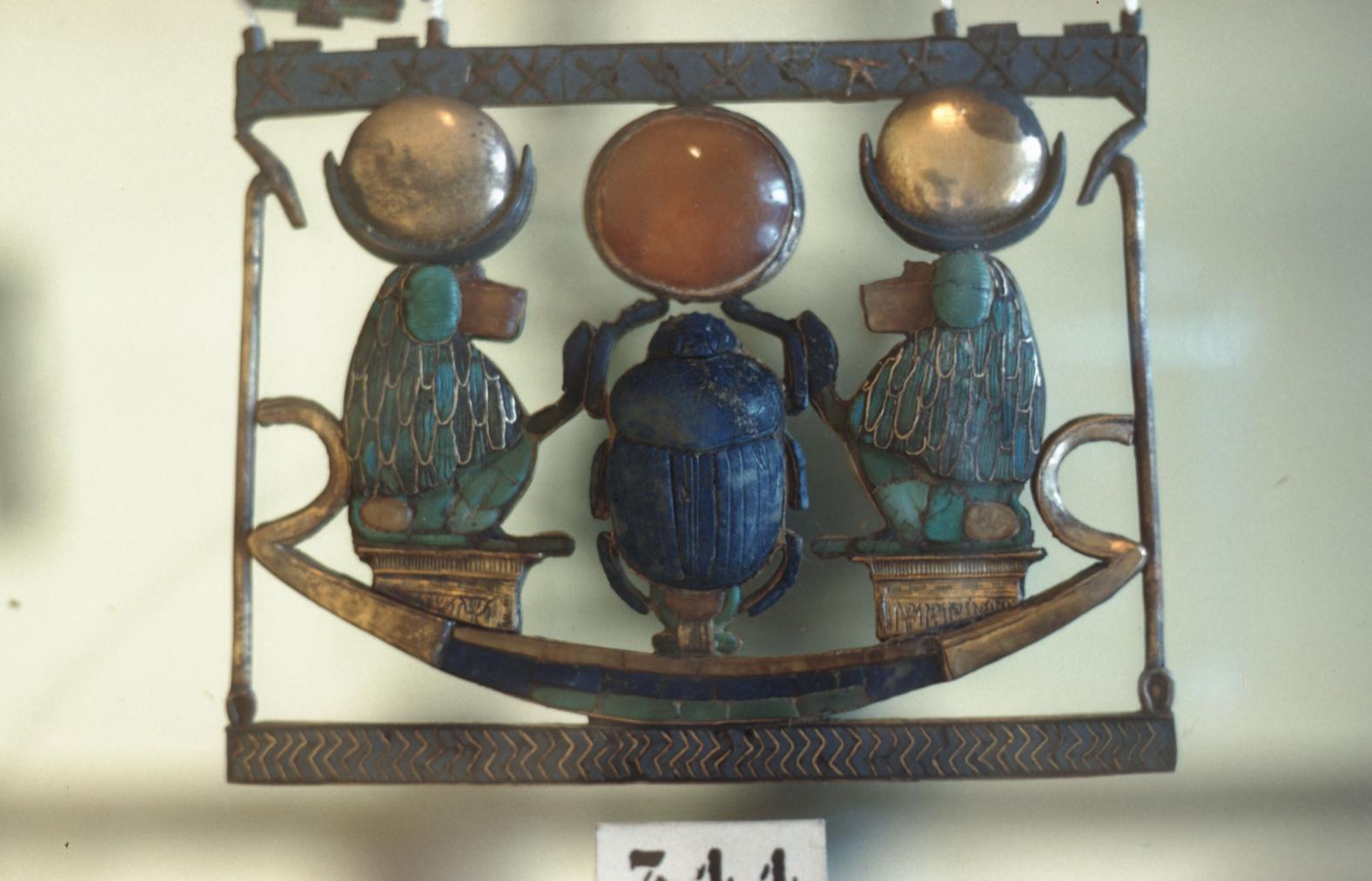
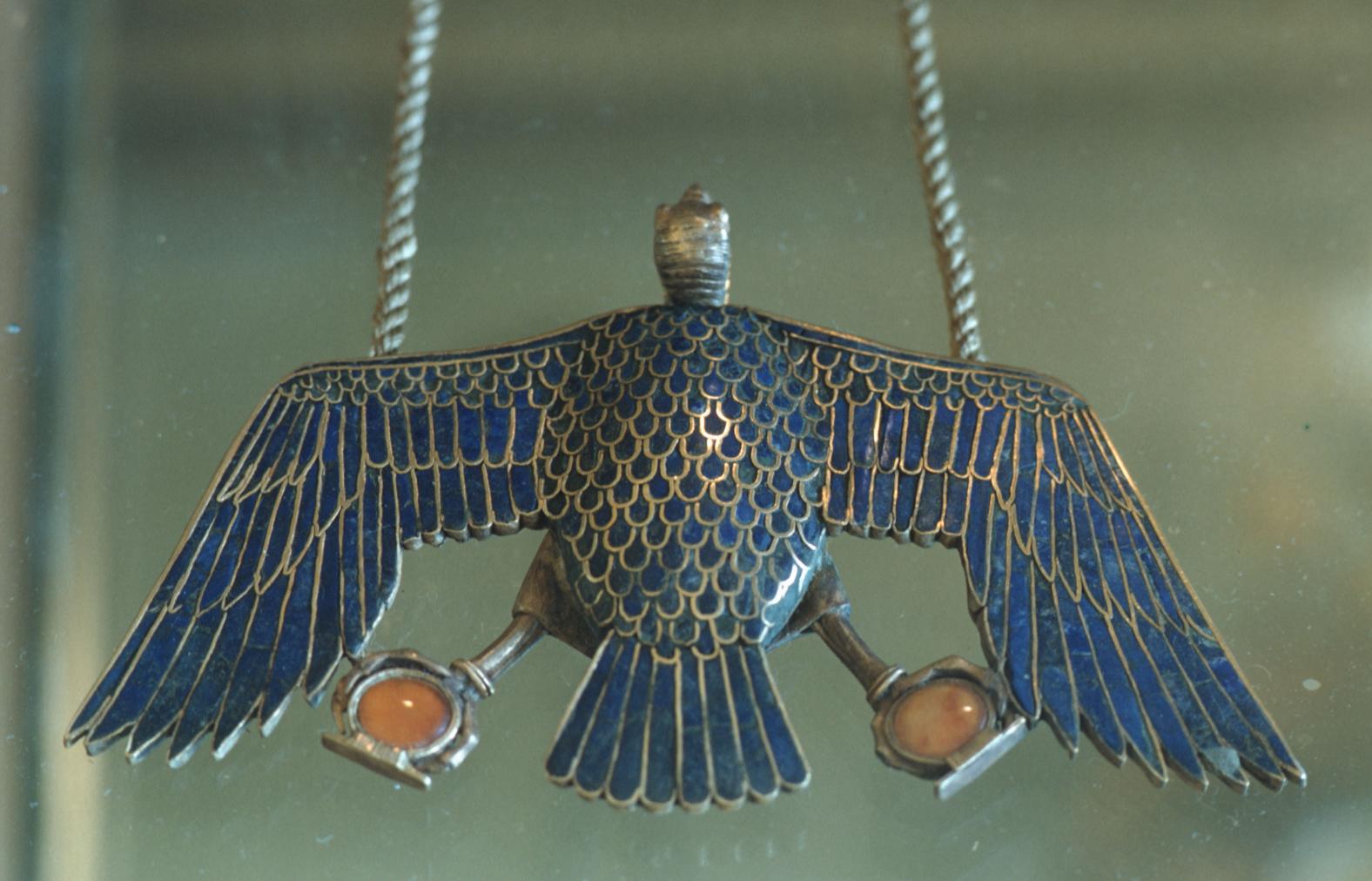
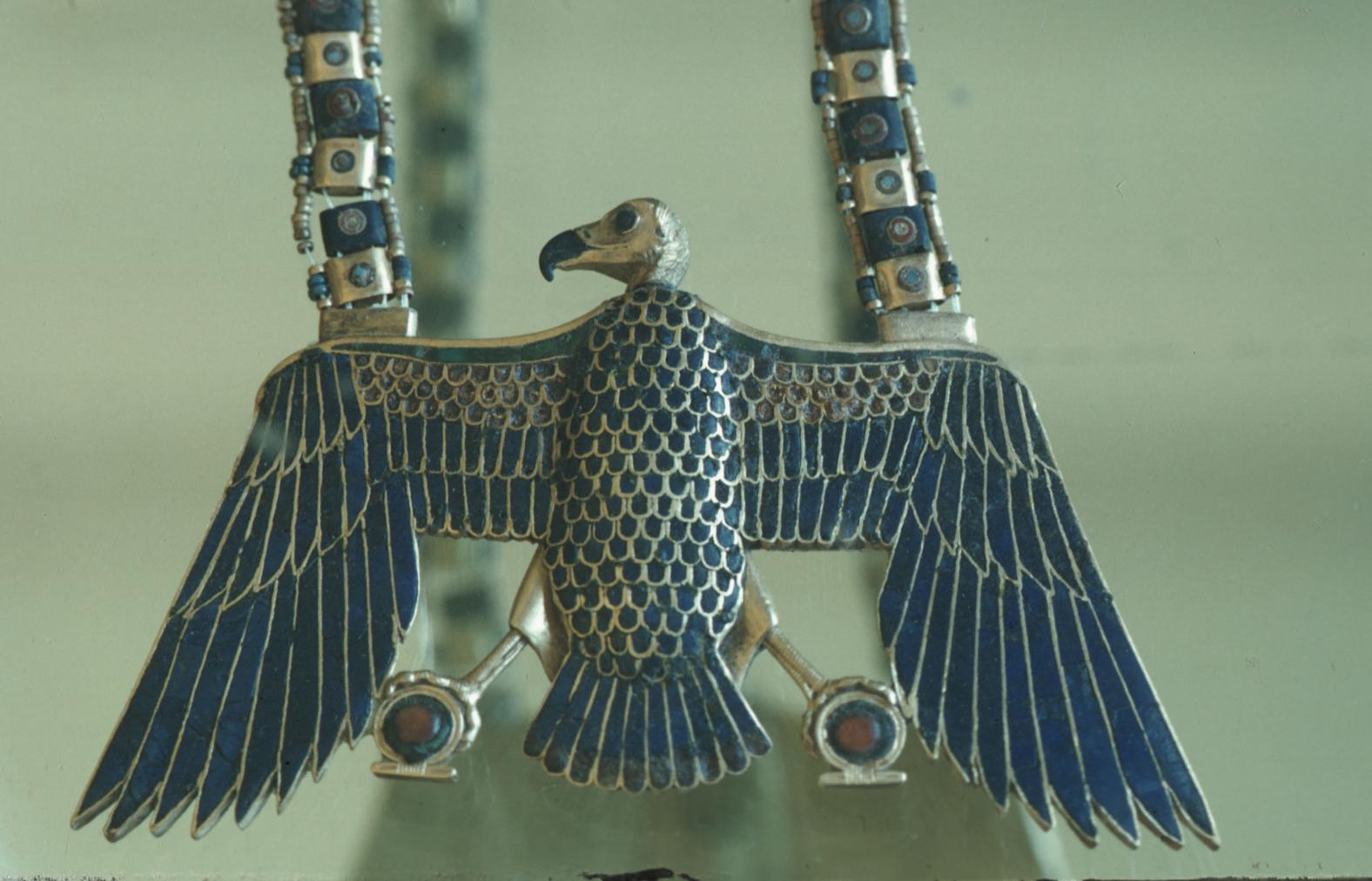
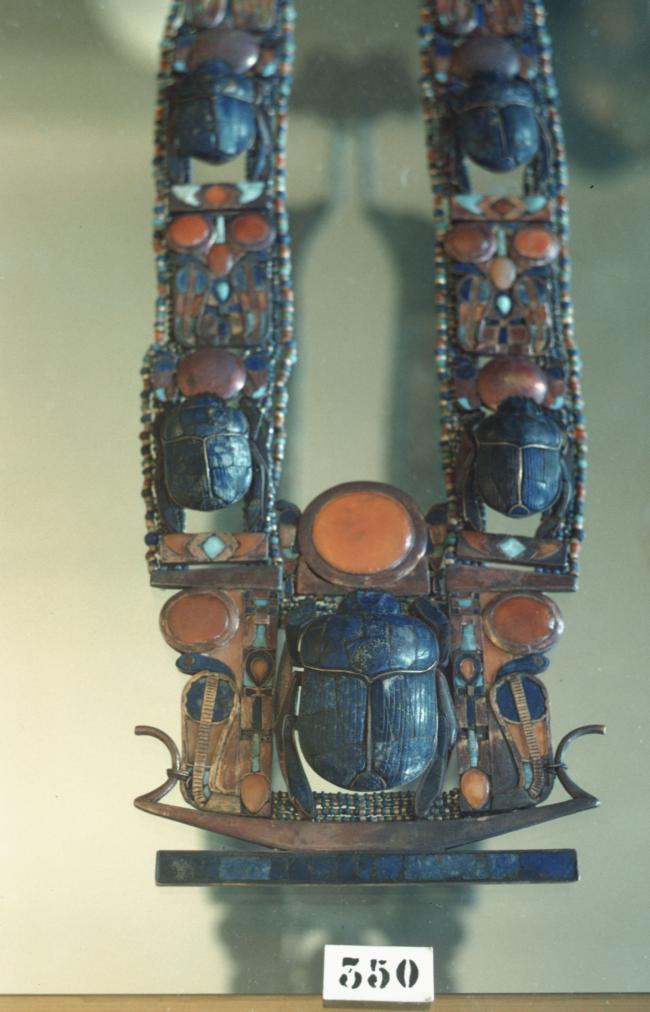
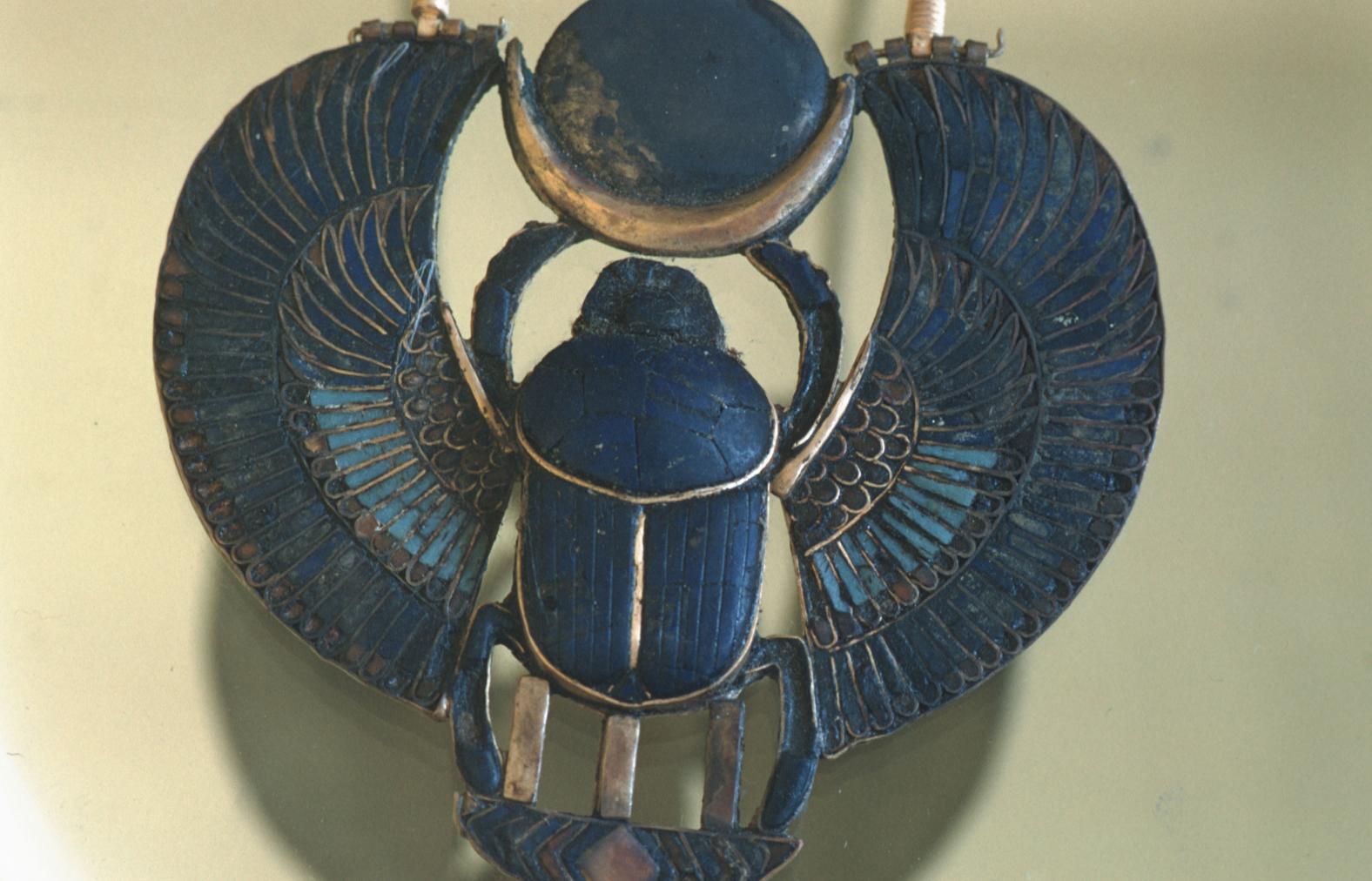
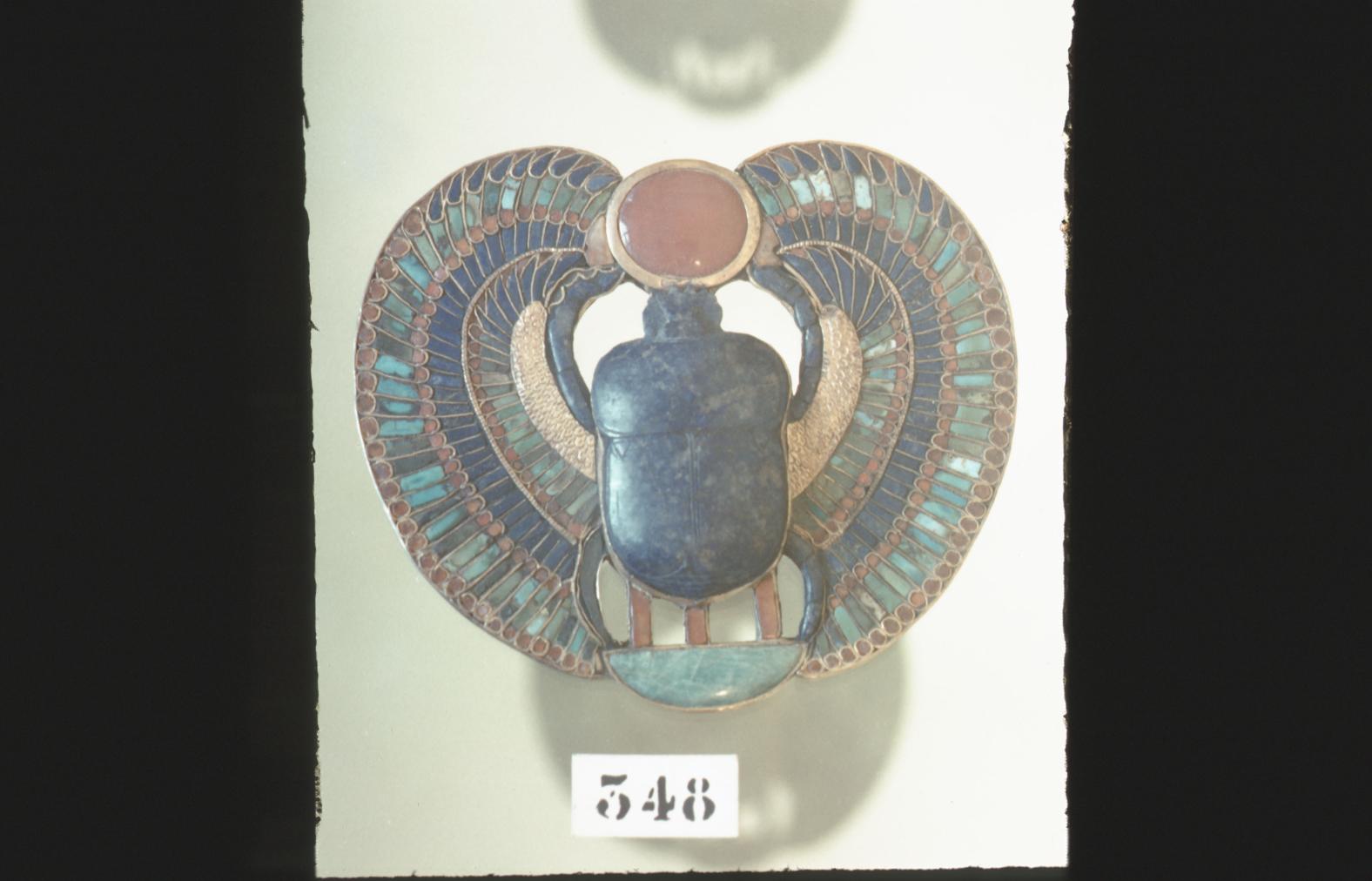
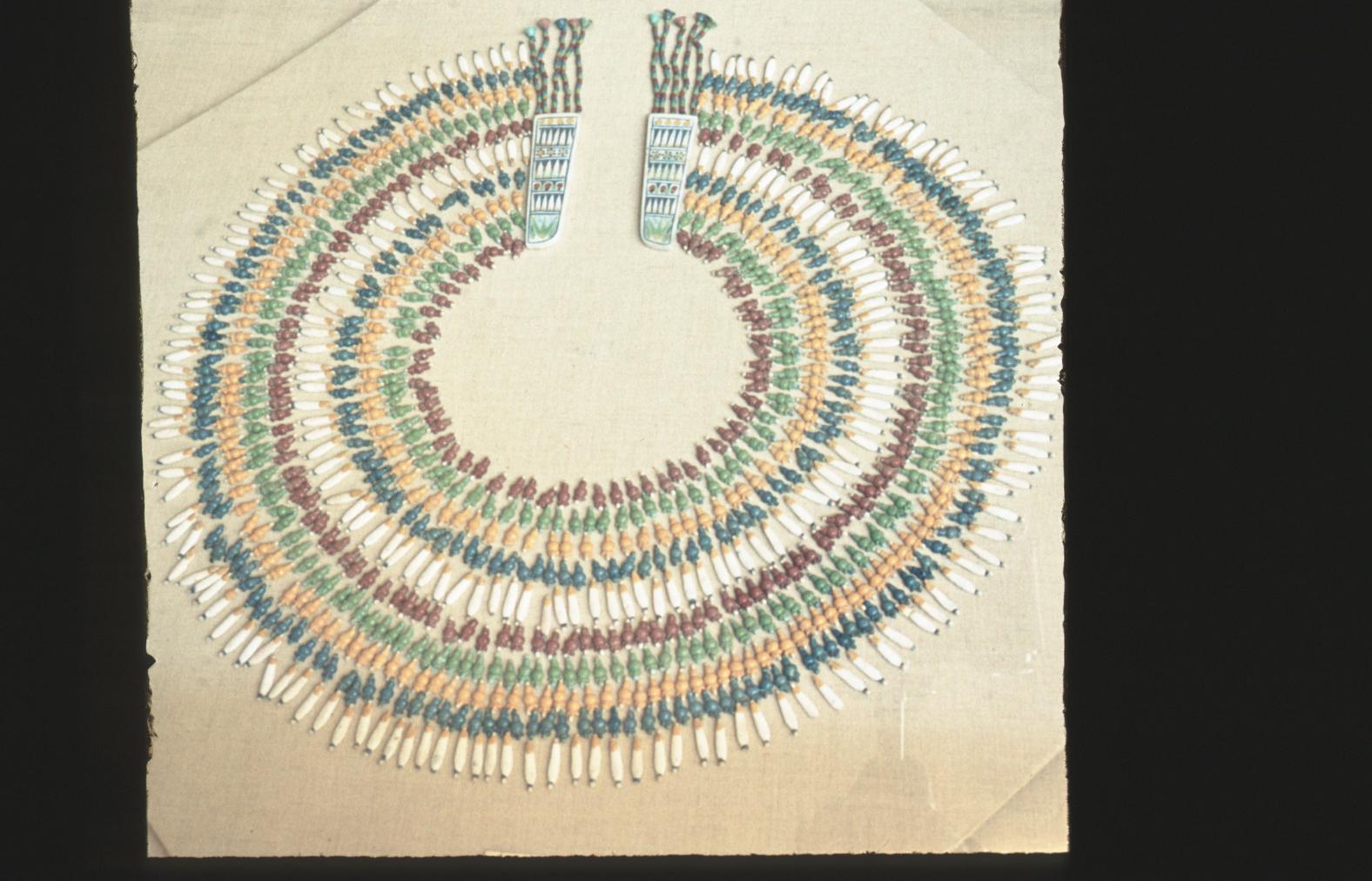
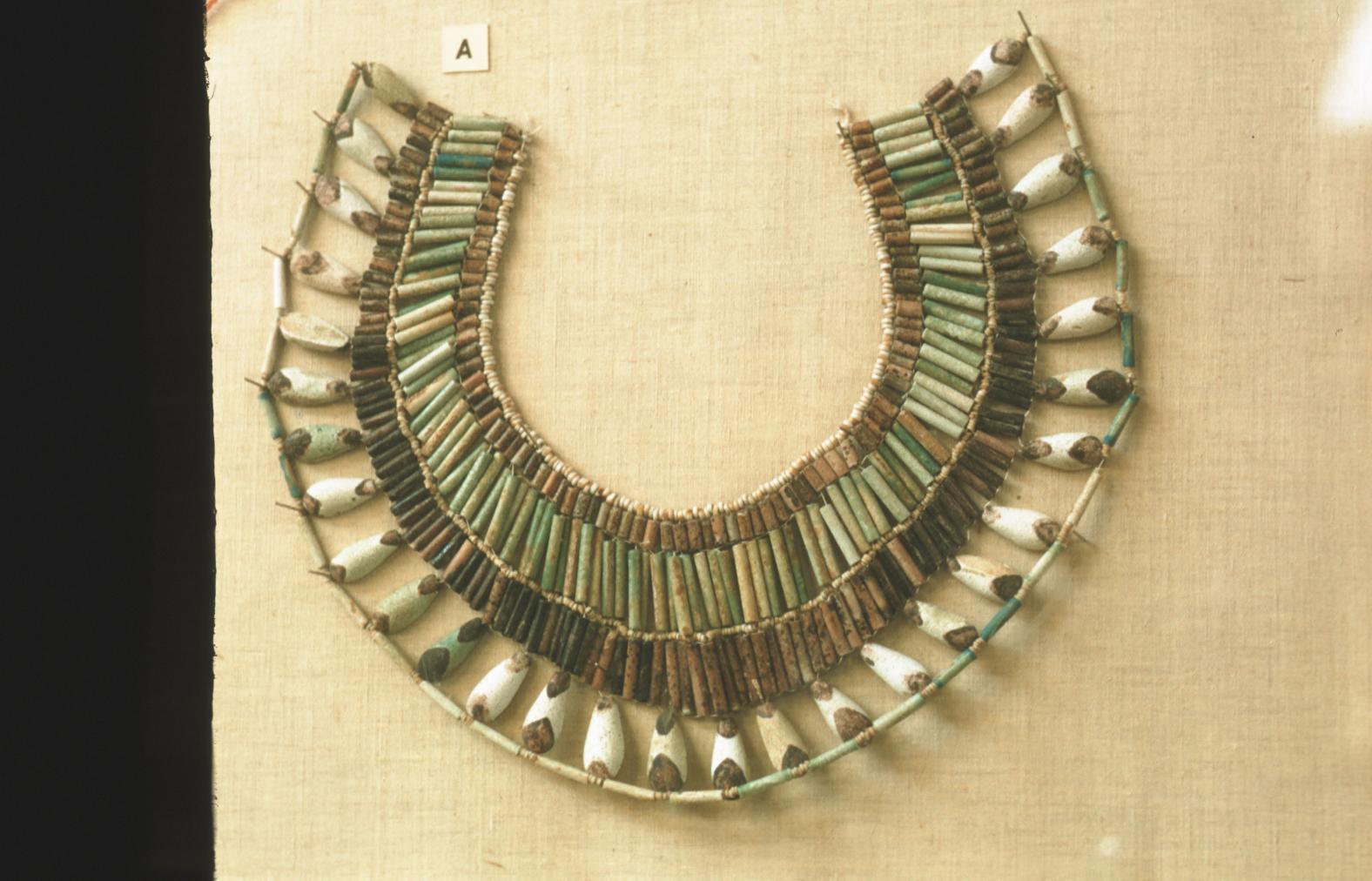
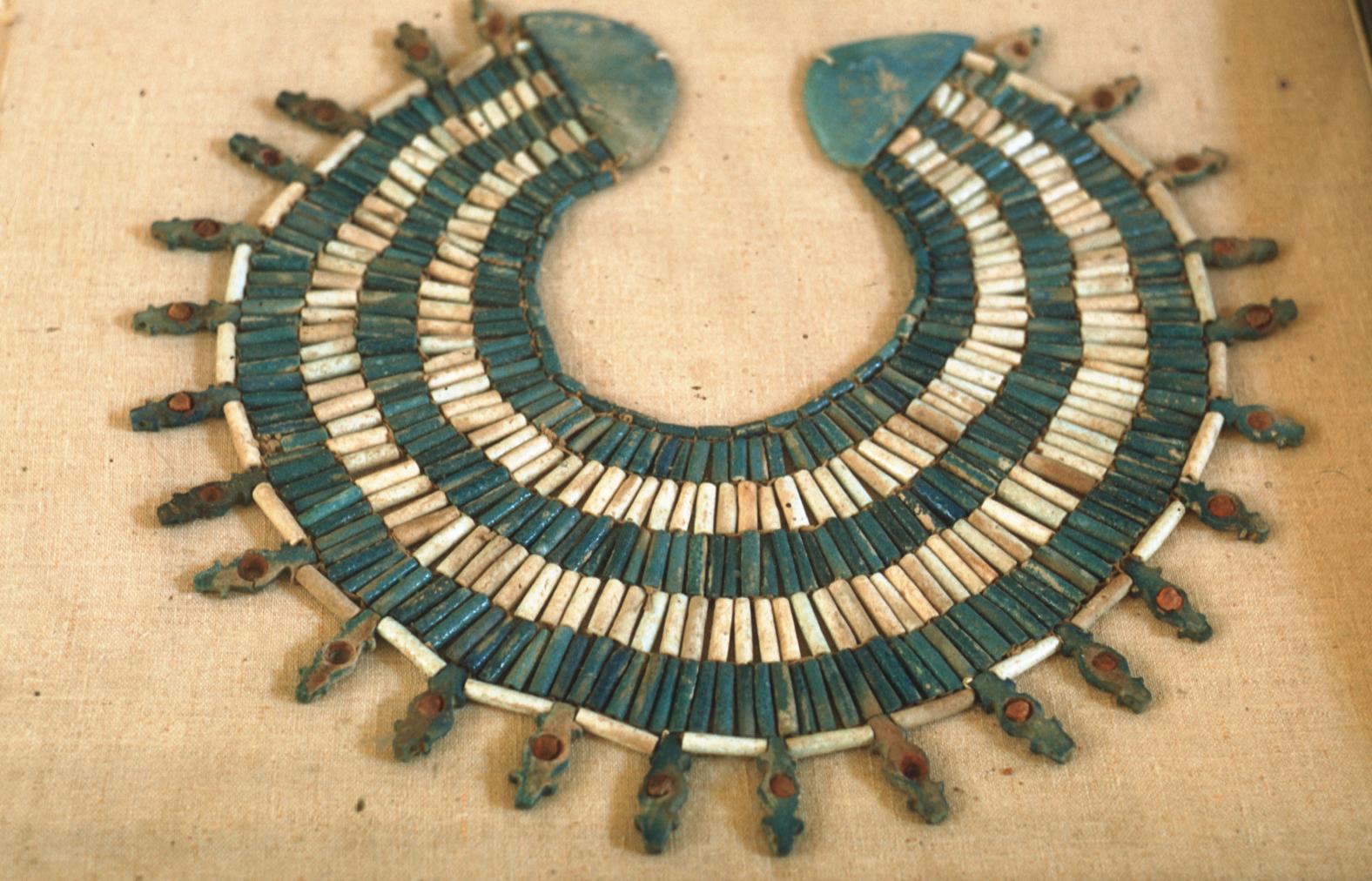
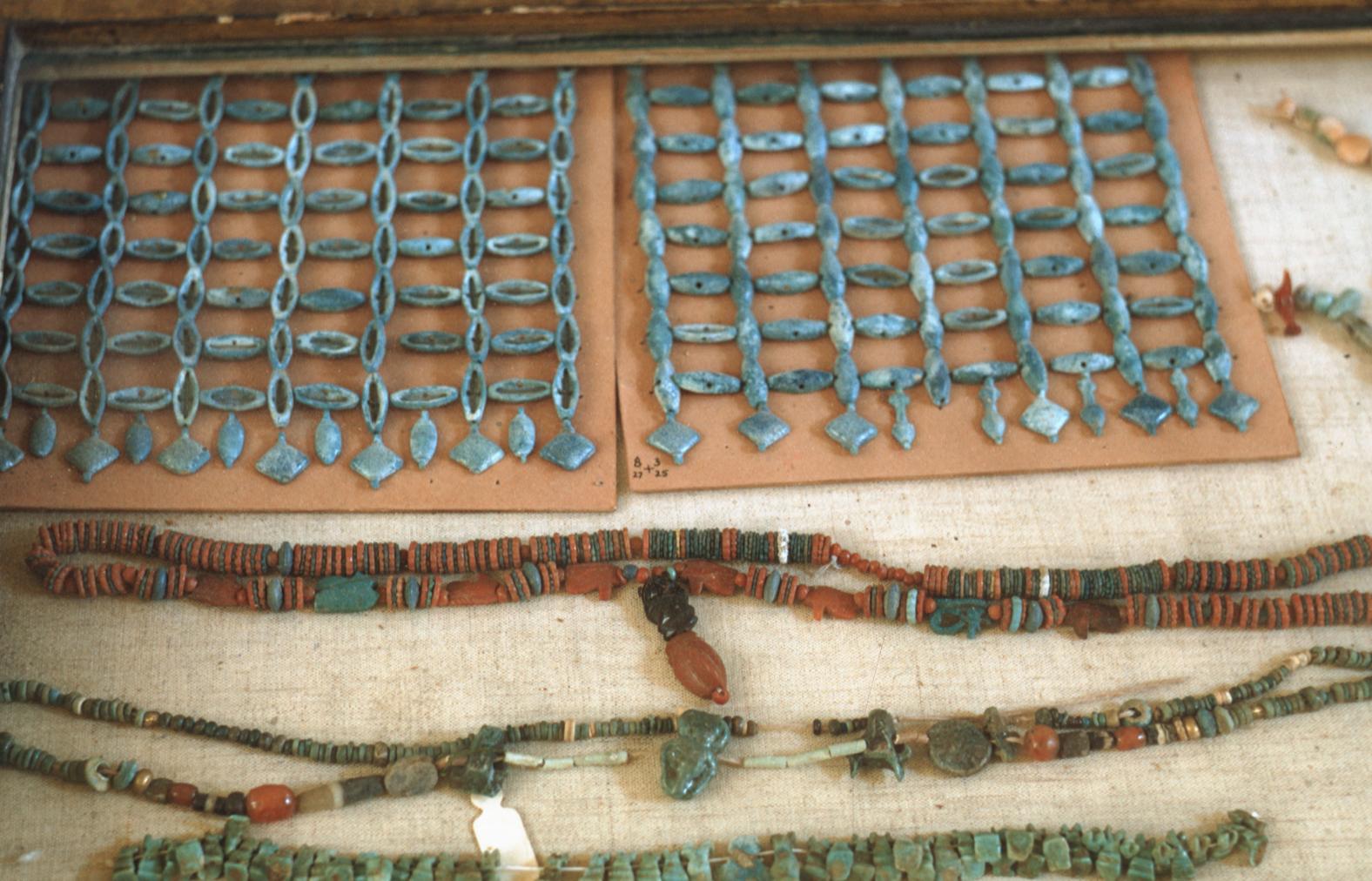
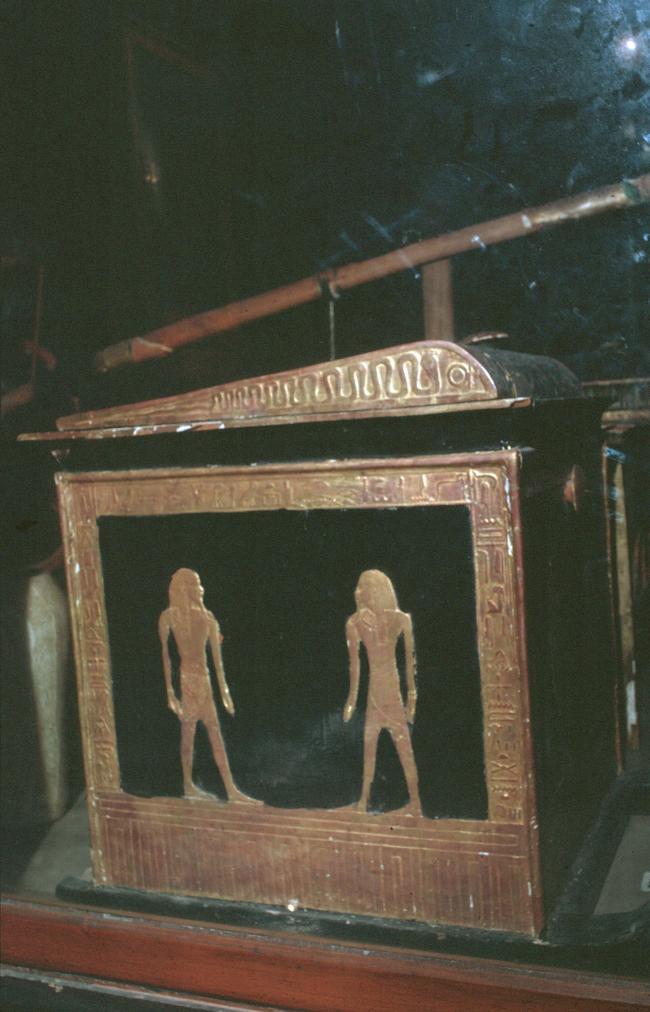
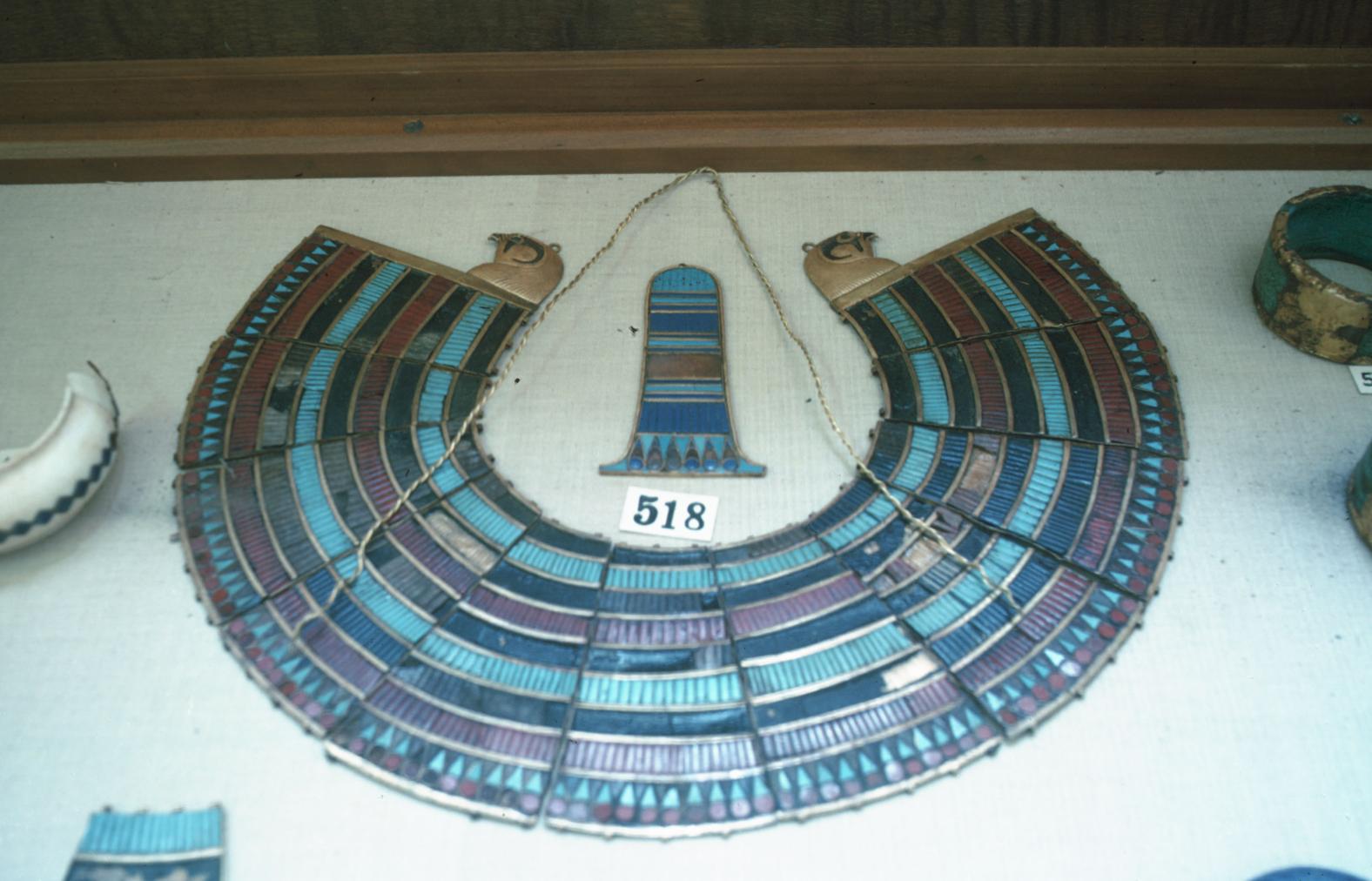
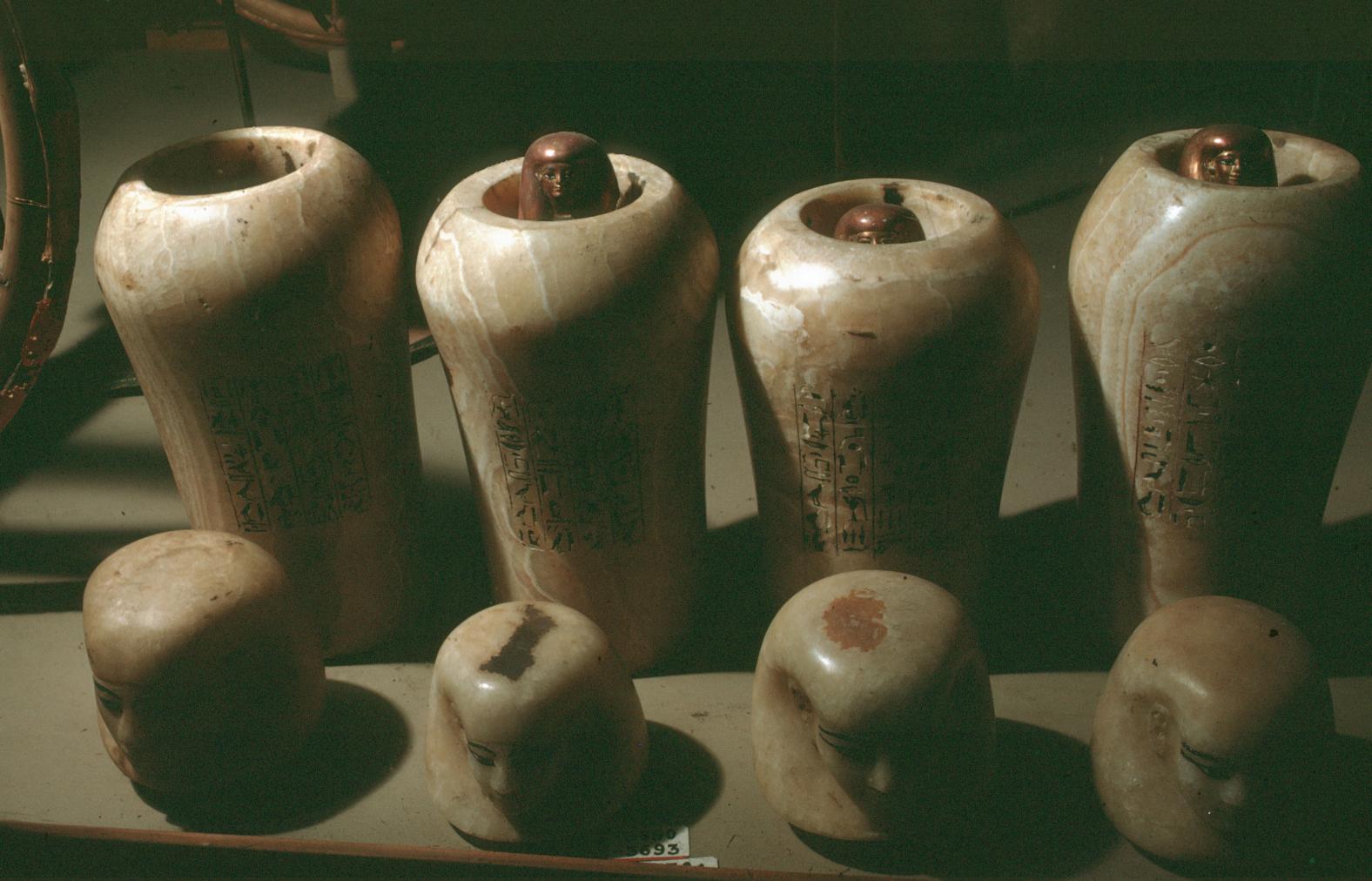
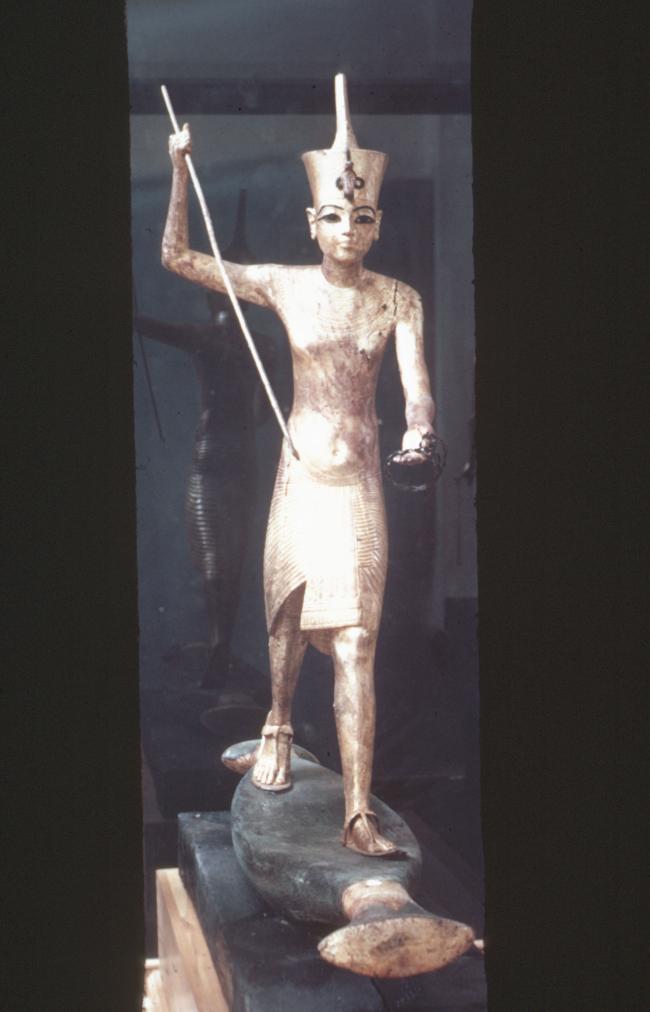
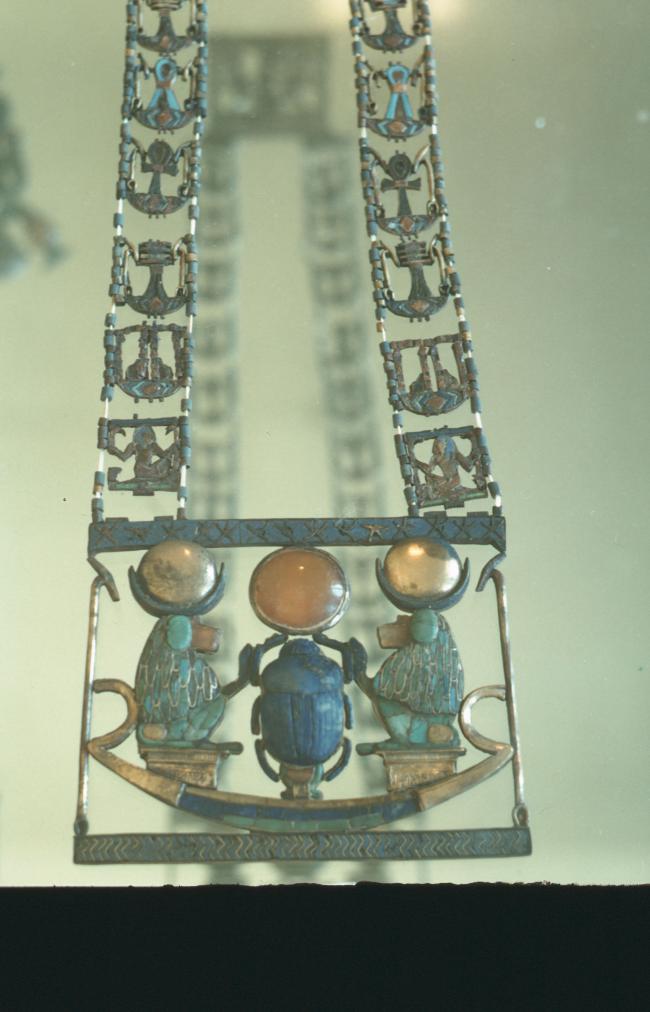
See entire tombSituated east of the burial chamber, chamber Ja (called the Treasury by Carter), is oriented north-south. This storeroom for Tutankhamen's canopic shrine held over five hundred objects. It is similar to the storerooms of other burial chambers in the Valley, and had the only doorway in KV 62 not sealed with plaster and rubble. Iin addition to the canopic chest in its shrine, the objects included a large figure of an Anubis jackal, shrines containing divine figures, a model granary and model boats, two fetuses in coffins, chests and a chariot.
Porter and Moss designation:
About
About
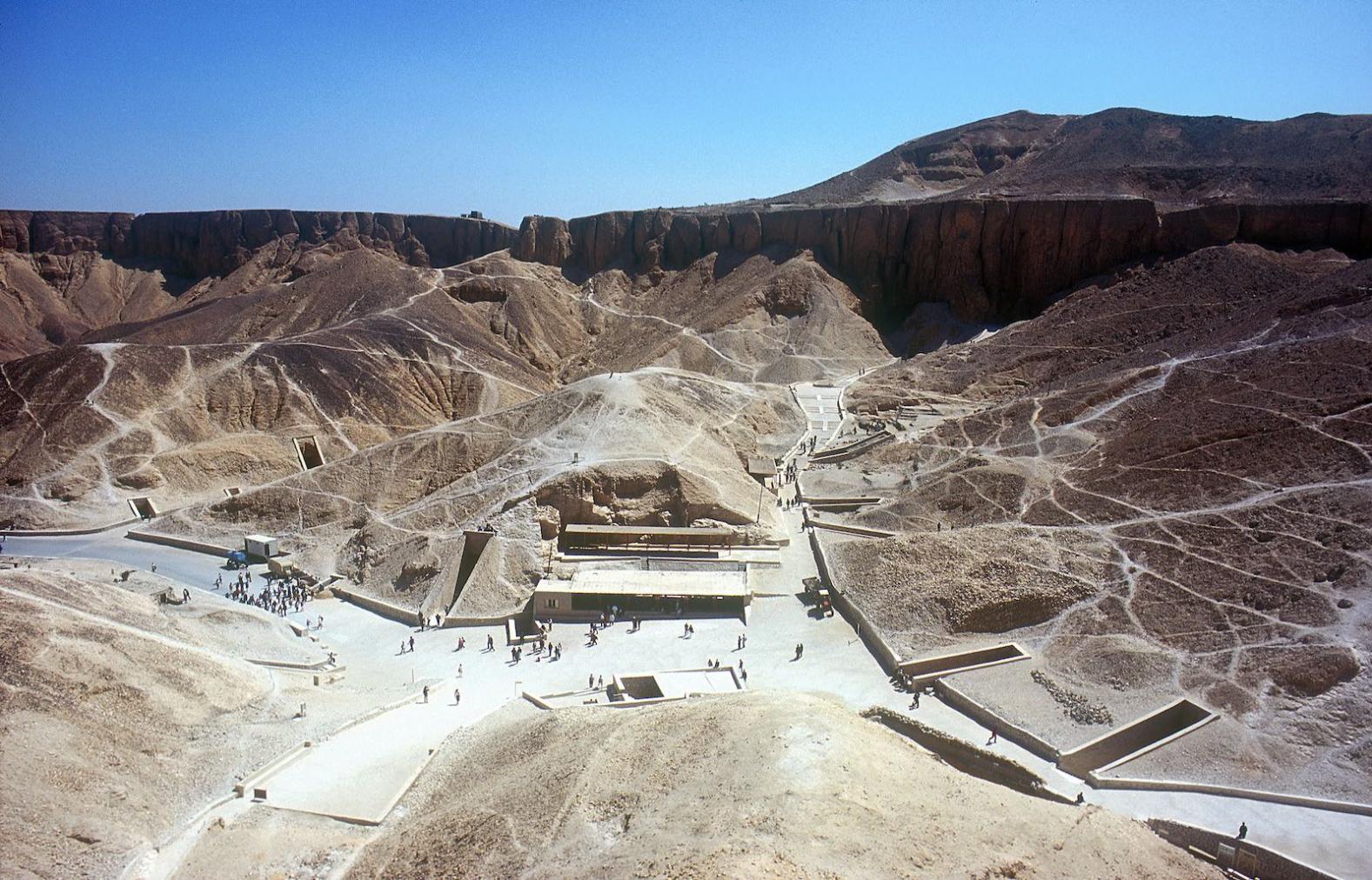
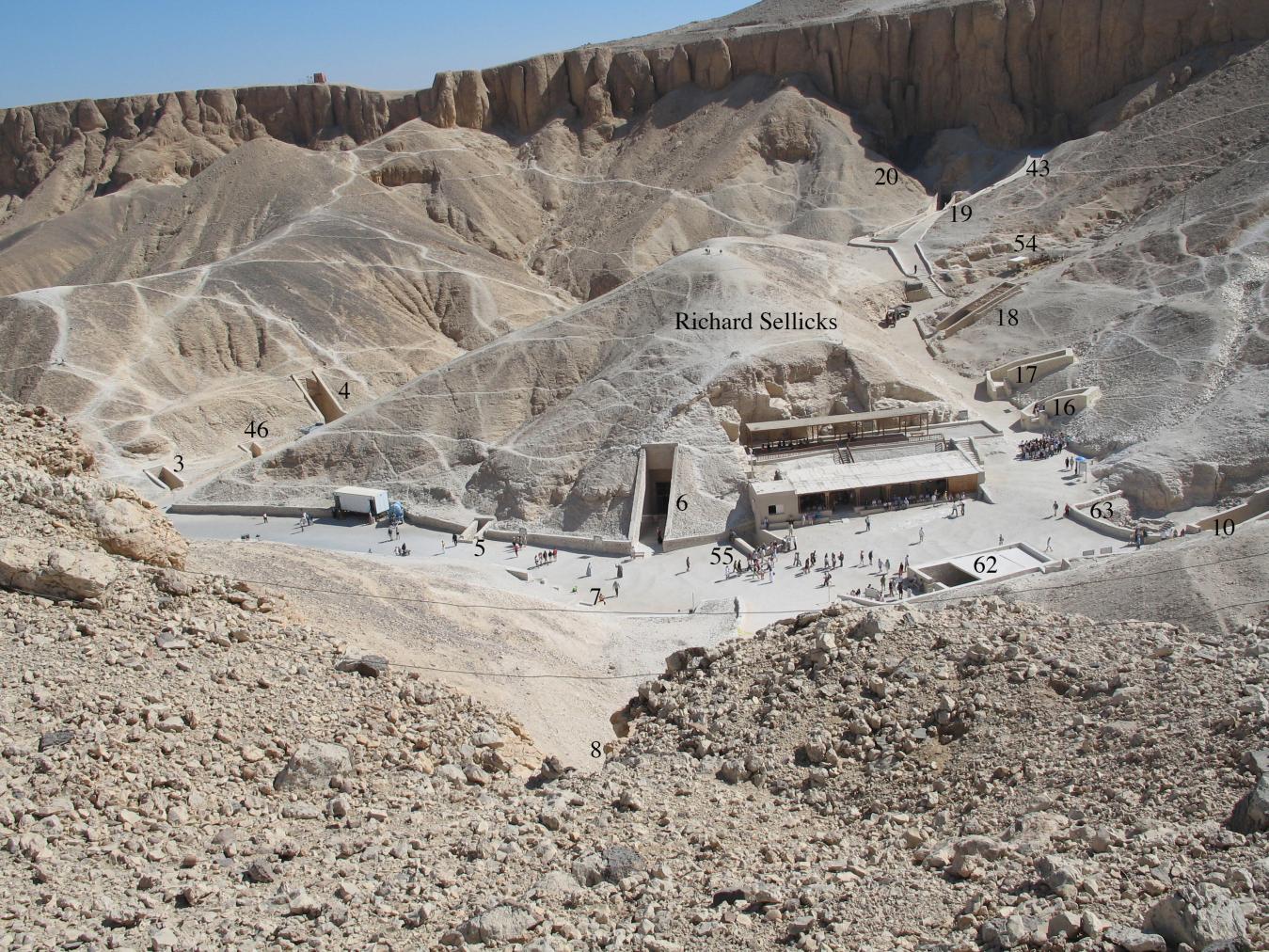
KV 62, located in the main Wadi, is the most famous tomb in the world because of the treasures it held intact for over three thousand years. The entryway A is cut into the floor of the valley below the beginning of the entry Ramp of KV 9, the tomb of Rameses VI. Even before the construction of KV 9, debris had already been dumped on top of the KV 62 entrance. The tomb was forgotten and a group of Rameside workmen's huts were built over it later in antiquity.
A descending corridor (B) leads to a rectangular chamber (I) with a side chamber (Ia). The burial chamber J opens off the right (north) end of chamber I with its floor level one meter lower. Another side chamber (Ja), is located off the right (east) wall of the burial chamber J. Howard Carter believed that the four chambers of KV 62, although small, relate directly to lower parts of more traditional royal tomb plans. The walls of the tomb were smoother but, except for burial chamber J, were left undecorated. The burial chamber J is decorated with scenes from the Opening of the Mouth ritual, Imydwat, Book of the Dead, and representations of the king with various deities.
Some have theorized that when Tutankhamen died suddenly at an early age, a tomb that was originally planned for him in the West Valley (KV 23 or KV 25) was not ready. It may have been decided to bury Tutankhamen in the main Valley in a tomb originally intended for Ay when he was still a God's Father, near the Amarna cache (KV 55). According to this theory, Ay later took the West Valley tomb (KV 23) after succeeding Tutankhamen to the throne.
Recently, Nicholas Reeves has suggested that Nefertiti is buried in a still-unopened chamber behind the burial chamber of KV 62. This idea has generated considerable international interest, but no definite answer has been forthcoming since its proposed entrance has not yet been opened. The most recent discussion of the idea may be found in Reeves (2020).
Noteworthy features:
This tomb originally designed for a non-royal personage nevertheless was used for royal burial, and possessed a nearly intact set of burial equipment.
Site History
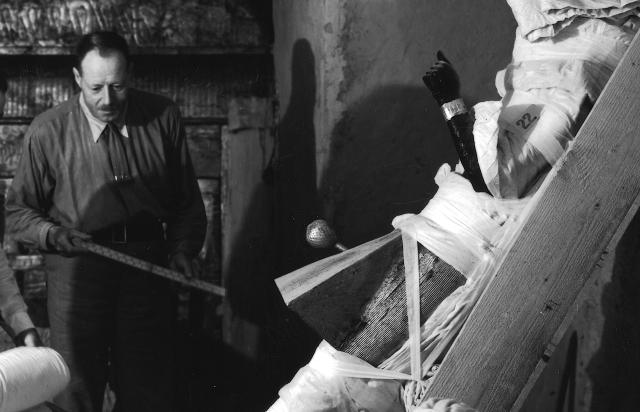
KV 62 may have been constructed for an important official or member of the royal family, probably in the latter half of Dynasty 18. When it was taken over for the burial of Tutankhamen, still unfinished, a burial chamber with side chamber was cut into the right (north) end of the first chamber. KV 62 was robbed at least twice in antiquity, judging from three different sets of seals on the doorways signifying three different closures of the tomb. Other evidence of theft, besides the disturbed appearance of the objects in chamber I and side chamber Ia, includes inventory dockets on various containers that list artifacts not found when the tomb was discovered. The looters appear to have penetrated past chamber I into side chamber Ia, chamber J and side chamber Ja, but did not breach the sealed doors of the shrines surrounding the Sarcophagus. After the final restoration of the burial, perhaps under Horemheb, the location of the tomb was lost as the debris from subsequent tomb construction filled the floor of the center of the Valley.
Dating
This site was used during the following period(s):
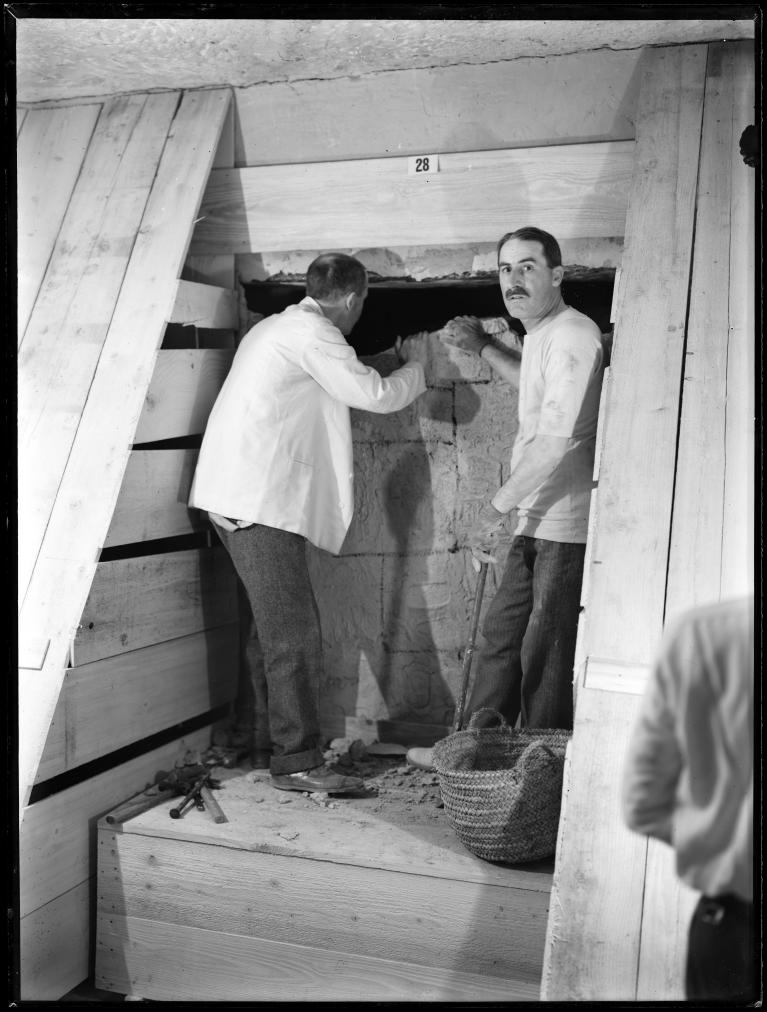
Exploration
Conservation
Conservation History
Following the 1994 floods, a new shelter was constructed over and around the entrance to protect it from water. Metal doors at the top and bottom of corridor B and a metal stairway have been installed.
A 10 year-long conservation of the tomb by The Getty Research Institute was completed in 2019. Conservators installed a new air filtration and ventilation system, investigated the tomb's microclimatic conditions, conserved and stabilized the wall paintings, and introduced new measures for visitor management.
Site Condition
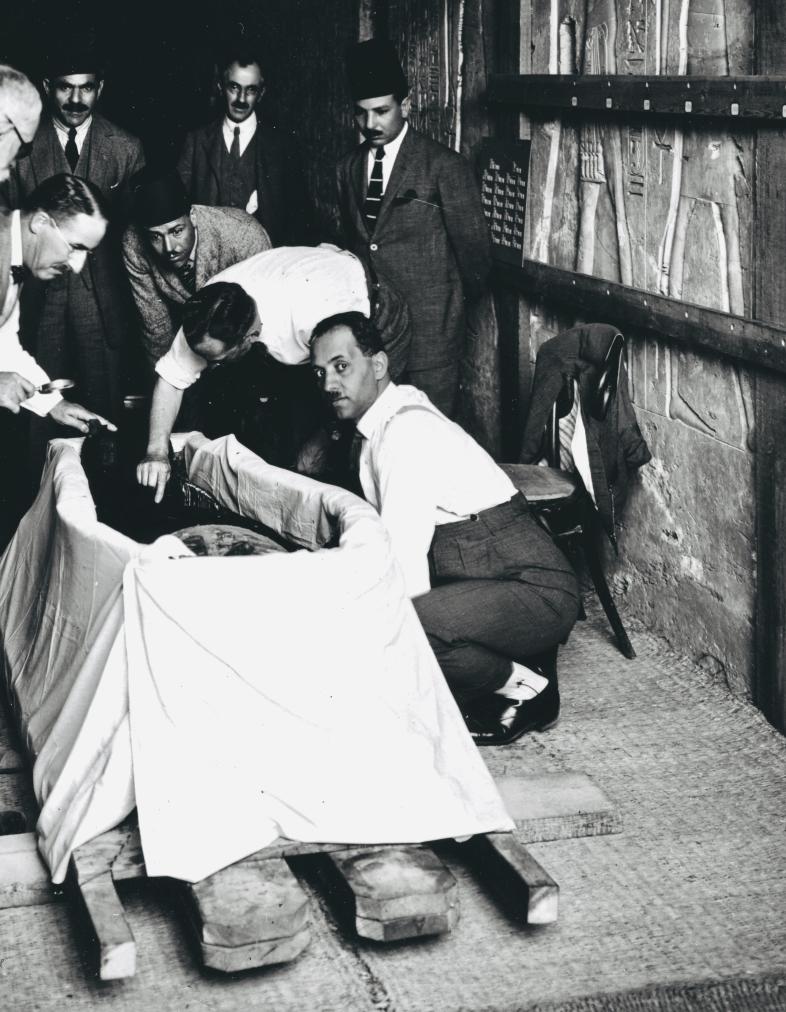
Since KV 62 was sealed throughout its history, flood debris did not fill the tomb. A fault line runs through the tomb, but it has remained stable and there has been no structural damage to the chambers. Carter and his team broke through the partition wall between chamber I and burial chamber J to remove Tutankhamen's funeral shrine and other large objects, partially destroying the scenes on the south (front) wall.
Soot on the burial chamber ceiling reminds us that ancient people painted by torchlight and oil lamps. A pink stain and black fungus spots have spread over decorated walls due to moisture. Small amounts of moisture came from the ancient offerings placed in the tomb such as vegetation, and also from the gypsum plaster on which the decoration was painted, which may not have been fully dry when the tomb was sealed.
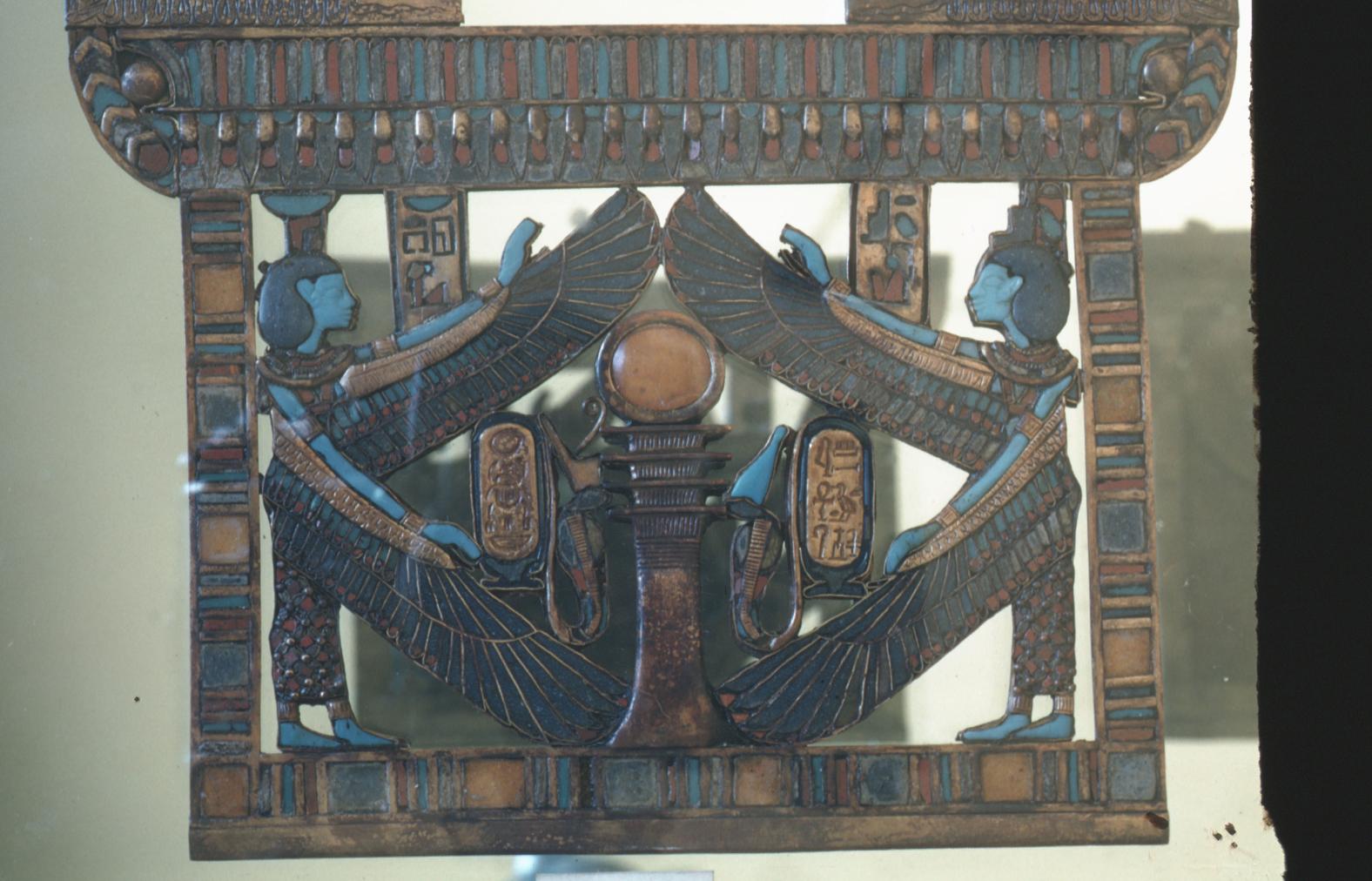
Hieroglyphs
Tutankhamen
 King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Lord of Manifestations is Ra, Son of Ra, Living Image of Amen, Ruler of Southern Heliopolis (Thebes)
niswt-bity nb-xprw-Raw sA-Raw twt-anx-Imn HqA-Iwnw-Sma
King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Lord of Manifestations is Ra, Son of Ra, Living Image of Amen, Ruler of Southern Heliopolis (Thebes)
niswt-bity nb-xprw-Raw sA-Raw twt-anx-Imn HqA-Iwnw-Sma
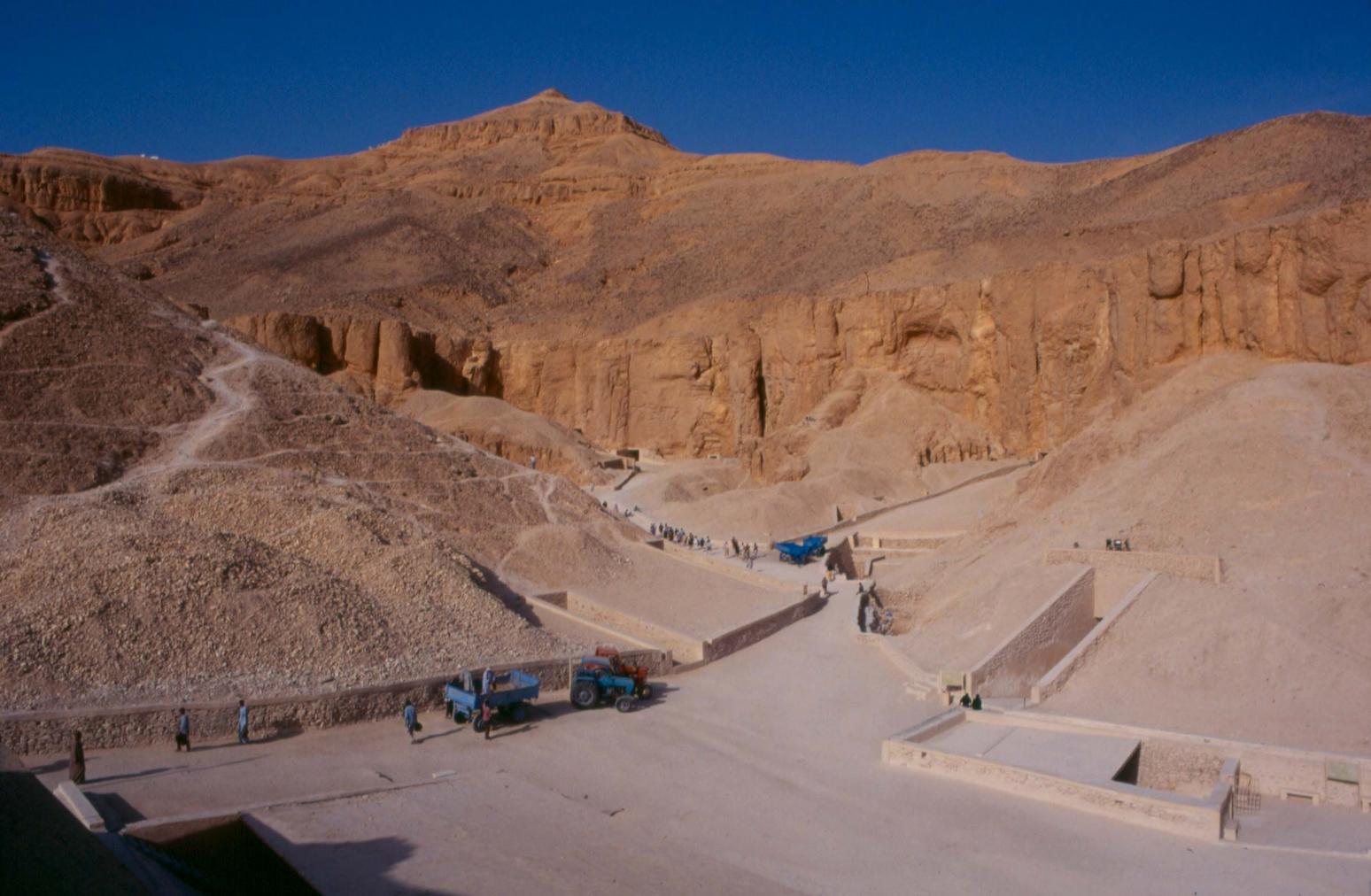
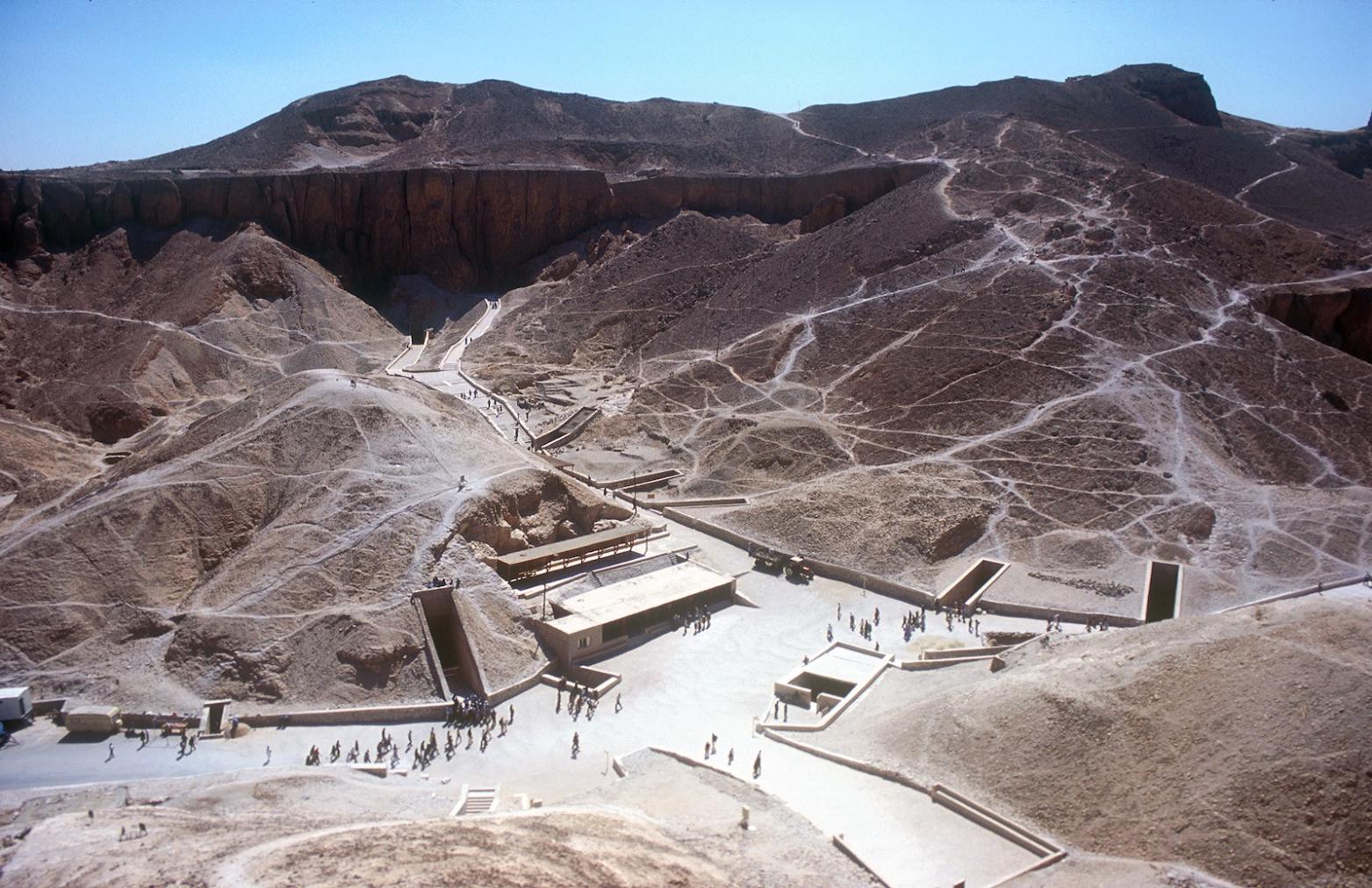
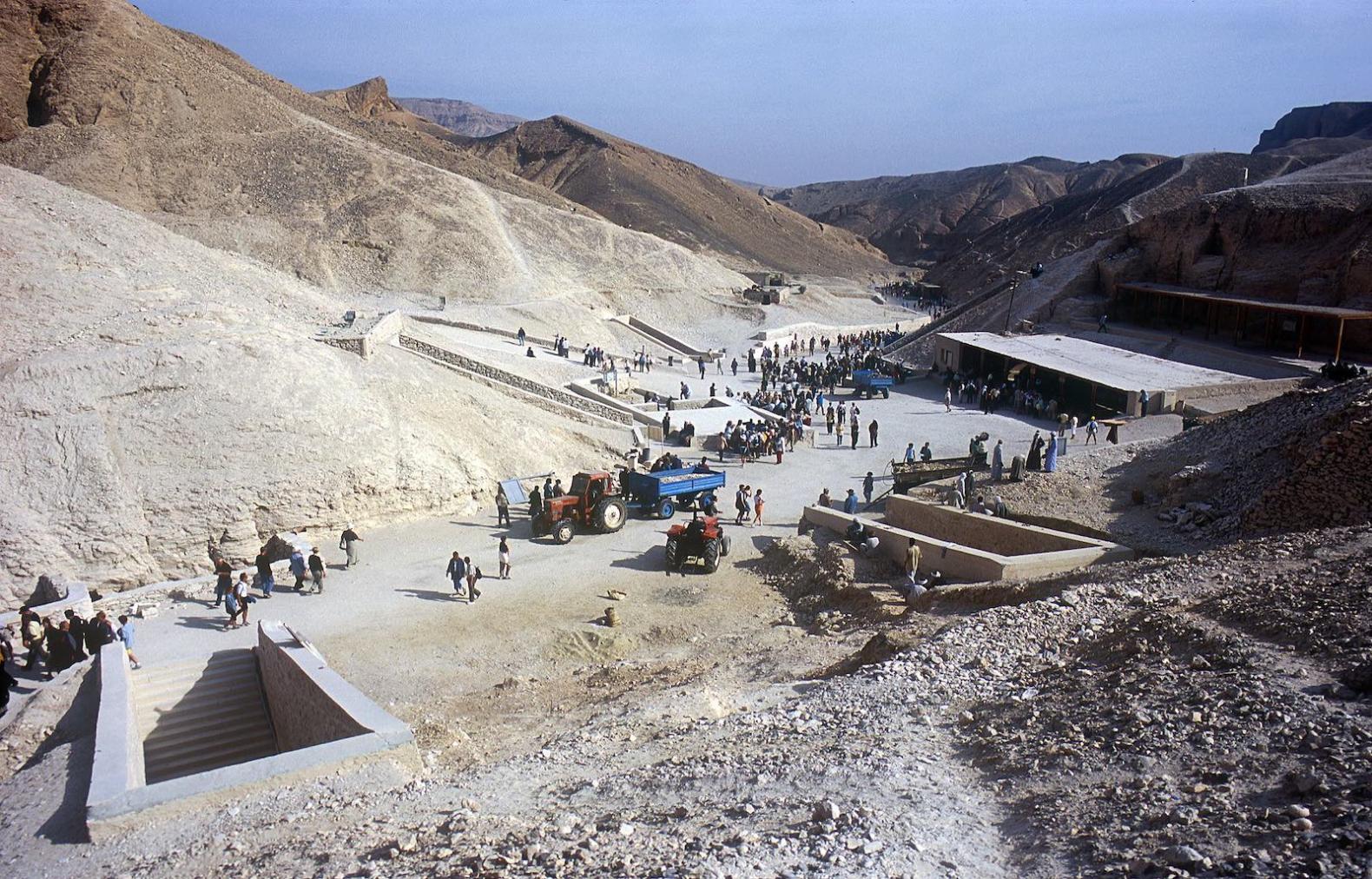
















Old rest house, KV 18, KV 17, KV 16, KV 55, KV 62, KV 9, KV 10 and KV 11.
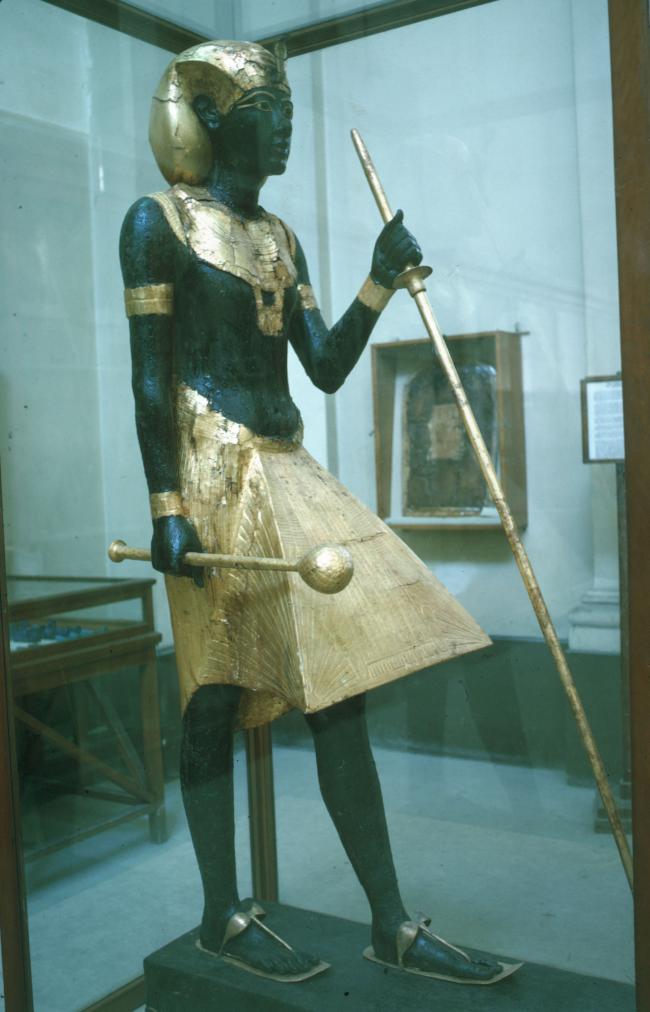
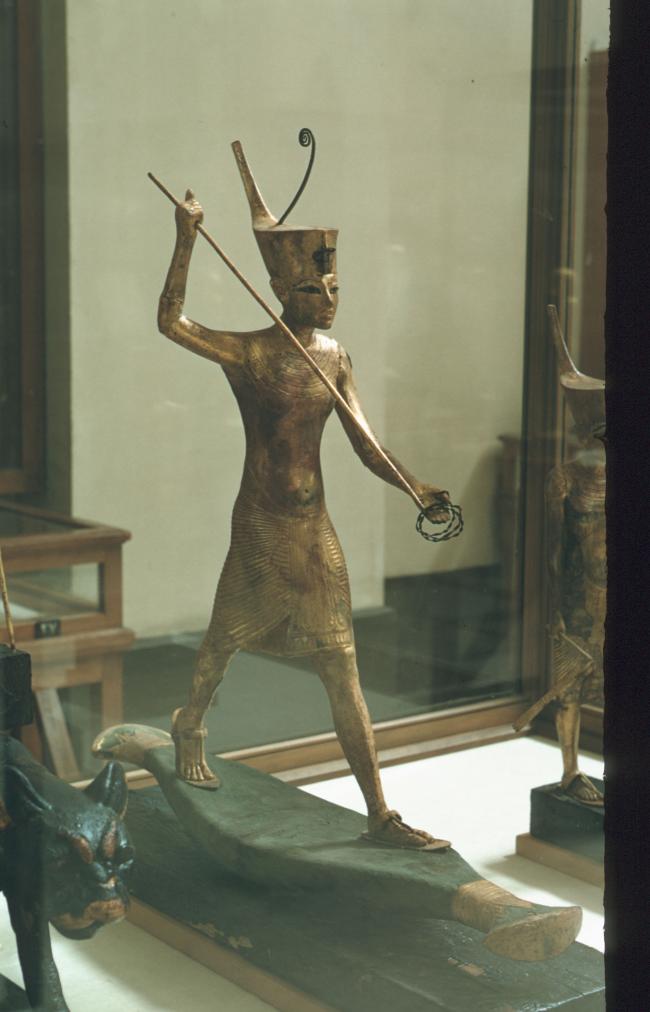
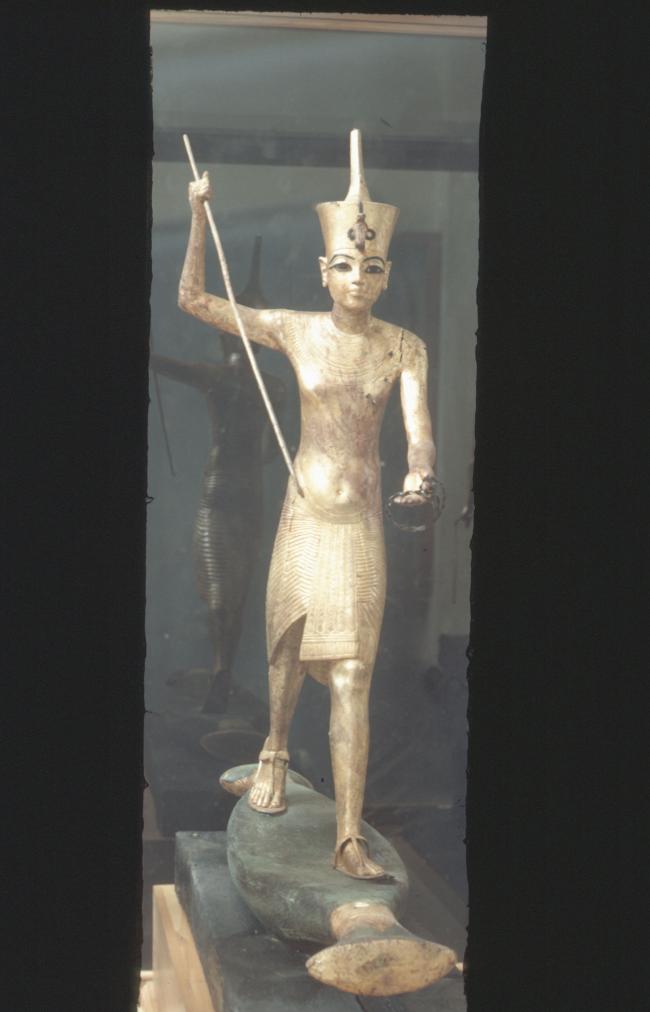
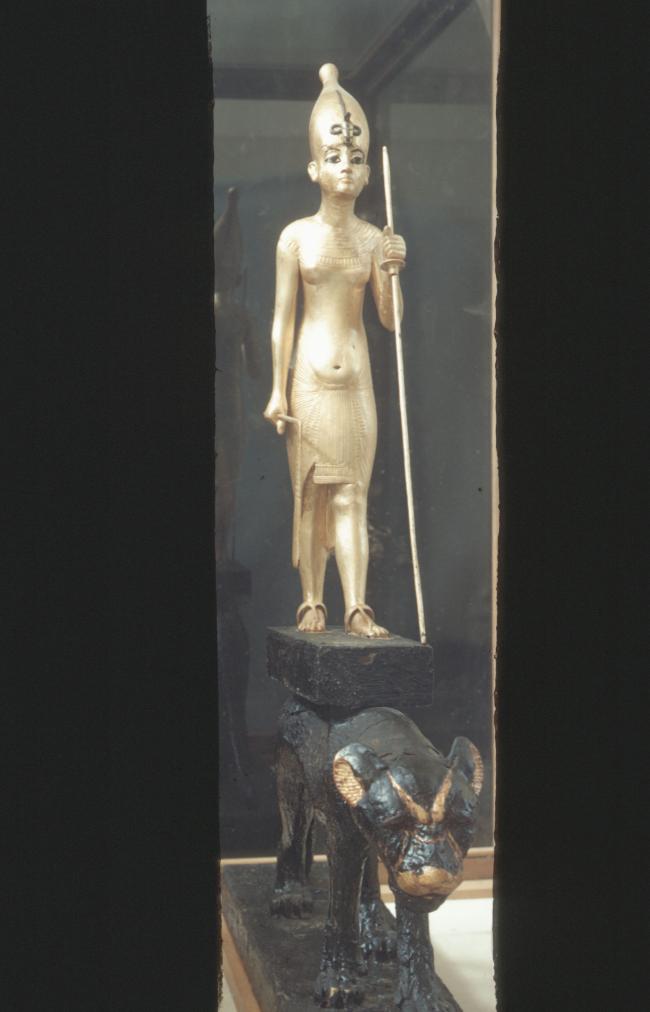
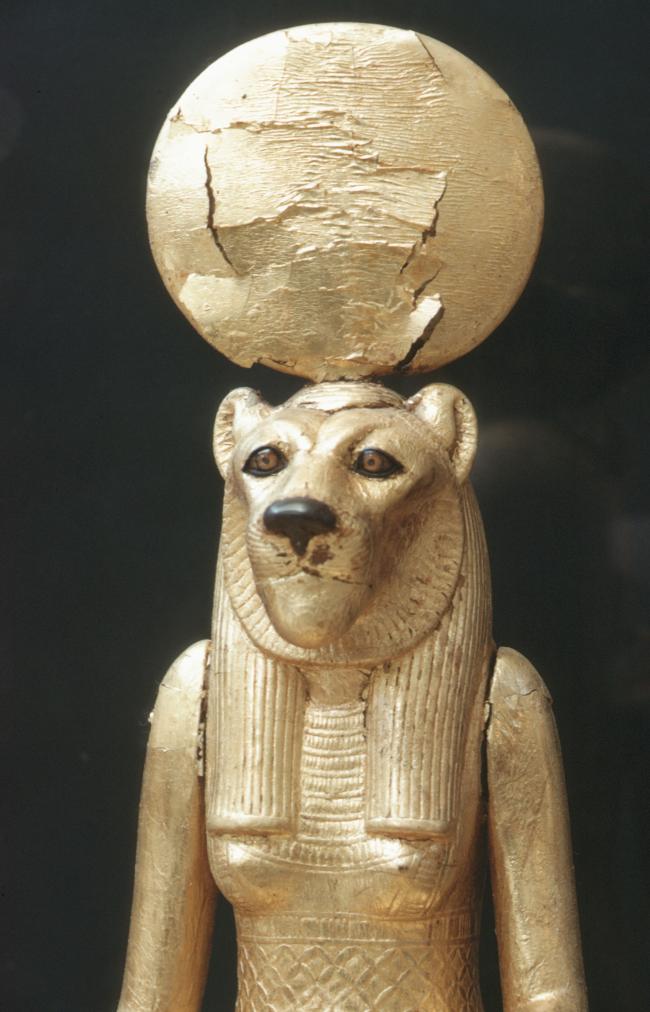
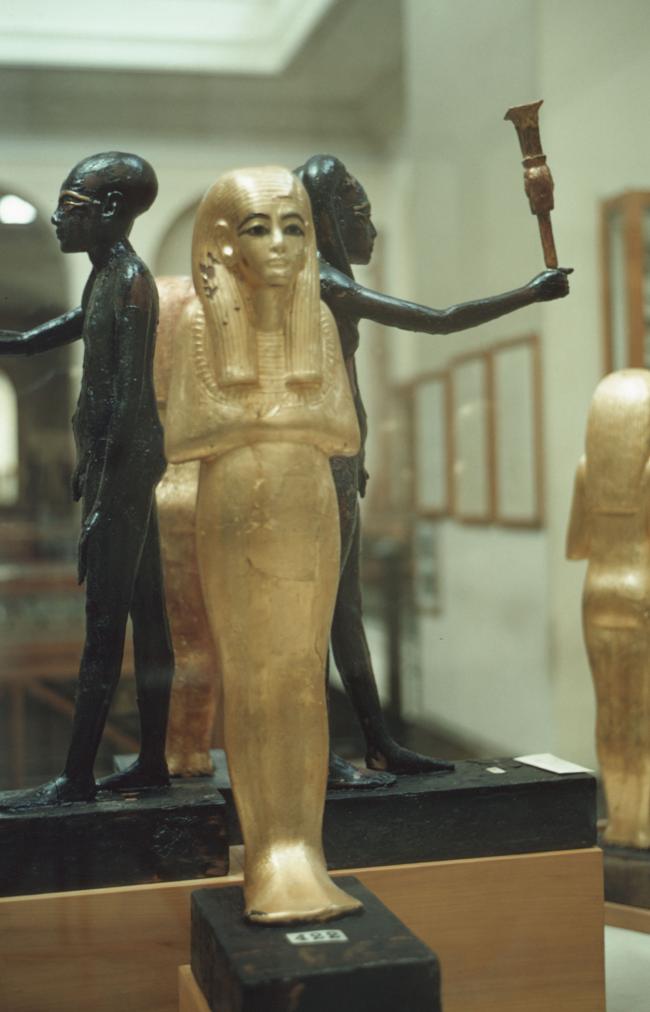
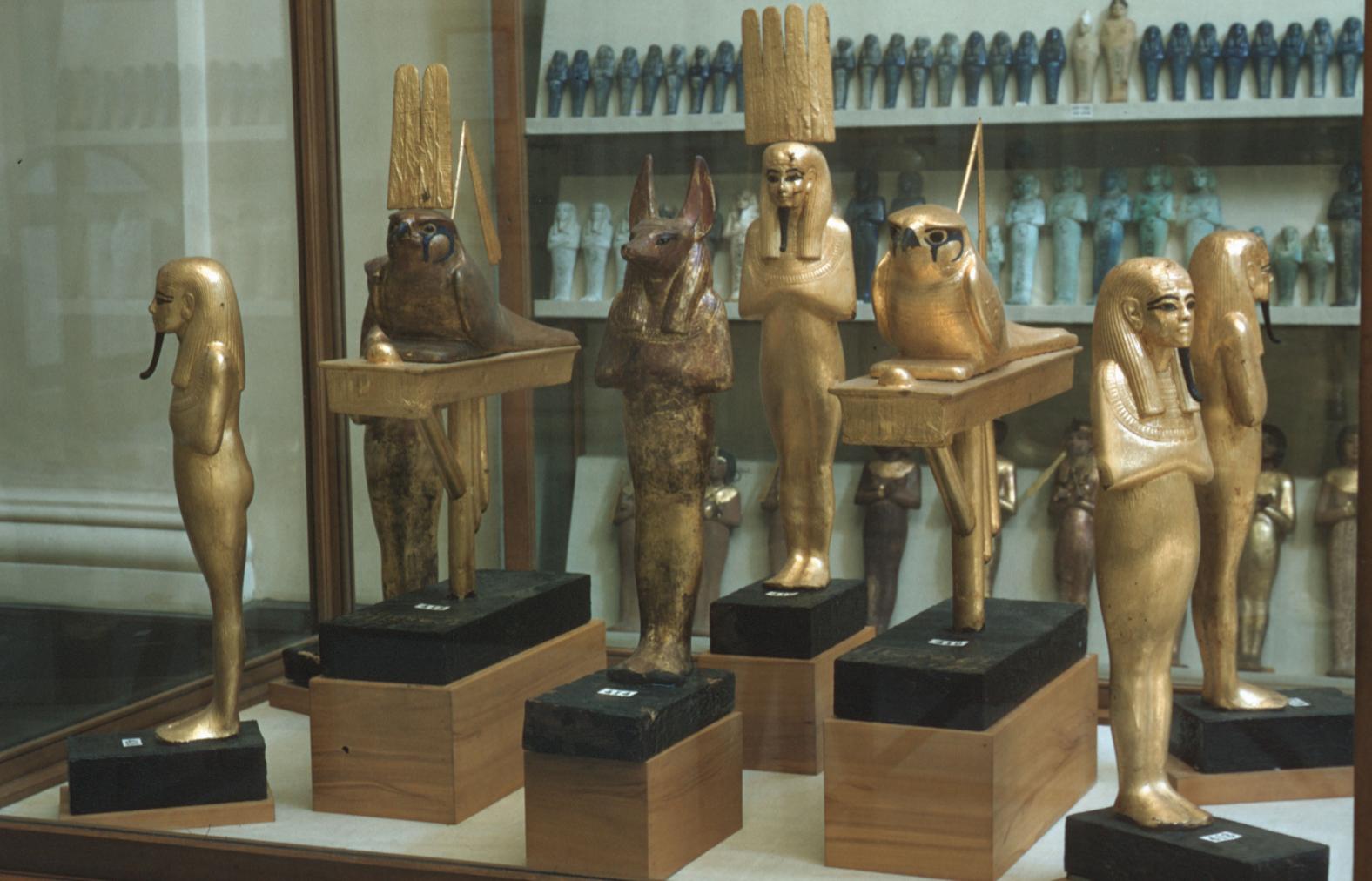
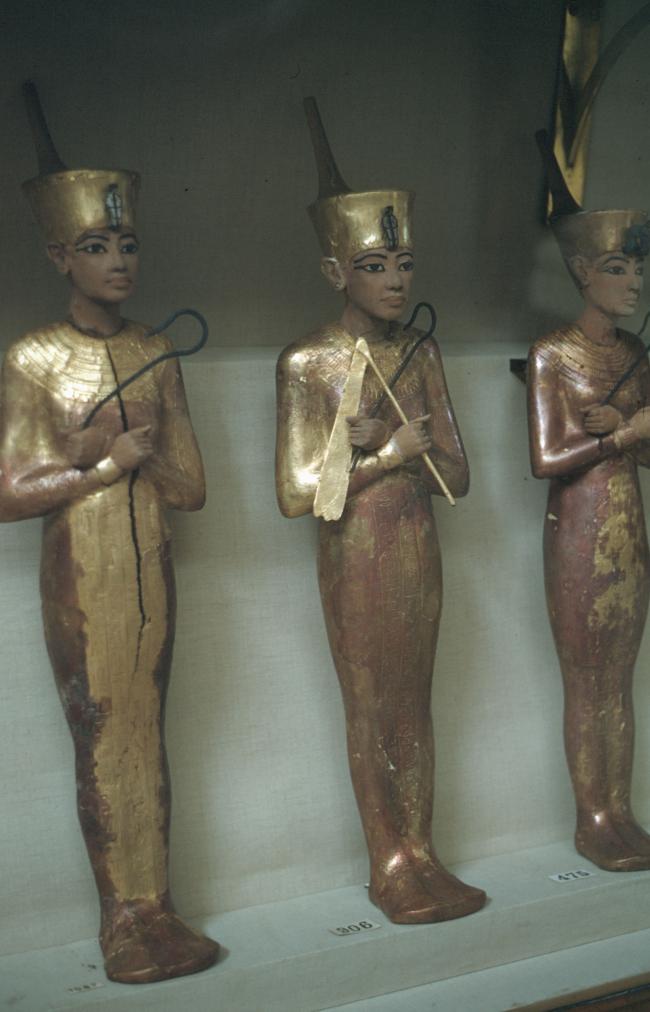
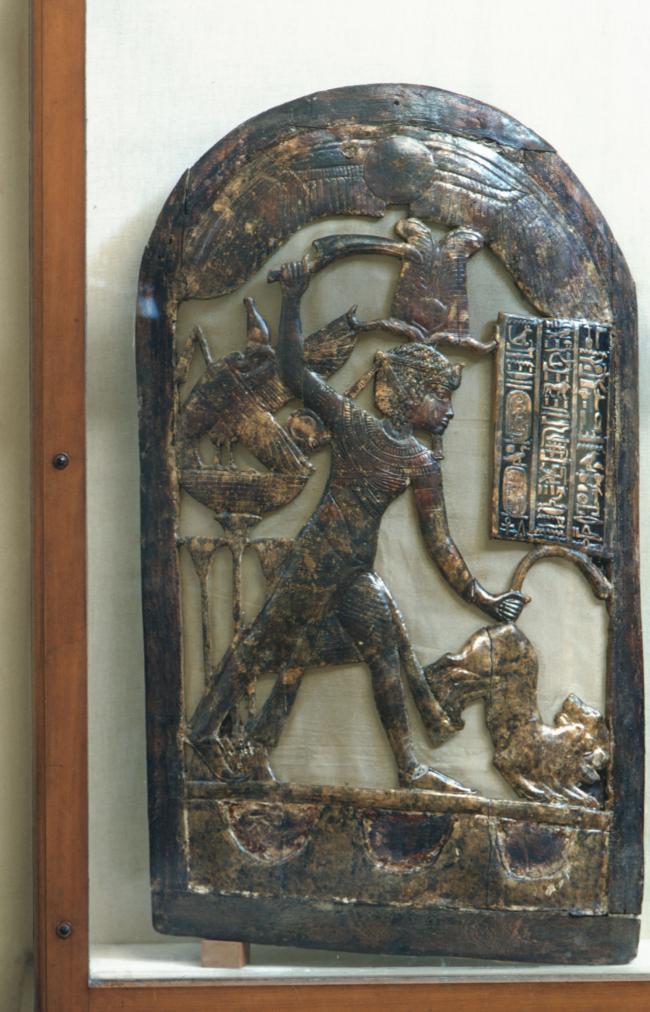
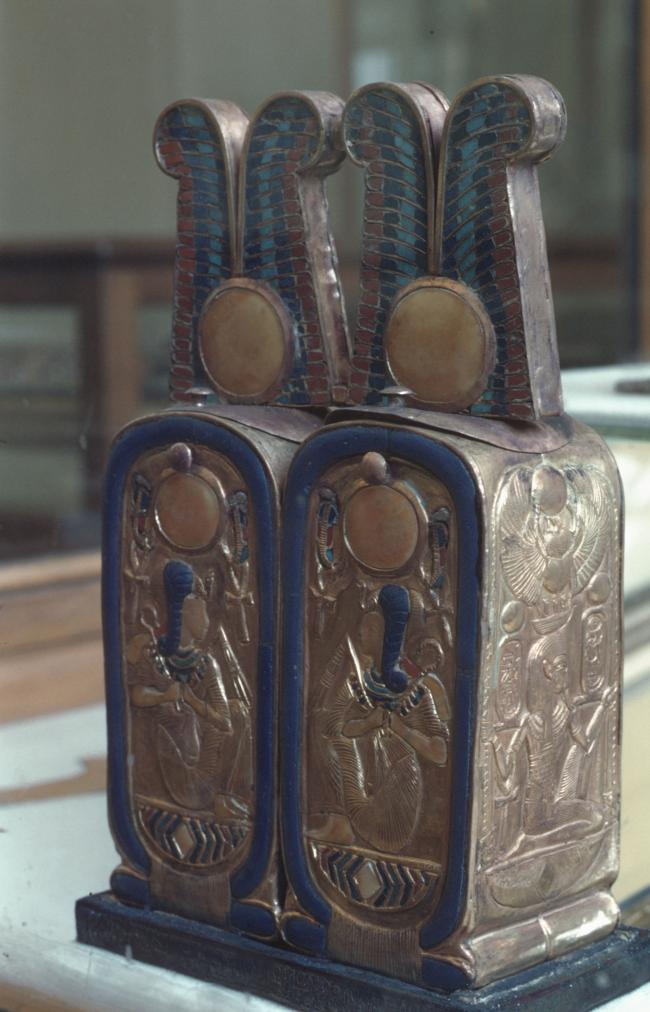
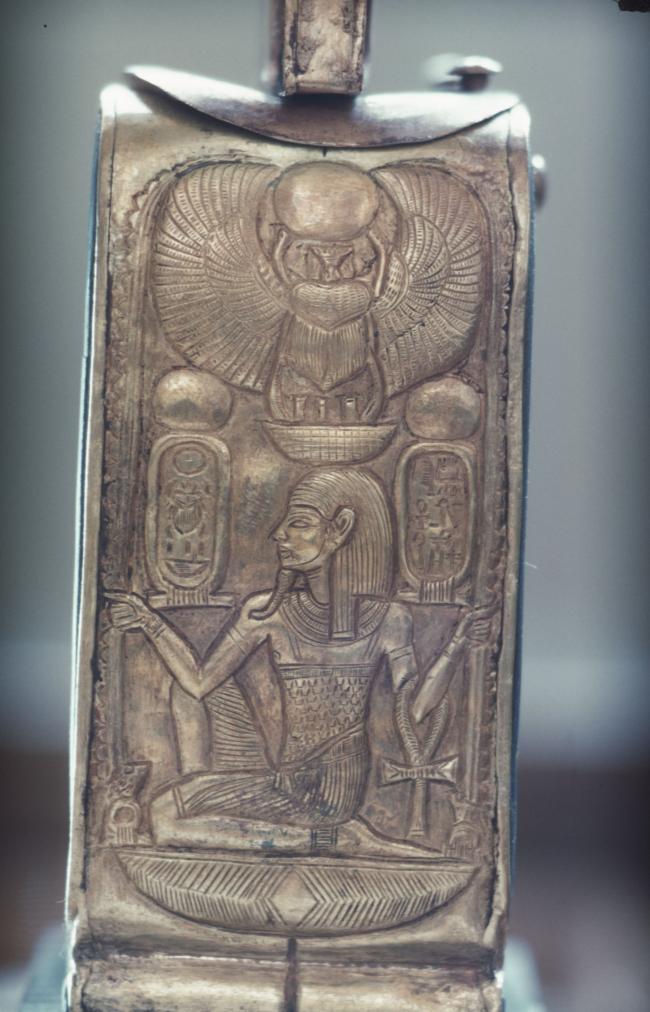
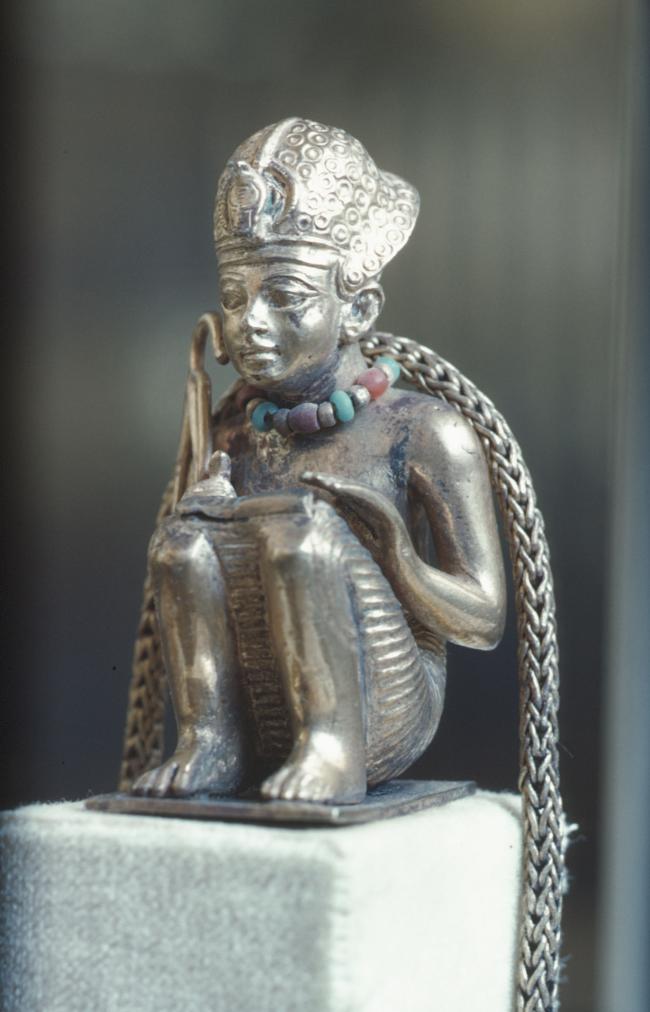
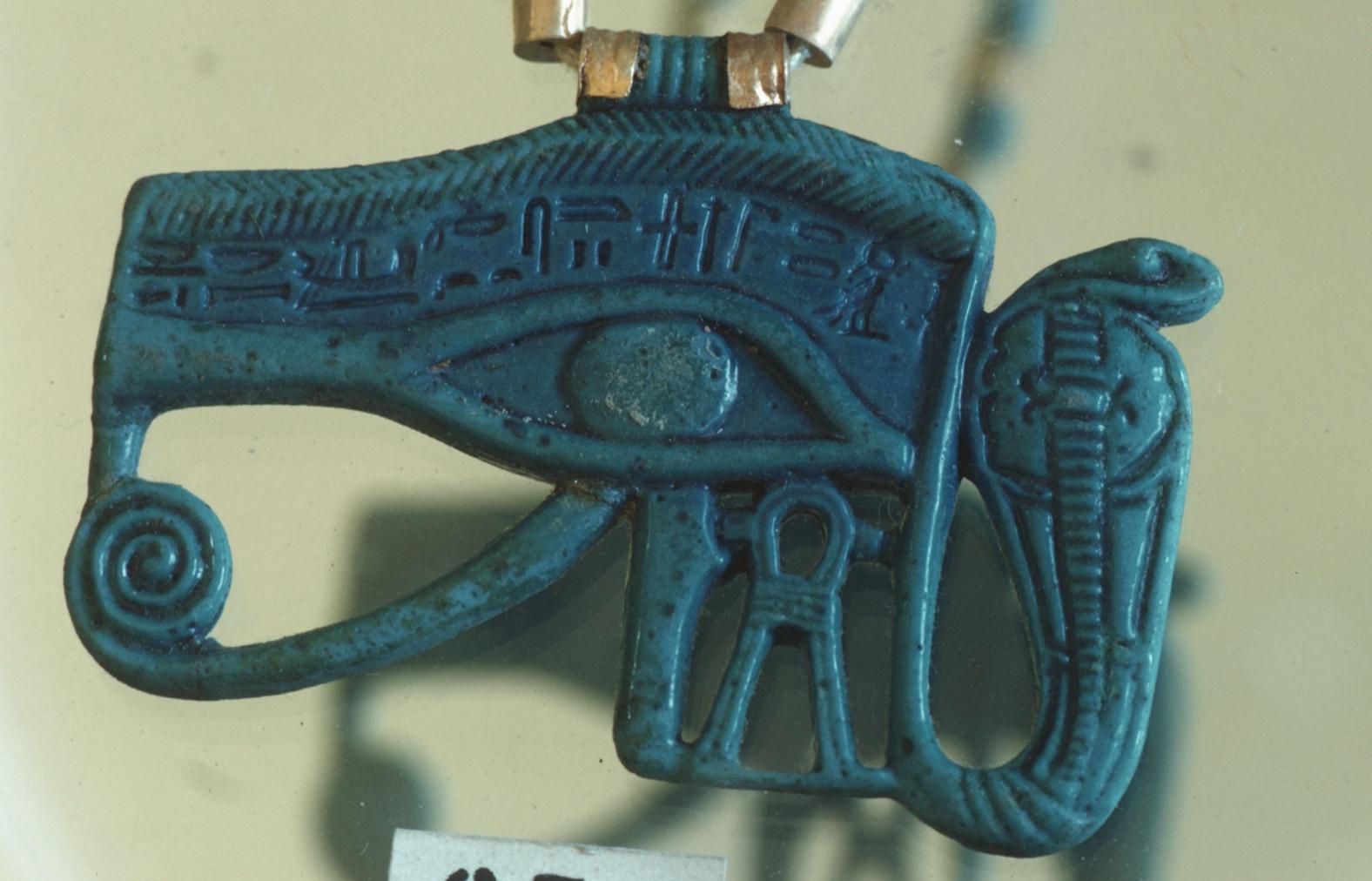
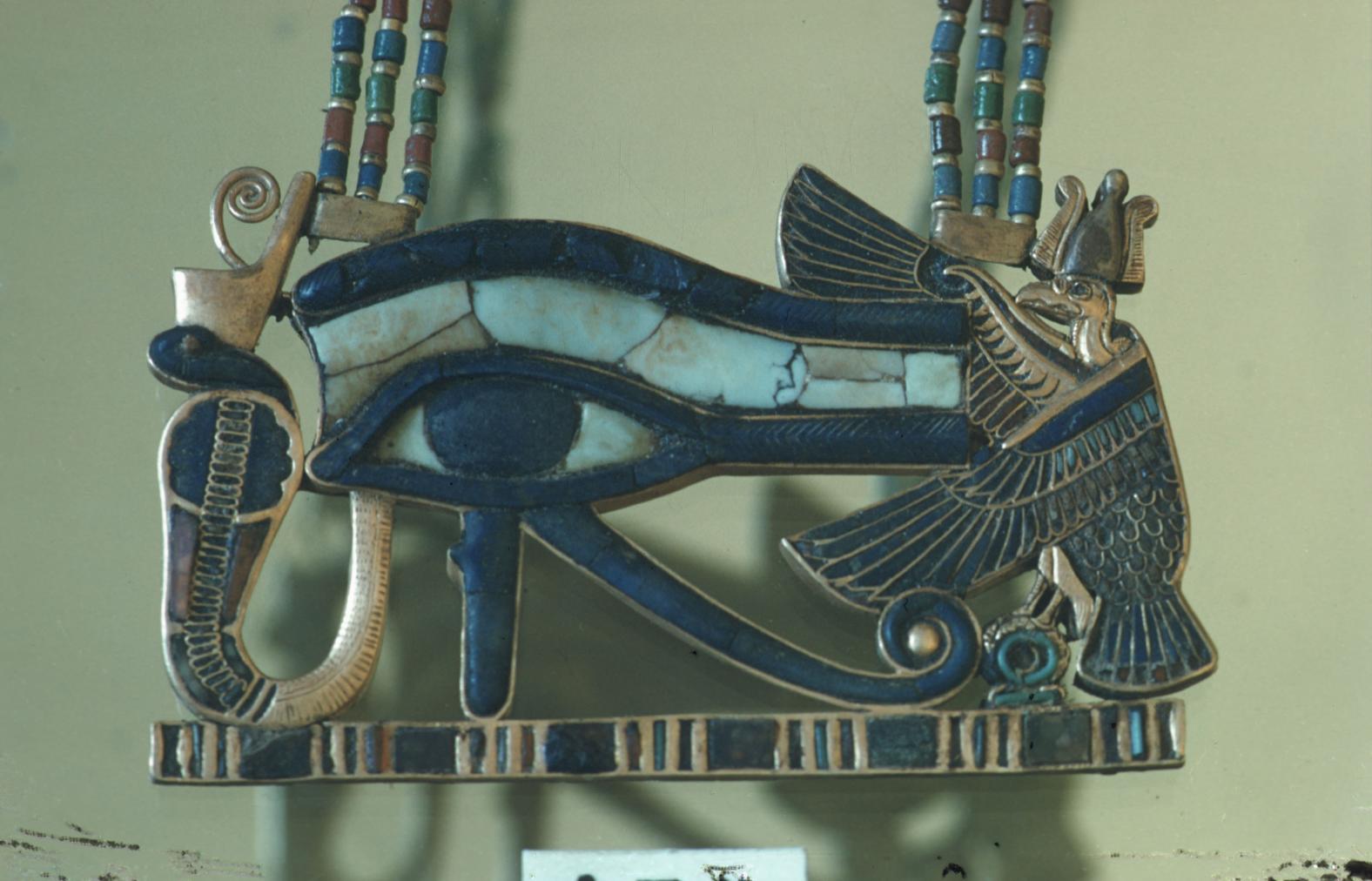
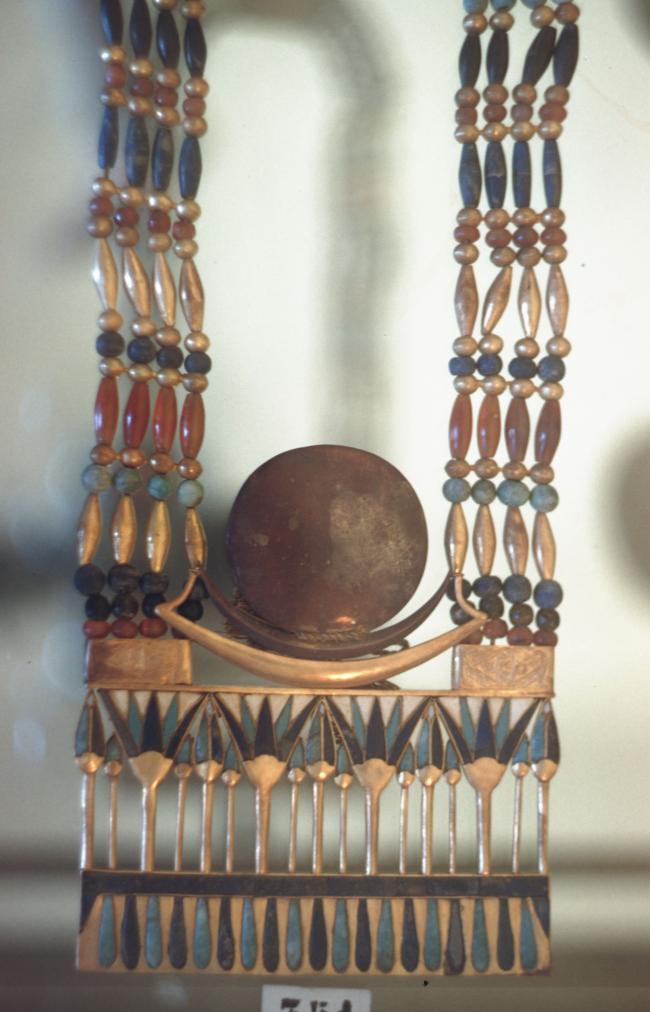
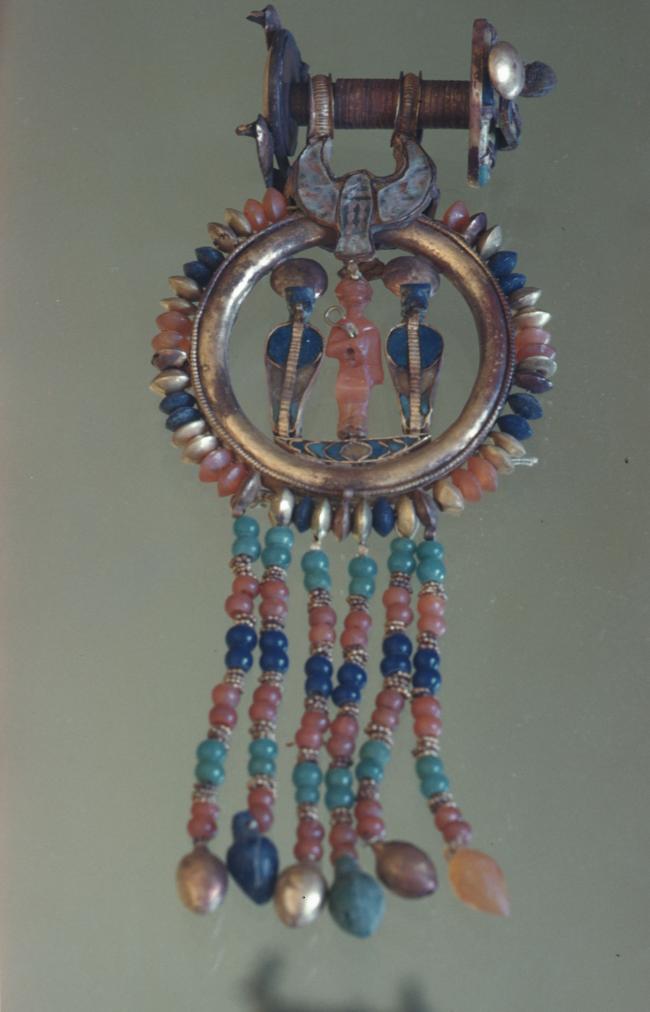
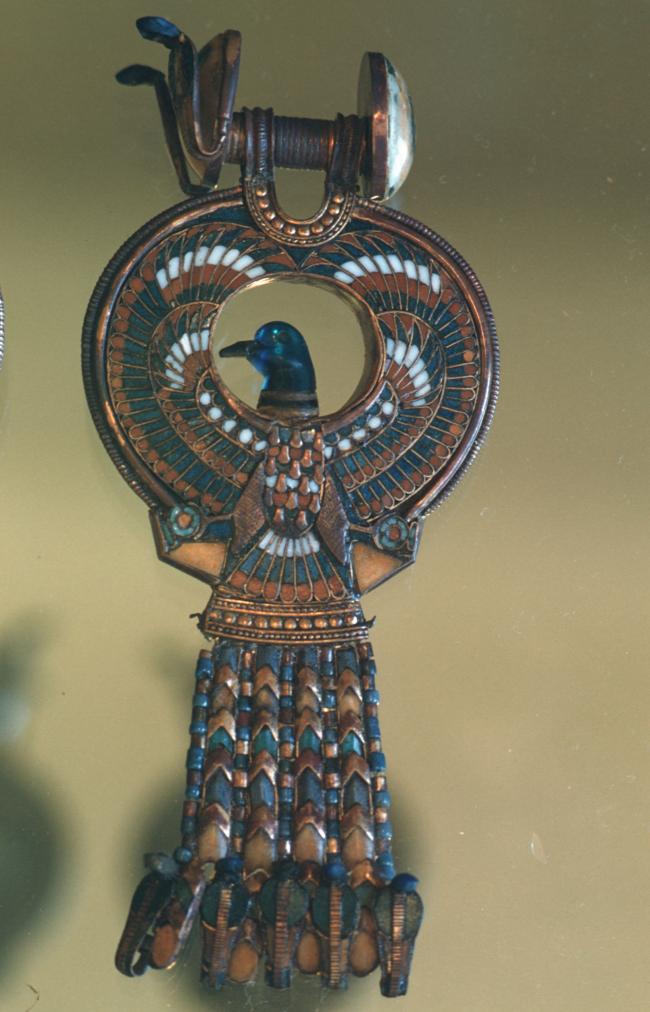
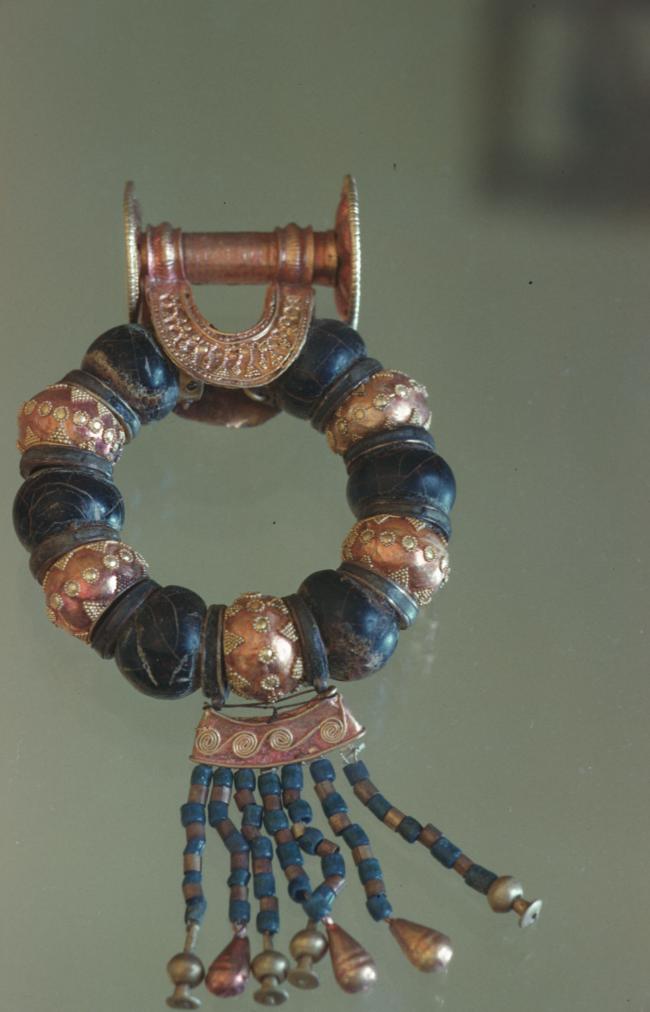
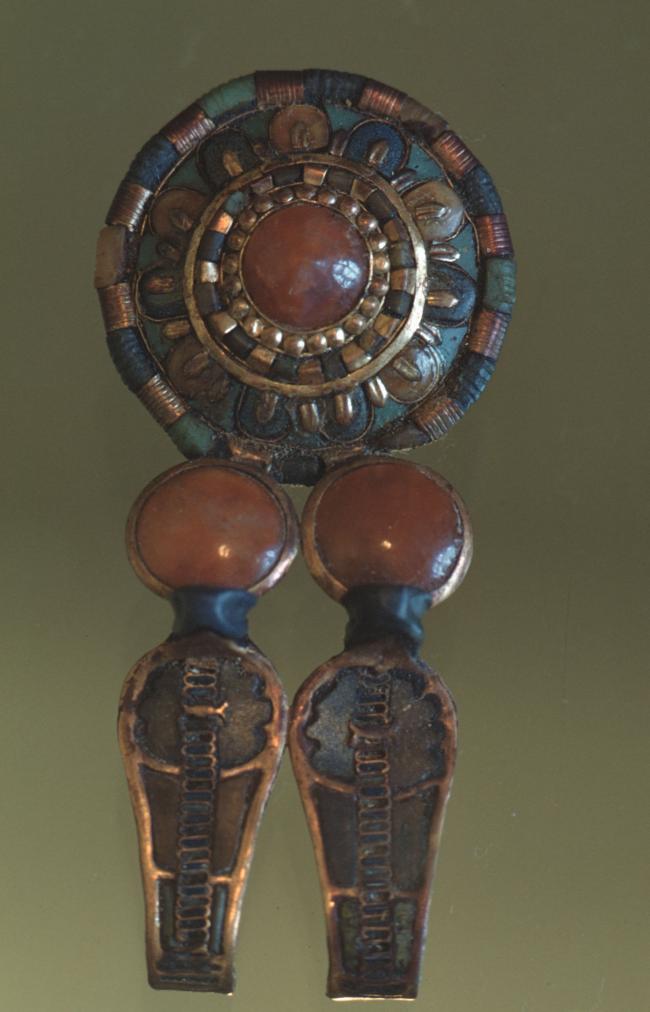
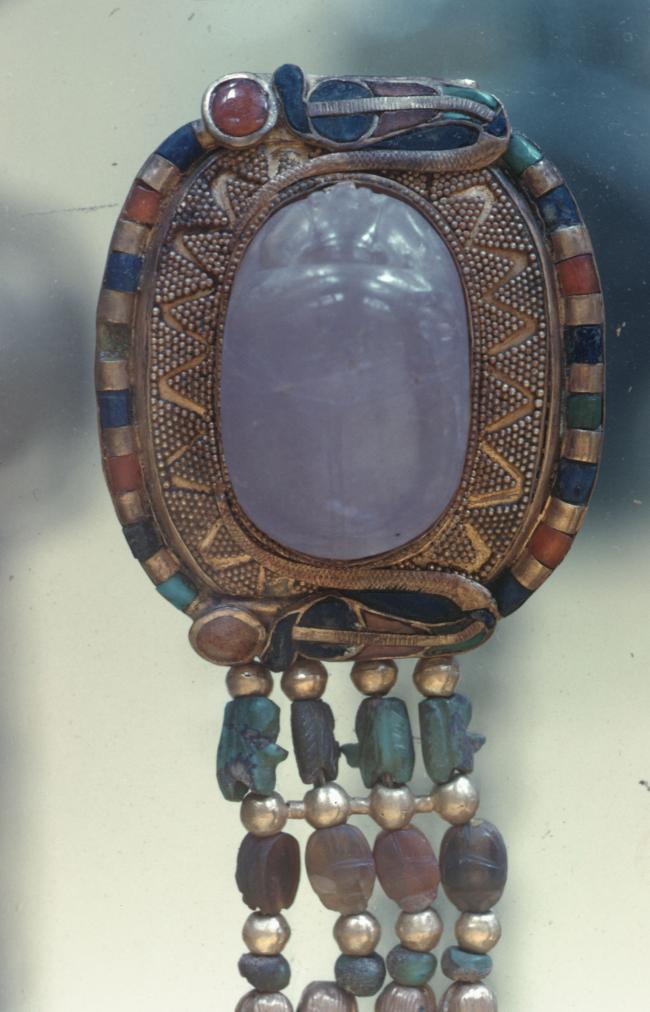











































































































































































Articles
Who's Who: Key Players in the Discovery of Tutankhamen's Tomb
Anatomy of a Tomb: Ancient and Modern Designations for Chambers and Features
Funerary Compositions
Bibliography
Abitz, Friedrich. Die religiöse Bedeutung der sogenannten Grabräuberschächte in den ägyptischen Königsgräbern der 18. bis 20. Dynastie (= Ägyptologische Abhandlungen, 26). Wiesbaden, 1974.
Aldred, Cyril. Tutankhamun's Egypt. London: British Broadcasting Corporation, 1972.
Aldred, Cyril. Tutankhamun: Craftsmanship in Gold in the Reign of the King. London: BBC, 1972. [Film]
Allen, Thomas G. Discoveries at the Tomb of Tutenkhamon. Current History 20 (1924): 363-373.
Asaad, Hany and Daniel Kolos. The Name of the Dead: Hieroglyphic Inscriptions of the Treasures of Tutankhamun Translated. Mississauga, Ontario: Benben, 1979.
Bacon, Edward. Tutankhamun's Treasures. Illustrated London News 260 (1972): 39-47.
Beinlich, Horst. Konkordanz der Tutanchamun-Kataloge. Göttingen Miszellen 71 (1984): 11-26.
Beinlich, Horst and Mohammed Saleh. Corpus der Hieroglyphischen Inschriften aus dem Grab des Tutanchamun: Mit Konkordanz der Nummerensysteme des “Journal d'Entrée” des Ägyptischen Museums Kairo, der Handlist to Howard Carter's Catalogue of Objects in Tut'ankhamun's Tomb und der Ausstellungs-Nummer des Ägyptischen Museums Kairo. Oxford: Griffith Institute, 1989.
Bell, Martha R. Notes on the Exterior Construction Signs from Tutankhamun’s Shrines. Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 76 (1990): 107-124.